Singapore ( ), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a autonomous island city state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude ( 137 kilometres or 85 miles ) north of the equator, off the southern topple of the Malay Peninsula, bordering the Straits of Malacca to the west, the Riau Islands ( Indonesia ) to the south, and the South China Sea to the east. The state ‘s district is composed of one independent island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying isle, the combined area of which has increased by 25 % since the country ‘s independence as a result of across-the-board land reclamation projects. It has the second greatest population density in the world. With a multicultural population and recognising the indigence to respect cultural identities, Singapore has four official languages ; English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil. English is the tongue franca. Multiracialism is enshrined in the constitution and continues to shape national policies in department of education, house, and politics. Modern Singapore was founded in 1819 by Sir Stamford Raffles as a deal post of the british Empire. In 1867, the colonies in Southeast Asia were reorganised and Singapore came under the direct control condition of Britain as depart of the Straits Settlements. During the second World War, Singapore was occupied by Japan in 1942, and returned to British control as a separate crown colony following Japan ‘s giving up in 1945. Singapore gained self-governance in 1959 and in 1963 became contribution of the new federation of Malaysia, aboard Malaya, North Borneo, and Sarawak. ideological differences led to Singapore being expelled from the federation two years late and it became an mugwump country.
Reading: Singapore – Wikipedia
After early years of turbulence and despite lacking natural resources and a backwoods, the state quickly developed to become one of the Four Asian Tigers based on external deal, becoming a highly develop area ; it is ranked one-ninth on the UN Human Development Index and has the second-highest GDP per caput ( PPP ) in the world. Singapore is the lone state in Asia with a AAA autonomous rate from all major rate agencies. It is a major fiscal and shipping hub, systematically ranked the most expensive city to live in since 2013, and has been identified as a tax seaport. Singapore is placed highly in cardinal social indicators : education, healthcare, quality of life, personal safety, and housing, with a home-ownership pace of 91 %. Singaporeans enjoy one of the universe ‘s longest life expectancies, fastest Internet connection speeds and one of the lowest baby mortality rates in the populace. [ 7 ] Singapore is a unitary parliamentary republic with a Westminster arrangement of unicameral parliamentary politics. While elections are considered by and large free, the government exercises significant command over politics and company, and the People ‘s Action Party has ruled continuously since independence. One of the five founding members of ASEAN, Singapore is besides the headquarter of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation ( APEC ) Secretariat and Pacific Economic Cooperation Council ( PECC ) Secretariat, a well as many external conferences and events. Singapore is besides a member of the United Nations, World Trade Organization, East Asia Summit, Non-Aligned Movement, and the Commonwealth of Nations .
name and etymology
The English name of “ Singapore ” is an anglicization of the native Malay name for the country, Singapura, which was in turn derived from the Sanskrit password for “ leo city ” ( romanised : Siṃhapura ; Brahmi : ??????? ; literally “ leo city ” ; siṃha means “ lion ”, pura means “ city ” or “ fortress ” ). [ 8 ] A chinese score from the third century referred to a set as Pú Luó Zhōng ( chinese : 蒲 羅 中 ), which sounds like Malay for “ island at the conclusion of a peninsula. ” [ 9 ] early references to the identify Temasek ( or Tumasik ) are found in the Nagarakretagama, a javanese epic poem poem written in 1365, and a vietnamese beginning from the same time period. The mention possibly means “ Sea Town ”, being derived from the Malay tasek, meaning “ sea ” or “ lake ”. [ 10 ] The chinese traveler Wang Dayuan visited a home around 1330 named Danmaxi ( taiwanese : 淡馬錫 ; pinyin : Dànmǎxí ; Wade–Giles : Tan Ma Hsi ) or Tam ma siak, depending on pronunciation. Danmaxi may be a transcription of Temasek ( Tumasik ), alternatively, it may be a combination of the Malay Tanah meaning “ domain ” and Chinese Xi meaning “ can, ” which was traded on the island. [ 11 ] [ 10 ] Variations of the diagnose Siṃhapura were used for a number of cities throughout the region anterior to the establishment of the Kingdom of Singapura. In Hindu-Buddhist culture, lions were associated with power and protective covering, which may explain the attraction of such a name. [ 13 ] The list Singapura supplanted Temasek sometime before the fifteenth century, after the establishment of the Kingdom of Singapura on the island by a flee Srivijayan Raja ( prince ) from Palembang. however, the precise time and reason for the appoint change is nameless. The semi-historical Malay Annals state that Temasek was christened Singapura by Sang Nila Utama, a 13th-century Srivijayan Raja from Palembang. The Annals express that Sang Nila Utama encountered a foreign beast on the island that he took to be a leo. Seeing this as an omen, he established the town of Singapura where he encountered the beast. The second hypothesis, puff from portuguese sources, postulates that this fabulous story is based on the very liveliness Parameswara of Palembang. Parameswara declared independence from Majapahit and mounted a Lion Throne, thus claiming the Srivijaya Empire. After then being driven into exile by the Javanese, he usurped control over Temasek. It is possible that he rechristened the area as Singapura, recalling the throne he had been driven from. [ 14 ] Under japanese occupation, Singapore was renamed Syonan ( japanese : 昭 南, Hepburn : Shōnan ), meaning “ Light of the South. ” [ 15 ] [ 16 ] Singapore is sometimes referred to by the nickname the “ Garden City, ” in address to its parks and tree-lined streets. [ 17 ] Another informal appoint, the “ small Red Dot, ” was adopted after an article publication in the Asian Wall Street Journal of 4 August 1998 regarded the third Indonesian President B. J. Habibie referred to Singapore as a crimson point on a map. [ 18 ] [ 19 ] [ 20 ] [ 21 ]
history
Ancient Singapore
In 1299, according to the Malay Annals, the Kingdom of Singapura was founded on the island by Sang Nila Utama. [ 22 ] Although the historicity of the accounts as given in the Malay Annals is the submit of academician debates, it is however known from respective documents that Singapore in the fourteenth hundred, then known as Temasek, was a deal port under the determine of both the Majapahit Empire and the Siamese kingdoms, and was a contribution of the Indosphere. [ 25 ] [ 26 ] [ 27 ] [ 28 ] [ 29 ] These Indianised kingdoms were characterised by surprising resilience, political integrity and administrative stability. [ 30 ] Historical sources besides indicate that around the end of the fourteenth hundred, its ruler Parameswara was attacked by either the Majapahit or the siamese cat, forcing him to move to Malacca where he founded the Sultanate of Malacca. archaeological evidence suggests that the chief settlement on Fort Canning was abandoned around this time, although a modest trade village continued in Singapore for some clock time afterwards. [ 14 ] In 1613, portuguese raiders burned down the colonization, and the island faded into obscurity for the following two centuries. [ 32 ] By then, Singapore was nominally part of the Johor Sultanate. [ 33 ] The wide maritime area and much trade was under Dutch see for the trace time period after the dutch conquest of Malacca. [ 34 ]
