not to be confused with Surat province in Thailand
Reading: Surat Thani province – Wikipedia
Surat Thani ( Thai : สุราษฎร์ธานี, pronounced [ sù.râːt tʰāː.nīː ] ), much shortened to Surat, is the largest of the southerly provinces ( changwat ) of Thailand. It lies on the western prop up of the Gulf of Thailand. Surat Thani means ‘city of dependable people ‘, a entitle given to the city by King Vajiravudh ( Rama VI ) ; Surat Thani is consequently the sole province in Southern Thailand for which the native name is in the Central Thai language .
geography [edit ]
Neighbouring provinces are ( from north, clockwise ) Chumphon, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Krabi, Phang Nga, and Ranong. geographically, the center of the state is the coastal plain of the Tapi River, largely grassland interspersed with rubber eraser trees and coconut plantations. In the west are the limestone mountains of the Phuket range which are largely covered with forest. Khao Sok National Park is found there. To the east the hills of the Nakhon Si Thammarat ( or Bantat ) mountain range start to rise, protected in the Tai Rom Yen National Park. The full forest area is 3,764 km2 ( 1,453 sq mile ) or 28.8 percentage of peasant area. [ 4 ] many islands in the Gulf of Thailand belong to the district, including the tourist islands Ko Samui, Ko Pha Ngan and Ko Tao, adenine well as the Ko Ang Thong Marine National Park. The main rivers of Surat Thani state are the Tapi River and the Phum Duang River, which join at the township Tha Kham concisely before they flow into Bandon Bay. The delta of these rivers, locally known as Nai Bang ( ในบาง ), is immediately north of the city of Surat Thani. It consists of several channels with small islands by and large covered by mangroves and orchards. early protected areas in the state are the Khlong Phanom and Kaeng Krung National Park, Than Sadet-Ko Pha Ngan Marine National Park, the non-hunting areas Khao Tha Phet and Nong Thung Thong and the wildlife sanctuaries Khlong Phraya, Khlong Saeng, and Khlong Yan. The Hat Khanom – Mu Ko Thale Tai, which has a few small islands south of Ko Samui, is presently being created .
history [edit ]
The area of Surat Thani was already inhabited in prehistoric times by Semang and Malayan tribes. Founded in the third century, the Srivijaya kingdom dominated the Malay Peninsula until the thirteenth hundred. The city of Chaiya contains ruins from the Srivijaya period, and it was credibly a regional capital of the kingdom. Some Thai historians even argue that it was the kingdom ‘s capital for a time, but this is disputed. Wiang Sa was another crucial settlement of the time .
 Wat Kaew in Chaiya, dating from Srivijavan times After the descent of the Srivijaya, the area was divided into the cities ( mueang ) of Chaiya, Thatong ( immediately Kanchanadit ), and Khirirat Nikhom. Chaiya was administered immediately from the Thai capital, while Thatong and Khirirat were controlled by the Nakhon Si Thammarat Kingdom. In 1899, they were all merged into a single province called Chaiya. In 1915, the court of the Monthon Chumphon was transferred to Bandon, which received the modern appoint of Surat Thani on 29 July 1915, during a visit of King Vajiravudh ( Rama VI ). This was likely influenced by the major interface city of Surat in Gujarat, India. The monthon was besides renamed Surat. In 1926 it was abolished and incorporated into monthon Nakhon Si Thammarat. The monthon was dissolved in 1933, and the province became a inaugural level administrative subsection .
Wat Kaew in Chaiya, dating from Srivijavan times After the descent of the Srivijaya, the area was divided into the cities ( mueang ) of Chaiya, Thatong ( immediately Kanchanadit ), and Khirirat Nikhom. Chaiya was administered immediately from the Thai capital, while Thatong and Khirirat were controlled by the Nakhon Si Thammarat Kingdom. In 1899, they were all merged into a single province called Chaiya. In 1915, the court of the Monthon Chumphon was transferred to Bandon, which received the modern appoint of Surat Thani on 29 July 1915, during a visit of King Vajiravudh ( Rama VI ). This was likely influenced by the major interface city of Surat in Gujarat, India. The monthon was besides renamed Surat. In 1926 it was abolished and incorporated into monthon Nakhon Si Thammarat. The monthon was dissolved in 1933, and the province became a inaugural level administrative subsection .