british colonization
The british governor Stamford Raffles arrived in Singapore on 28 January 1819 and soon recognised the island as a natural choice for the new port. [ 35 ] The island was then nominally ruled by Tengku Abdul Rahman, the Sultan of Johor, who was controlled by the dutch and the Bugis. [ 36 ] however, the Sultanate was weakened by factional division : the Temenggong ( Chief Minister ) of Tengku Abdul Rahman, ampere well as his officials, were loyal to the Sultan ‘s elder brother Tengku Long, who was living in exile in Riau. With the Temenggong ‘s help, Raffles managed to smuggle Tengku Long back into Singapore. Raffles offered to recognise Tengku Long as the rightful Sultan of Johor, under the title of Sultan Hussein, a well as leave him with a annual payment of $ 5000 and another $ 3000 to the Temenggong ; in hark back, Sultan Hussein would grant the british the right to establish a trading post on Singapore. [ 37 ] A formal treaty was signed on 6 February 1819. [ 38 ] [ 39 ]
In 1824, a far treaty with the Sultan led to the entire island becoming a british possession. [ 40 ] In 1826, Singapore became part of the Straits Settlements, then under the legal power of british India. Singapore became the regional capital in 1836. [ 41 ] Prior to Raffles ‘ arrival, there were alone about a thousand people living on the island, largely autochthonal Malays along with a handful of Chinese. [ 42 ] By 1860 the population had swelled to over 80,000, more than half being chinese. [ 40 ] Many of these early immigrants came to work on the pepper and gambier plantations. [ 43 ] In 1867, the Straits Settlements were separated from british India, coming under the direct control of Britain. [ 44 ] Later, in the 1890s, when the arctic diligence became established in Malaya and Singapore, [ 45 ] the island became a ball-shaped kernel for rubber sorting and export. [ 40 ] Singapore was not greatly affected by the First World War ( 1914–18 ), as the conflict did not spread to Southeast Asia. The only significant event during the war was the 1915 Singapore Mutiny by Muslim sepoys from british India, who were garrisoned in Singapore. [ 46 ] After hearing rumours that they were to be sent to fight the Ottoman Empire, a Muslim submit, the soldiers rebelled, killing their officers and several british civilians before the mutiny was suppressed by non-Muslim troops arriving from Johore and Burma. [ 47 ] After World War I, the british built the bombastic Singapore Naval Base as separate of the defensive Singapore scheme. [ 48 ] Originally announced in 1921, the construction of the base proceeded at a boring pace until the japanese invasion of Manchuria in 1931. Costing $ 60 million and not in full completed in 1938, it was however the largest dry dock in the world, the third-largest floating dock, and had adequate fuel tanks to support the integral british dark blue for six months. [ 48 ] [ 49 ] [ 50 ] The foundation was defended by heavy 15-inch ( 380 millimeter ) naval guns stationed at Fort Siloso, Fort Canning and Labrador, american samoa well as a Royal Air Force airfield at Tengah Air Base. Winston Churchill touted it as the “ Gibraltar of the East ”, and military discussions often referred to the base as merely “ East of Suez “. however, the british Home Fleet was stationed in Europe, and the British could not afford to build a second fleet to protect their interests in Asia. The plan was for the Home Fleet to sail cursorily to Singapore in the consequence of an emergency. As a consequence, after World War II broke out in 1939, the fleet was amply occupied with defending Britain, leaving Singapore vulnerable to japanese invasion. [ 51 ] [ 52 ]
World War II
During the Pacific War, the japanese invasion of Malaya culminated in the Battle of Singapore. When the british force of 60,000 troops surrendered on 15 February 1942, British prime minister Winston Churchill called the defeat “ the worst catastrophe and largest capitulation in british history ”. [ 53 ] british and Empire losses during the active for Singapore were heavy, with a full of about 85,000 personnel captured. About 5,000 were killed or wounded, [ 55 ] of which Australians made up the majority. [ 57 ] [ 58 ] japanese casualties during the fight in Singapore amounted to 1,714 killed and 3,378 wounded. [ bel ] The occupation was to become a major turning point in the histories of several nations, including those of Japan, Britain, and Singapore. japanese newspapers triumphantly declared the victory as deciding the general site of the war. [ 60 ] Between 5,000 and 25,000 cultural chinese people were killed in the subsequent Sook Ching massacre. [ 61 ] british forces had planned to liberate Singapore in 1945 ; however, the war ended before these operations could be carried out. [ 63 ]
Post-war period
After the japanese surrender to the Allies on 15 August 1945, Singapore fell into a brief state of violence and disorder ; looting and revenge-killing were widespread. british, australian, and indian troops led by Lord Louis Mountbatten returned to Singapore to receive the conventional capitulation of japanese forces in the region from General Seishirō Itagaki on behalf of General Hisaichi Terauchi on 12 September 1945. [ 63 ] interim, Tomoyuki Yamashita was tried by a US military commission for war crimes, but not for crimes committed by his troops in Malaya or Singapore. He was convicted and hanged in the Philippines on 23 February 1946. [ 65 ] a lot of Singapore ‘s infrastructure had been destroyed during the war, including those needed to supply utilities. A deficit of food led to malnutrition, disease, and rampant crime and violence. A series of strikes in 1947 caused massive stoppages in public tape drive and early services. however, by late 1947 the economy began to recover, facilitated by a growing international demand for can and rubber. [ 66 ] The failure of Britain to successfully defend its colony against the japanese changed its double in the eyes of Singaporeans. british military government ended on 1 April 1946, with Singapore becoming a divide Crown Colony. [ 66 ] In July 1947, disjoined executive and legislative Councils were established and the election of six members of the Legislative Council was scheduled in the come year. [ 67 ] During the 1950s, chinese communists, with firm ties to the trade unions and chinese schools, waged a guerrilla war against the government, leading to the Malayan Emergency. The 1954 National Service riots, Hock Lee bus riots, and chinese middle schools riots in Singapore were all linked to these events. [ 68 ] David Marshall, pro-independence drawing card of the Labour Front, won Singapore ‘s beginning general election in 1955. [ 69 ] He led a delegating to London, and Britain rejected his need for complete self-government. He resigned and was replaced by Lim Yew Hock in 1956, and after far negotiations Britain to grant Singapore full inner self-government for all matters except defense and foreign affairs. [ 70 ] During the subsequent May 1959 elections, the People ‘s Action Party ( PAP ) won a landslide victory. [ 71 ] Governor Sir William Allmond Codrington Goode served as the first Yang di-Pertuan Negara ( Head of State ). [ 72 ]