 Srivijaya-style pagoda, Chaiya The provincial administration was in a construction in Tha Kham ( Phunphin District ). shortly before World War II, it was moved to the city of Surat Thani, on the banks of the Tapi River, which is named after the Tapi River in southern Gujarat, India. When the Japanese invaded Thailand on 8 December 1941, the administrative build was destroyed during the conflict for the city. It was rebuilt in 1954, but on 19 March 1982, a bomb planted by communist rebels blew up the building, killing five people. The one-third and present build up was relocated to the south of the city, and the former site of the provincial mansion is now the site of the city column shrine ( Lak Mueang ) .
Srivijaya-style pagoda, Chaiya The provincial administration was in a construction in Tha Kham ( Phunphin District ). shortly before World War II, it was moved to the city of Surat Thani, on the banks of the Tapi River, which is named after the Tapi River in southern Gujarat, India. When the Japanese invaded Thailand on 8 December 1941, the administrative build was destroyed during the conflict for the city. It was rebuilt in 1954, but on 19 March 1982, a bomb planted by communist rebels blew up the building, killing five people. The one-third and present build up was relocated to the south of the city, and the former site of the provincial mansion is now the site of the city column shrine ( Lak Mueang ) .
Symbols [edit ]
The varnish of the province shows the pagoda of Wat Phra Borommathat Chaiya, which is believed to have been built 1,200 years ago. [ 5 ] The flag of the province shows the pagoda in middle, placed on a horizontally split flag with orange on lead and yellow on the bottom. The peasant flower is the bua phut ( Rafflesia kerrii ), a parasitic plant with one of the biggest flowers of all plants. The provincial tree is the long ton kiam ( Cotylelobium melanoxylon ). The provincial motto is “ เมืองร้อยเกาะ เงาะอร่อย หอยใหญ่ ไข่แดง แหล่งธรรมะ ชักพระประเพณี ”, which translates to ‘city of 100 islands, delicious rambutan, big shells and red eggs, plaza of Buddhism ‘. “ Red egg ” are a local culinary peculiarity of pickle duck eggs, while the “ boastfully shells ” refers to historically abundant shellfish available. “ Center of Buddhism ” refers to the Chaiya pagoda and Chak Phra Festivals .
administrative divisions [edit ]
 Map of 19 districts
Map of 19 districts
Read more: FIFA 21 Pro Clubs
peasant government [edit ]
The province is divided into 19 districts ( amphoes ), which are further divided into 131 subdistricts ( tambons ) and 1,028 villages ( mubans ) .
local politics [edit ]
As of 26 November 2019 there are : [ 6 ] one Surat Thani Provincial Administration Organisation ( ongkan borihan suan changwat ) and 40 municipal ( thesaban ) areas in the state. Surat Thani and Ko Samui have city ( thesaban nakhon ) condition. Tha Kham, Na San and Don Sak have town ( thesaban mueang ) status. further 35 subdistrict municipalities ( thesaban tambon ). The non-municipal areas are administered by 97 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations – SAO ( ongkan borihan suan tambon ). [ 2 ]
For national elections, the province is divided into two constituencies, each eligible to elect three members of parliament .
economy [edit ]
In the 2008 census, the state had a GPP of 132,637.3 million baht ( US $ 4,019.31 million ) and GPP per head of 134,427 ( US $ 4,073.54 ) [ citation needed ] compared with a GPP of 122,398 million baht ( US $ 3,599.94 million ) and GPP per head of 125,651 baht ( US $ 3,695.62 ) in the 2007 census, with a GPP growth rate of 8.37 percentage and per caput emergence rate of 6.98 percentage. The main agricultural products of the province are coconut and rambutan. The coconuts are frequently picked from the tree by particularly trained monkeys, by and large pig-tailed macaques ( Macaca nemestrina ). The imp educate of the deep Somporn Saekhow is the most know education center. Rambutan trees were first planted in Surat Thani in 1926 by the chinese Malay Mr. K. Vong in Ban Na San District. An annual rambutan fair is held in early-August and includes a parade of highly decorated floats on the Tapi River. Rubber tree plantations are besides common in the state. A noteworthy local anesthetic product is the hand-woven silk fabric from the coastal greenwich village Phum Riang in Chaiya District. Chaiya is besides the most celebrated source of bolshevik eggs, a local anesthetic forte. Ducks are fed with crabs and fish and the eggs are then preserved by placing them in a soil-salt mix. tourism is the major reference of provincial income. The province earned 64 billion baht from tourism in 2018. That tax income accounted for 63 percentage of Surat Thani ‘s overall tourism income, most of it attributable to its island attractions : Ko Samui, Ko Pha Ngan, Ko Tao, and Mu Ko Ang Thong National Park. [ 7 ]
Human accomplishment index 2017 [edit ]
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 28 | 50 | 59 | 15 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |

|
 |

|
|
| 73 | 37 | 30 | 70 |
| Province Surat Thani, with an HAI 2017 value of 0.5476 is “low”, occupies place 65 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme ( UNDP ) in Thailand has tracked progress on homo development at sub-national level using the Human accomplishment exponent ( HAI ), a complex exponent covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board ( NESDB ) has taken over this tax since 2017. [ 3 ]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 – 15 | “high” |
| 16 – 30 | “somewhat high” |
| 31 – 45 | “average” |
| 45 – 60 | “somewhat low” |
| 61 – 77 | “low” |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |
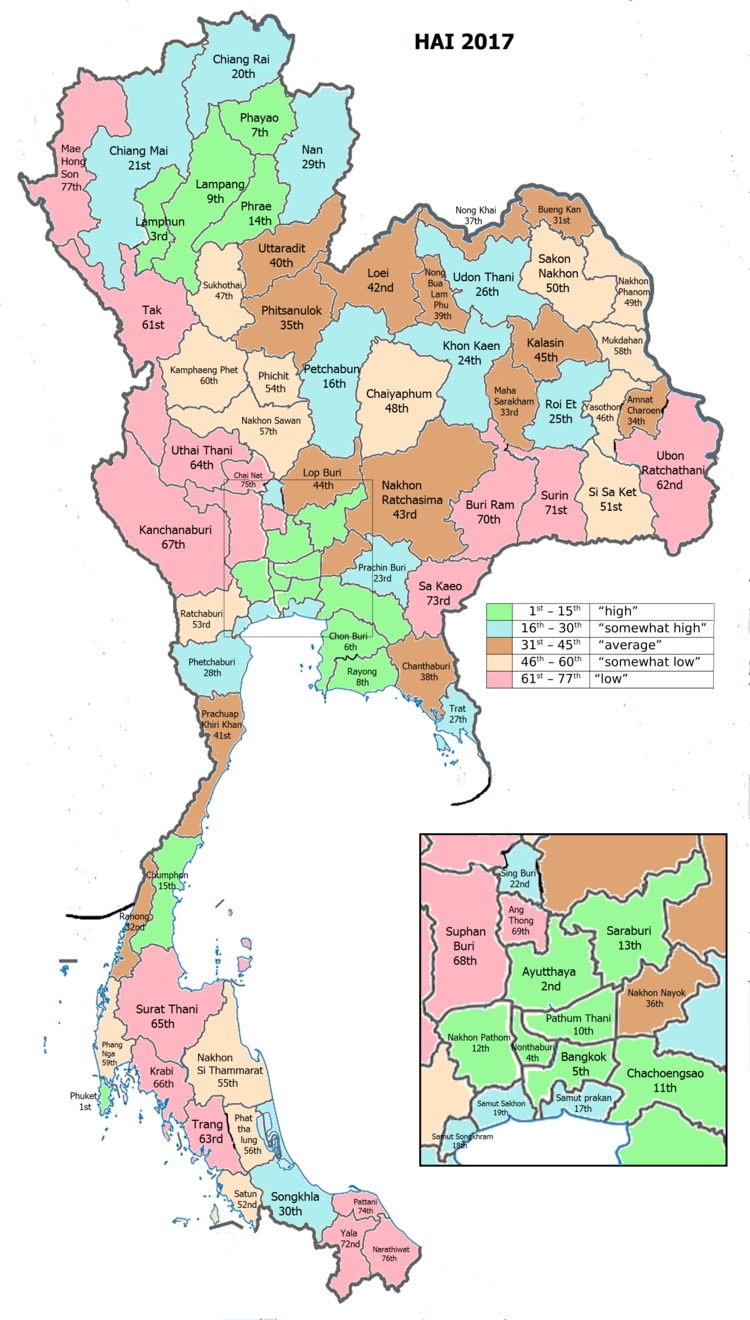
|
National parks [edit ]
veranda [edit ]
References [edit ]
Read more: Cha Bum-kun – Wikipedia
Coordinates :