Within Malaysia
 Singapore thrived as an entrepôt. In the 1960s, bumboats were used to transport cargoes and supplies between nearshore ships and Singapore River. PAP leaders believed that Singapore ‘s future ballad with Malaya, due to strong ties between the two. It was thought that reuniting with Malaya would benefit the economy by creating a common market, alleviating ongoing unemployment woes in Singapore. however, a goodly pro-communist wing of the PAP was powerfully opposed to the amalgamation, fearing a loss of charm, and therefore formed the Barisan Sosialis, splitting from the PAP. [ 73 ] [ 74 ] The ruling party of Malaya, United Malays National Organisation ( UMNO ), was staunchly anti-communist, and it was suspected UMNO would support the non-communist factions of PAP. UMNO, initially doubting of the idea of a amalgamation ascribable to distrust of the PAP government and concern that the boastfully cultural taiwanese population in Singapore would alter the racial balance in Malaya on which their political world power free-base depended, became supportive of the mind of the fusion due to joint fear of a communist takeover. [ 75 ] On 27 May 1961, Malaya ‘s prime minister, Tunku Abdul Rahman, made a surprise proposal for a new Federation called Malaysia, which would unite the current and erstwhile british possessions in the area : the Federation of Malaya, Singapore, Brunei, North Borneo, and Sarawak. [ 75 ] UMNO leaders believed that the extra Malay population in the Bornean territories would balance Singapore ‘s chinese population. [ 70 ] The british government, for its separate, believed that the fusion would prevent Singapore from becoming a haven for communism. [ 76 ] To obtain a mandate for a amalgamation, the PAP held a referendum on the amalgamation. This referendum included a choice of different terms for a amalgamation with Malaysia and had no choice for avoiding amalgamation raw. On 16 September 1963, Singapore joined with Malaya, the North Borneo, and Sarawak to form the new Federation of Malaysia under the terms of the Malaysia Agreement. Under this Agreement, Singapore had a relatively high flush of autonomy compared to the other states of Malaysia. [ 77 ] Indonesia opposed the constitution of Malaysia due to its own claims over Borneo and launched Konfrontasi ( Confrontation in Indonesian ) in reply to the formation of Malaysia. [ 78 ] On 10 March 1965, a turkey planted by indonesian saboteurs on a mezzanine floor of MacDonald House exploded, killing three people and injuring 33 others. It was the deadliest of at least 42 turkey incidents which occurred during the confrontation. [ 79 ] Two members of the indonesian Marine Corps, Osman bin Haji Mohamed Ali and Harun bin Said, were finally convicted and executed for the crime. [ 80 ] The plosion caused US $ 250,000 ( equivalent to US $ 2,053,062 in 2020 ) in damages to MacDonald House. [ 81 ] [ 82 ] even after the fusion, the singaporean government and the malaysian central government disagreed on many political and economic issues. Despite an agreement to establish a common market, Singapore continued to face restrictions when deal with the rest of Malaysia. In retaliation, Singapore did not extend to Sabah and Sarawak the full extent of the loans agreed to for economic development of the two easterly states. Talks soon broke down, and abusive speeches and writing became prevailing on both sides. This led to communal strife in Singapore, culminating in the 1964 subspecies riots. [ 83 ] On 7 August 1965, Malaysian choice curate Tunku Abdul Rahman, seeing no alternative to avoid further bloodshed, advised the Parliament of Malaysia that it should vote to expel Singapore from Malaysia. [ 84 ] On 9 August 1965, the Malaysian Parliament voted 126 to 0 to move a placard to amend the fundamental law, expelling Singapore from Malaysia, which left Singapore as a newly mugwump state. [ 70 ] [ 85 ] [ 86 ] [ 87 ]
Singapore thrived as an entrepôt. In the 1960s, bumboats were used to transport cargoes and supplies between nearshore ships and Singapore River. PAP leaders believed that Singapore ‘s future ballad with Malaya, due to strong ties between the two. It was thought that reuniting with Malaya would benefit the economy by creating a common market, alleviating ongoing unemployment woes in Singapore. however, a goodly pro-communist wing of the PAP was powerfully opposed to the amalgamation, fearing a loss of charm, and therefore formed the Barisan Sosialis, splitting from the PAP. [ 73 ] [ 74 ] The ruling party of Malaya, United Malays National Organisation ( UMNO ), was staunchly anti-communist, and it was suspected UMNO would support the non-communist factions of PAP. UMNO, initially doubting of the idea of a amalgamation ascribable to distrust of the PAP government and concern that the boastfully cultural taiwanese population in Singapore would alter the racial balance in Malaya on which their political world power free-base depended, became supportive of the mind of the fusion due to joint fear of a communist takeover. [ 75 ] On 27 May 1961, Malaya ‘s prime minister, Tunku Abdul Rahman, made a surprise proposal for a new Federation called Malaysia, which would unite the current and erstwhile british possessions in the area : the Federation of Malaya, Singapore, Brunei, North Borneo, and Sarawak. [ 75 ] UMNO leaders believed that the extra Malay population in the Bornean territories would balance Singapore ‘s chinese population. [ 70 ] The british government, for its separate, believed that the fusion would prevent Singapore from becoming a haven for communism. [ 76 ] To obtain a mandate for a amalgamation, the PAP held a referendum on the amalgamation. This referendum included a choice of different terms for a amalgamation with Malaysia and had no choice for avoiding amalgamation raw. On 16 September 1963, Singapore joined with Malaya, the North Borneo, and Sarawak to form the new Federation of Malaysia under the terms of the Malaysia Agreement. Under this Agreement, Singapore had a relatively high flush of autonomy compared to the other states of Malaysia. [ 77 ] Indonesia opposed the constitution of Malaysia due to its own claims over Borneo and launched Konfrontasi ( Confrontation in Indonesian ) in reply to the formation of Malaysia. [ 78 ] On 10 March 1965, a turkey planted by indonesian saboteurs on a mezzanine floor of MacDonald House exploded, killing three people and injuring 33 others. It was the deadliest of at least 42 turkey incidents which occurred during the confrontation. [ 79 ] Two members of the indonesian Marine Corps, Osman bin Haji Mohamed Ali and Harun bin Said, were finally convicted and executed for the crime. [ 80 ] The plosion caused US $ 250,000 ( equivalent to US $ 2,053,062 in 2020 ) in damages to MacDonald House. [ 81 ] [ 82 ] even after the fusion, the singaporean government and the malaysian central government disagreed on many political and economic issues. Despite an agreement to establish a common market, Singapore continued to face restrictions when deal with the rest of Malaysia. In retaliation, Singapore did not extend to Sabah and Sarawak the full extent of the loans agreed to for economic development of the two easterly states. Talks soon broke down, and abusive speeches and writing became prevailing on both sides. This led to communal strife in Singapore, culminating in the 1964 subspecies riots. [ 83 ] On 7 August 1965, Malaysian choice curate Tunku Abdul Rahman, seeing no alternative to avoid further bloodshed, advised the Parliament of Malaysia that it should vote to expel Singapore from Malaysia. [ 84 ] On 9 August 1965, the Malaysian Parliament voted 126 to 0 to move a placard to amend the fundamental law, expelling Singapore from Malaysia, which left Singapore as a newly mugwump state. [ 70 ] [ 85 ] [ 86 ] [ 87 ]
Republic of Singapore
After being expelled from Malaysia, Singapore became autonomous as the Republic of Singapore on 9 August 1965, with Lee Kuan Yew and Yusof bin Ishak as the first prime minister and president of the united states respectively. [ 88 ] [ 89 ] In 1967, the state co-founded the Association of Southeast asian Nations ( ASEAN ). [ 90 ] Race riots broke out once more in 1969. [ 91 ] Lee Kuan Yew ‘s vehemence on rapid economic growth, support for business entrepreneurship, and limitations on inner democracy shaped Singapore ‘s policies for the adjacent half-century. [ 92 ] [ 93 ] Economic growth continued throughout the 1980s, with the unemployment rate falling to 3 % and substantial GDP growth averaging at about 8 % up until 1999. During the 1980s, Singapore began to shift towards high-tech industries, such as the wafer lying sector, in club to remain competitive as neighbouring countries began manufacturing with cheaper parturiency. Singapore Changi Airport was opened in 1981 and Singapore Airlines was formed. [ 94 ] The Port of Singapore became one of the world ‘s busy ports and the serve and tourism industries besides grew vastly during this menstruation. [ 95 ] [ 96 ] The PAP, which has remained in power since independence, is believed to rule in an authoritarian manner by some activists and opposition politicians who see the rigorous regulation of political and media activities by the government as an misdemeanor on political rights. [ 97 ] In reaction, Singapore has seen respective significant political changes, such as the introduction of the Non-Constituency members of fantan in 1984 to allow up to three losing candidates from opposition parties to be appointed as MPs. Group Representation Constituencies ( GRCs ) were introduced in 1988 to create multi-seat electoral divisions, intended to ensure minority representation in fantan. [ 98 ] Nominated members of parliament were introduced in 1990 to allow non-elected non-partisan MPs. [ 99 ] The Constitution was amended in 1991 to provide for an Elected President who has veto power in the use of home reserves and appointments to public agency. [ 100 ] In 1990, Goh Chok Tong succeeded Lee and became Singapore ‘s second prime minister. [ 101 ] During Goh ‘s tenure, the area went through the 1997 asian fiscal crisis and the 2003 SARS outbreak. [ 102 ] [ 103 ] In 2004, Lee Hsien Loong, the eldest son of Lee Kuan Yew, became the nation ‘s third prime minister. [ 103 ] Lee Hsien Loong ‘s tenure included the 2008 ball-shaped fiscal crisis, the resolution of a dispute over land possession at Tanjong Pagar railroad track station between Singapore and Malaysia, and the initiation of the 2 integrated resorts ( IRs ), located at the Marina Bay Sands and Resorts World Sentosa. [ 104 ] The People ‘s Action Party ( PAP ) suffered its worst always electoral results in 2011, winning barely 60 % of votes, amidst argument over issues including the inflow of foreign workers and the high cost of live. [ 105 ] On 23 March 2015, Lee Kuan Yew died, and a one-week period of populace mourning was observed nationally. [ 93 ] Subsequently, the PAP regained its dominance in Parliament through the September cosmopolitan election, receiving 69.9 % of the democratic vote, although this remained lower than the 2001 tally of 75.3 % [ 106 ] and the 1968 reckoning of 86.7 %. [ 107 ] The 2020 election saw the PAP drop to 61 % of the vote, while the opposition Workers ‘ Party took 10 of the 93 seats, the highest number ever won by an opposition party. [ 108 ]
Government and politics
 The Istana is the official residence and office of the President, as well as the working office of the Prime Minister. Singapore is a parliamentary democracy based on the Westminster system. The constitution of Singapore is the sovereign jurisprudence of the area, establishing the structure and responsibility of government. The president of the united states is head of state and exercises executive ability on the advice of her ministers. The prime minister is head of government and is appointed by the president of the united states as the person most likely to command the confidence of a majority of Parliament. Cabinet is chosen by the choice minister and formally appointed by the president. [ 109 ] The politics is separated into three branches :
The Istana is the official residence and office of the President, as well as the working office of the Prime Minister. Singapore is a parliamentary democracy based on the Westminster system. The constitution of Singapore is the sovereign jurisprudence of the area, establishing the structure and responsibility of government. The president of the united states is head of state and exercises executive ability on the advice of her ministers. The prime minister is head of government and is appointed by the president of the united states as the person most likely to command the confidence of a majority of Parliament. Cabinet is chosen by the choice minister and formally appointed by the president. [ 109 ] The politics is separated into three branches :
The president is directly elected by popular right to vote for a renewable six-year term. Requirements for this position are highly rigorous, such that no more than several thousand people qualify [ clarification needed ] for campaigning. [ 114 ] To be qualified, a campaigner needs to be a person at least 45 years of age who is no longer a penis of a political party, to have held office for at least 3 years in a count of specific public serve roles, to besides have 3 years experience adenine head executive of a individual sector company with rules limiting which roles and companies qualify, and more. [ 115 ] The Constitution requires that presidential elections be “ reserved “ for a racial community if no one from that cultural group has been elected to the presidency in the five most holocene terms. [ 116 ] only members of that community may qualify as candidates in a reserve presidential election. [ 117 ] In the 2017 presidential election, this combination of rigorous requirements and a reserved election that required the candidate to be of the 13 % Malay cultural group led to a single person being qualified for the position ; [ 118 ] Halimah Yacob won in an uncontested election. Members of Parliament ( MPs ) are elected at least every five years ( or sooner in the shell of a snap election ). The current Parliament has 100 members ; 88 were directly elected from the 29 constituencies, nine are nonpartisan nominate members appointed by the president of the united states, and three are non-constituency members from opposition parties who were not elected in the last general election but appointed to the legislature to increase confrontation party representation. In group representation constituencies ( GRCs ), political parties assemble teams of candidates ( preferably than nominate individuals ) to contest elections. At least one MP in a GRC must be of an heathen minority backdrop. All elections are held using first-past-the-post vote. [ 119 ] The People ‘s Action Party ( PAP ) occupies a dominant allele position in singaporean politics, having won large parliamentary majorities in every election since self-governance was granted in 1959. [ 120 ] even its candidates who lose elections are frequently turned to by constituency residents for aid. The most effective resistance party is the Workers ‘ Party. [ 108 ] The judicial organization is based on English common law, continuing the legal tradition established during british principle and with substantial local differences. criminal law is based on the indian Penal Code originally intended for british India, and was at the clock as a crown colony besides adopted by the british colonial authorities in Singapore and remains the basis of the criminal code in the area with a few exceptions, amendments and repeals since it came into force. [ 121 ] Trial by jury was abolished in 1970. [ 122 ] Both bodily punishment ( caning ) [ 123 ] [ 124 ] and capital punishment ( by hanging ) continue to be applied as legal penalties. [ 125 ]
extraneous relations
Singapore ‘s express foreign policy priority is maintaining security in Southeast Asia and surrounding territories. An implicit in principle is political and economic stability in the region. [ 126 ] It has diplomatic relations with more than 180 sovereign states. [ 127 ] As one of the five founding members of ASEAN, [ 128 ] Singapore is a potent garter of the ASEAN Free Trade Area ( AFTA ) and the ASEAN Investment Area ( AIA ) as its economy is close linked to that of the region as a whole. [ 129 ] [ failed verification ] Former prime minister Goh Chok Tong has proposed the formation of an ASEAN Economic Community ( AEC ), a step beyond the AFTA, bringing it closer to a common market. [ 130 ] This was agreed to in 2007 for execution by 2015. early regional organisations are important to Singapore, [ 131 ] [ failed verification ] and it is the host of the APEC Secretariat. [ 132 ] Singapore maintains membership in other regional organisations, such as Asia–Europe Meeting, the Forum for East Asia-Latin american Cooperation, the indian Ocean Rim Association, and the East Asia Summit. [ 126 ] It is besides a member of the Non-Aligned Movement, [ 133 ] the United Nations and the Commonwealth. [ 134 ] [ 135 ] While Singapore is not a formal member of the G20, it has been invited to participate in G20 processes in most years since 2010. [ 136 ] Singapore is besides the location of the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council ( PECC ) Secretariat. [ 137 ] In general, bilateral relations with other ASEAN members are firm ; however, disagreements have arisen, [ 138 ] and relations with neighbor Malaysia and Indonesia have sometimes been strained. [ 139 ] Malaysia and Singapore have clashed over the delivery of fresh water to Singapore, [ 140 ] and entree by the Singapore Armed Forces to malaysian airspace. [ 139 ] Border issues exist with Malaysia and Indonesia, and both have banned the sale of nautical backbone to Singapore over disputes about Singapore ‘s domain reclamation. [ 141 ] Some previous disputes, such as the Pedra Branca challenge, have been resolved by the International Court of Justice. [ 142 ] Piracy in the Strait of Malacca has been a causal agent of business for all three countries. [ 140 ] Close economic ties exist with Brunei, and the two contribution a peg currency rate, through a Currency Interchangeability Agreement between the two countries which makes both Brunei dollar and Singapore dollar banknotes and coins legal tender in either nation. [ 143 ] [ 144 ] The first diplomatic touch with China was made in the 1970s, with full moon diplomatic relations established in the 1990s. Since then the two countries have been major players in strengthening the ASEAN–China kinship, [ 145 ] [ failed verification ] and has maintained a long-standing and greatly prioritised conclusion relationship partially due to China ‘s growing influence and essentiality in the Asia-Pacific region, specifying that “ its park interest with China is far greater than any differences ”. Furthermore, Singapore has positioned itself as a hard patron of China ‘s constructive date and passive exploitation in the region. In summation, China has been Singapore ‘s largest trade partner since 2013, after surpassing Malaysia. [ 146 ] [ 147 ] [ 148 ] [ 149 ] [ 150 ] Singapore and the United States partake a long-standing conclusion relationship, in finical in defense, the economy, health, and education. Singapore has besides pushed regional counter-terrorism initiatives, with a strong decide to deal with terrorists inside its borders. To this end, the country has stepped up co-operation with ASEAN members and China to strengthen regional security and battle terrorism, adenine well as participating in the organization ‘s first joint nautical exert with the latter. [ 151 ] It has besides given subscribe to the US-led coalescence to fight terrorism, with bilateral co-operation in counter-terrorism and counter-proliferation initiatives, and joint military exercises. [ 138 ] As Singapore has diplomatic relations with both the United States and North Korea, and was one of the few countries that have relationships with both countries, [ 152 ] on 12 June 2018, Singapore hosted a historic summit between US President Donald Trump and north korean drawing card Kim Jong-un, the first-ever converge between the sitting leaders of the two nations. [ 153 ] [ 154 ] It has besides hosted the Ma–Xi meeting on 7 November 2015, the first confluence between the political leaders of the two sides of the Taiwan Strait since the end of the Chinese Civil War in 1950. [ 155 ] [ 156 ] [ 157 ]
military
The Singaporean military, arguably the most technologically advanced in Southeast Asia, [ 158 ] consists of the united states army, navy, and the air out pull. It is seen as the guarantor of the country ‘s independence, [ 159 ] translating into Singapore culture, involving all citizens in the area ‘s defense mechanism. [ 160 ] The government spends 4.9 % of the nation ‘s GDP on the military—high by regional standards [ 158 ] —and one out of every four dollars of government spend is spent on defense. [ 161 ] After its independence, Singapore had merely two infantry regiments commanded by british officers. Considered excessively small to provide effective security for the fresh country, the development of its military forces became a precedence. [ 162 ] In summation, in October 1971, Britain pulled its military out of Singapore, leaving behind only a modest british, australian and New Zealand wedge as a nominal military presence. [ 163 ] A big deal of initial hold came from Israel, [ 162 ] a state unrecognised by Singapore ‘s neighbor Muslim-majority nations of Malaysia and Indonesia. [ 164 ] [ 165 ] [ 166 ] The Israeli Defense Force ( IDF ) commanders were tasked by the Singapore government to create the Singapore Armed Forces ( SAF ) from abrasion, and israeli instructors were brought in to train singaporean soldiers. military courses were conducted according to the IDF ‘s format, and Singapore adopted a organization of conscription and reserve avail based on the Israeli exemplary. [ 162 ] Singapore still maintains strong security ties with Israel and is one of the biggest buyers of Israeli arms and weapons systems [ 167 ] with one holocene example being the MATADOR anti-tank weapon. [ 168 ]
 In 2007, singaporean troopers were deployed in Afghanistan as part of a multinational alliance. The SAF is being developed to respond to a wide-eyed range of issues in both ceremonious and improper war. The Defence Science and Technology Agency is creditworthy for procuring resources for the military. [ 169 ] The geographic restrictions of Singapore average that the SAF must plan to fully repulse an attack, as they can not fall back and re-group. The little size of the population has besides affected the way the SAF has been designed, with a little active force and a large number of reserves. [ 160 ] Singapore has conscription for all able males at old age 18, except those with a criminal phonograph record or who can prove that their loss would bring hardship to their families. Males who have yet to complete pre-university education or are awarded the Public Service Commission eruditeness can opt to defer their blueprint. [ 170 ] Though not required to perform military service, the numeral of women in the SAF has been increasing : since 1989 they have been allowed to fill military vocations once reserved for men. Before generalization into a specific branch of the armed forces, recruits undergo at least 9 weeks of basic military discipline. [ 171 ] Because of the scarcity of open land on the main island, training involving activities such as alive ignition and amphibious war are frequently carried out on smaller islands, typically barred to civilian access. however, large-scale drills, considered excessively dangerous to be performed in the state, have been performed in Taiwan since 1975 [ 171 ] and in about a twelve early countries. In general, military exercises are held with foreign forces once or doubly per week. [ 160 ] due to airspace and land constraints, the Republic of Singapore Air Force ( RSAF ) maintains a count of overseas bases in Australia, the United States, and France. The RSAF ‘s 130 Squadron is based in RAAF Base Pearce, Western Australia, [ 172 ] and its 126 Squadron is based in the Oakey Army Aviation Centre, Queensland. [ 173 ] The RSAF has one squadron—the 150 Squadron—based in Cazaux Air Base in southern France. [ 174 ] [ 175 ] The RSAF ‘s overseas detachments in the United States are : Luke Air Force Base ( Arizona ), Marana ( Arizona ), Mountain Home Air Force Base ( Idaho ), and Andersen Air Force Base ( Guam ). [ 176 ] [ 177 ] [ 178 ] The SAF has sent forces to assist in operations outside the state, in areas such as Iraq [ 179 ] and Afghanistan, [ 180 ] [ 181 ] in both military and civilian roles. In the region, they have helped to stabilise East Timor and have provided help to Aceh in Indonesia following the 2004 amerind Ocean earthquake and tsunami. Since 2009, the Republic of Singapore Navy ( RSN ) has deployed ships to the Gulf of Aden to aid in rejoinder piracy efforts as part of Task Force 151. [ 182 ] The SAF besides helped in relief efforts during Hurricane Katrina [ 183 ] and Typhoon Haiyan. [ 184 ] Singapore is partially of the Five Power Defence Arrangements, a military alliance with Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom. [ 160 ] In 2019, the nation was placed 7th most peaceful country on the Global Peace Index. [ 185 ]
In 2007, singaporean troopers were deployed in Afghanistan as part of a multinational alliance. The SAF is being developed to respond to a wide-eyed range of issues in both ceremonious and improper war. The Defence Science and Technology Agency is creditworthy for procuring resources for the military. [ 169 ] The geographic restrictions of Singapore average that the SAF must plan to fully repulse an attack, as they can not fall back and re-group. The little size of the population has besides affected the way the SAF has been designed, with a little active force and a large number of reserves. [ 160 ] Singapore has conscription for all able males at old age 18, except those with a criminal phonograph record or who can prove that their loss would bring hardship to their families. Males who have yet to complete pre-university education or are awarded the Public Service Commission eruditeness can opt to defer their blueprint. [ 170 ] Though not required to perform military service, the numeral of women in the SAF has been increasing : since 1989 they have been allowed to fill military vocations once reserved for men. Before generalization into a specific branch of the armed forces, recruits undergo at least 9 weeks of basic military discipline. [ 171 ] Because of the scarcity of open land on the main island, training involving activities such as alive ignition and amphibious war are frequently carried out on smaller islands, typically barred to civilian access. however, large-scale drills, considered excessively dangerous to be performed in the state, have been performed in Taiwan since 1975 [ 171 ] and in about a twelve early countries. In general, military exercises are held with foreign forces once or doubly per week. [ 160 ] due to airspace and land constraints, the Republic of Singapore Air Force ( RSAF ) maintains a count of overseas bases in Australia, the United States, and France. The RSAF ‘s 130 Squadron is based in RAAF Base Pearce, Western Australia, [ 172 ] and its 126 Squadron is based in the Oakey Army Aviation Centre, Queensland. [ 173 ] The RSAF has one squadron—the 150 Squadron—based in Cazaux Air Base in southern France. [ 174 ] [ 175 ] The RSAF ‘s overseas detachments in the United States are : Luke Air Force Base ( Arizona ), Marana ( Arizona ), Mountain Home Air Force Base ( Idaho ), and Andersen Air Force Base ( Guam ). [ 176 ] [ 177 ] [ 178 ] The SAF has sent forces to assist in operations outside the state, in areas such as Iraq [ 179 ] and Afghanistan, [ 180 ] [ 181 ] in both military and civilian roles. In the region, they have helped to stabilise East Timor and have provided help to Aceh in Indonesia following the 2004 amerind Ocean earthquake and tsunami. Since 2009, the Republic of Singapore Navy ( RSN ) has deployed ships to the Gulf of Aden to aid in rejoinder piracy efforts as part of Task Force 151. [ 182 ] The SAF besides helped in relief efforts during Hurricane Katrina [ 183 ] and Typhoon Haiyan. [ 184 ] Singapore is partially of the Five Power Defence Arrangements, a military alliance with Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom. [ 160 ] In 2019, the nation was placed 7th most peaceful country on the Global Peace Index. [ 185 ]
Human rights
 Speakers’ Corner in Chinatown provides a public demonstration and “free speech” area usually restricted in other parts of the island. In 2020, Singapore was ranked 158th out of 180 nations by Reporters Without Borders in the Worldwide Press Freedom Index. [ 186 ] Historically, the government has restricted freedom of speech and exemption of the wardrobe and has limited some civil and political rights. [ 187 ] The mighty to freedom of language and affiliation guaranteed by Article 14 ( 1 ) of the Constitution of Singapore is restricted by the subsequent subsection ( 2 ) of the same Article. [ 188 ] Freedom House ranks Singapore as “ partially detached ” in its Freedom in the World composition, [ 120 ] and The Economist Intelligence Unit ranks Singapore as a “ flaw majority rule ”, the second best rate of four, in its “ Democracy Index “. [ 189 ] [ 190 ] In the 2015 Singaporean general election, the People ‘s Action Party ( PAP ) won 83 of 89 seats contested with 70 % of the popular vote. [ 191 ] The latest elections were in July 2020, with the People ‘s Action Party ( PAP ) winning 83 of 93 seats contested with 61 % of the popular vote. Amnesty International has said that some legal provisions of the Singapore arrangement conflict with “ the correct to be presumed innocent until prove guilty ”. [ 192 ] The government has disputed Amnesty ‘s claims, stating that their “ military position on abolition of the death penalty is by no means uncontested internationally ” and that the Report contains “ sculpt errors of facts and misrepresentations ”. [ 193 ] Singapore ‘s judicial system is considered one of the most reliable in Asia. [ 194 ] Sex trafficking in Singapore is a significant trouble. Singaporean and extraneous women and girls have been forced into prostitution in brothels and been physically and psychologically abused. [ 195 ] [ 196 ] [ 197 ] A police dating from 1938 bans intimate relations between men, however the law is rarely enforced. intimate relations between women are legal. [ 198 ] In the Corruption Perceptions Index which ranks countries by “ sensed levels of public sector putrescence ”, Singapore has systematically ranked as one of the least corrupt. [ 199 ] Singapore ‘s singular combination of a potent about authoritarian politics with an vehemence on meritocracy and good government is known as the “ Singapore model “, and is regarded as a key factor behind Singapore ‘s political stability, economic growth, and harmonious sociable ordering. [ 200 ] [ 201 ] In 2019, the World Justice Project ‘s Rule of Law Index ranked Singapore as 13th overall among the earth ‘s 126 countries for attachment to the rule of jurisprudence. Singapore ranked high gear on the factors of order and security system ( # 1 ), absence of corruption ( # 3 ), regulative enforcement ( # 3 ), civil department of justice ( # 5 ), and criminal department of justice ( # 6 ), and ranked significantly lower on factors of open government ( # 25 ), constraints on government powers ( # 27 ), and fundamental rights ( # 30 ). [ 202 ] All public gatherings of five or more people require patrol permits, and protests may legally be held lone at the Speakers ‘ Corner. [ 203 ] lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender ( LGBT ) people in Singapore face a number of challenges. Same-sex marriage is not recognised and sexual relations between men are illegal, though the latter is rarely enforced. [ 204 ] Singaporean company is generally regarded as conservative. Despite this, LGBT acceptance is growing in the area. Pink Dot SG, an event held in support of the community, has drawn thousands of people per annum since 2009 with increasing attendance. [ 205 ] According to a view conducted by the Institute of Policy Studies in 2019, Singaporean society is quickly becoming more liberal on LGBT rights. The review more than 20 % of people said that intimate relations between adults of the same arouse were not improper at all or not incorrect most of the time, improving from 10 % in 2013. The survey found that 27 % felt the same way about same-sex marriage ( an increase from 15 % in 2013 ) and 30 % did so about same-sex couples adopting a child ( an increase from 24 % in 2013 ). [ 206 ] [ 207 ]
Speakers’ Corner in Chinatown provides a public demonstration and “free speech” area usually restricted in other parts of the island. In 2020, Singapore was ranked 158th out of 180 nations by Reporters Without Borders in the Worldwide Press Freedom Index. [ 186 ] Historically, the government has restricted freedom of speech and exemption of the wardrobe and has limited some civil and political rights. [ 187 ] The mighty to freedom of language and affiliation guaranteed by Article 14 ( 1 ) of the Constitution of Singapore is restricted by the subsequent subsection ( 2 ) of the same Article. [ 188 ] Freedom House ranks Singapore as “ partially detached ” in its Freedom in the World composition, [ 120 ] and The Economist Intelligence Unit ranks Singapore as a “ flaw majority rule ”, the second best rate of four, in its “ Democracy Index “. [ 189 ] [ 190 ] In the 2015 Singaporean general election, the People ‘s Action Party ( PAP ) won 83 of 89 seats contested with 70 % of the popular vote. [ 191 ] The latest elections were in July 2020, with the People ‘s Action Party ( PAP ) winning 83 of 93 seats contested with 61 % of the popular vote. Amnesty International has said that some legal provisions of the Singapore arrangement conflict with “ the correct to be presumed innocent until prove guilty ”. [ 192 ] The government has disputed Amnesty ‘s claims, stating that their “ military position on abolition of the death penalty is by no means uncontested internationally ” and that the Report contains “ sculpt errors of facts and misrepresentations ”. [ 193 ] Singapore ‘s judicial system is considered one of the most reliable in Asia. [ 194 ] Sex trafficking in Singapore is a significant trouble. Singaporean and extraneous women and girls have been forced into prostitution in brothels and been physically and psychologically abused. [ 195 ] [ 196 ] [ 197 ] A police dating from 1938 bans intimate relations between men, however the law is rarely enforced. intimate relations between women are legal. [ 198 ] In the Corruption Perceptions Index which ranks countries by “ sensed levels of public sector putrescence ”, Singapore has systematically ranked as one of the least corrupt. [ 199 ] Singapore ‘s singular combination of a potent about authoritarian politics with an vehemence on meritocracy and good government is known as the “ Singapore model “, and is regarded as a key factor behind Singapore ‘s political stability, economic growth, and harmonious sociable ordering. [ 200 ] [ 201 ] In 2019, the World Justice Project ‘s Rule of Law Index ranked Singapore as 13th overall among the earth ‘s 126 countries for attachment to the rule of jurisprudence. Singapore ranked high gear on the factors of order and security system ( # 1 ), absence of corruption ( # 3 ), regulative enforcement ( # 3 ), civil department of justice ( # 5 ), and criminal department of justice ( # 6 ), and ranked significantly lower on factors of open government ( # 25 ), constraints on government powers ( # 27 ), and fundamental rights ( # 30 ). [ 202 ] All public gatherings of five or more people require patrol permits, and protests may legally be held lone at the Speakers ‘ Corner. [ 203 ] lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender ( LGBT ) people in Singapore face a number of challenges. Same-sex marriage is not recognised and sexual relations between men are illegal, though the latter is rarely enforced. [ 204 ] Singaporean company is generally regarded as conservative. Despite this, LGBT acceptance is growing in the area. Pink Dot SG, an event held in support of the community, has drawn thousands of people per annum since 2009 with increasing attendance. [ 205 ] According to a view conducted by the Institute of Policy Studies in 2019, Singaporean society is quickly becoming more liberal on LGBT rights. The review more than 20 % of people said that intimate relations between adults of the same arouse were not improper at all or not incorrect most of the time, improving from 10 % in 2013. The survey found that 27 % felt the same way about same-sex marriage ( an increase from 15 % in 2013 ) and 30 % did so about same-sex couples adopting a child ( an increase from 24 % in 2013 ). [ 206 ] [ 207 ]
geography
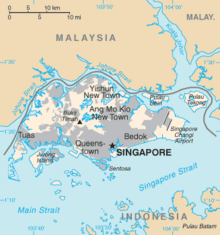 An draft of Singapore and the surrounding islands and waterways Singapore consists of 63 islands, including the main island, Pulau Ujong. [ 208 ] There are two-man-made connections to Johor, Malaysia : the Johor–Singapore Causeway in the north and the Tuas Second Link in the west. Jurong Island, Pulau Tekong, Pulau Ubin and Sentosa are the largest of Singapore ‘s smaller islands. The highest natural point is Bukit Timah Hill at 163.63 megabyte ( 537 foot ). [ 209 ] Under British rule, Christmas Island and the Cocos Islands were share of Singapore, and both were transferred to Australia in 1957. [ 210 ] [ 211 ] [ 212 ] Pedra Branca is the nation ‘s easternmost point. [ 213 ] Land reclamation projects have increased Singapore ‘s country area from 580 km2 ( 220 sq nautical mile ) in the 1960s to 710 km2 ( 270 sq nautical mile ) by 2015, an increase of some 22 % ( 130 km2 ). [ 214 ] The country is projected to reclaim another 56 km2 ( 20 sq mile ). [ 215 ] Some projects involve merging smaller islands through estate reclamation to form larger, more functional and habitable islands, as has been done with Jurong Island. [ 216 ] The type of sand used in reclamation is found in rivers and beaches, preferably than deserts, and is in capital demand global. In 2010 Singapore imported about 15 million tons of sand for its projects, the necessitate being such that Indonesia, Malaysia, and Vietnam have all restricted or barred the export of sand to Singapore in holocene years. As a result, in 2016 Singapore switched to using polders for reclamation, in which an area is enclosed and then pumped dry. [ 217 ]
An draft of Singapore and the surrounding islands and waterways Singapore consists of 63 islands, including the main island, Pulau Ujong. [ 208 ] There are two-man-made connections to Johor, Malaysia : the Johor–Singapore Causeway in the north and the Tuas Second Link in the west. Jurong Island, Pulau Tekong, Pulau Ubin and Sentosa are the largest of Singapore ‘s smaller islands. The highest natural point is Bukit Timah Hill at 163.63 megabyte ( 537 foot ). [ 209 ] Under British rule, Christmas Island and the Cocos Islands were share of Singapore, and both were transferred to Australia in 1957. [ 210 ] [ 211 ] [ 212 ] Pedra Branca is the nation ‘s easternmost point. [ 213 ] Land reclamation projects have increased Singapore ‘s country area from 580 km2 ( 220 sq nautical mile ) in the 1960s to 710 km2 ( 270 sq nautical mile ) by 2015, an increase of some 22 % ( 130 km2 ). [ 214 ] The country is projected to reclaim another 56 km2 ( 20 sq mile ). [ 215 ] Some projects involve merging smaller islands through estate reclamation to form larger, more functional and habitable islands, as has been done with Jurong Island. [ 216 ] The type of sand used in reclamation is found in rivers and beaches, preferably than deserts, and is in capital demand global. In 2010 Singapore imported about 15 million tons of sand for its projects, the necessitate being such that Indonesia, Malaysia, and Vietnam have all restricted or barred the export of sand to Singapore in holocene years. As a result, in 2016 Singapore switched to using polders for reclamation, in which an area is enclosed and then pumped dry. [ 217 ]
 Singapore Botanic Gardens is a UNESCO World Heritage Site – one of three gardens in the populace, and the only tropical garden, to be recognised as such .
Singapore Botanic Gardens is a UNESCO World Heritage Site – one of three gardens in the populace, and the only tropical garden, to be recognised as such .
nature
Singapore ‘s urbanization means that it has lost 95 % of its historic forests, [ 218 ] and now over half of the naturally occurring fauna and flora in Singapore is present in nature reserves, such as the Bukit Timah Nature Reserve and the Sungei Buloh Wetland Reserve, which comprise alone 0.25 % of Singapore ‘s land area. [ 218 ] In 1967, to combat this descent in natural space, the government introduced the imagination of making Singapore a “ garden city ”, [ 219 ] aiming to improve choice of life. [ 220 ] Since then, about 10 % of Singapore ‘s land has been set aside for parks and nature reserves. [ 221 ] The government has created plans to preserve the nation ‘s remaining wildlife. [ 222 ] Singapore ‘s well known gardens include the Singapore Botanic Gardens, a 161-year-old tropical garden and Singapore ‘s first gear UNESCO World Heritage Site. [ 223 ]
climate
Singapore has a tropical rain forest climate ( Köppen : Af ) with no distinctive seasons, uniform temperature and pressure, high humidity, and abundant rain. [ 224 ] [ 225 ] Temperatures normally range from 23 to 32 °C ( 73 to 90 °F ). While temperature does not vary greatly throughout the year, there is a bedwetter monsoon season from November to February. [ 226 ] From July to October, there is much haze caused by bush-league fires in neighbouring Indonesia, normally from the island of Sumatra. [ 227 ] Singapore follows the GMT+8 meter zone, one hour ahead of the typical partition for its geographic localization. [ 228 ] This causes the sun to rise and set particularly former during February, where the sunday rises at 7:15 am and sets around 7:20 phase modulation. During July, the sun sets at around 7:15 prime minister. The earliest the sunday rises and sets is in late October and early November when the sun rises at 6:46 am and sets at 6:50 prime minister. [ 229 ] Singapore recognises that climate change and rising sea levels in the decades ahead will have major implications for its low-lying coastline. It estimates that the nation will need to spend $ 100 billion over the course of the adjacent hundred to address the issue. In its 2020 budget, the government set aside an initial $ 5 billion towards a Coastline and Flood Protection Fund. [ 230 ] [ 231 ] Singapore is the first country in Southeast Asia to levy a carbon tax on its largest carbon-emitting corporations producing more than 25,000 tons of carbon dioxide per year, at $ 5 per short ton. [ 232 ] To reduce the nation ‘s dependence on dodo fuels, it has ramped up deployment of solar panels on rooftops and vertical surfaces of buildings, and early initiatives like building one of the populace ‘s largest floating solar farms at Tengeh Reservoir in Tuas. [ 233 ]
| Climate data for Singapore (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1929–1941 and 1948–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 35.2 (95.4) |
35.2 (95.4) |
36.0 (96.8) |
35.8 (96.4) |
35.4 (95.7) |
35.0 (95.0) |
34.0 (93.2) |
34.2 (93.6) |
34.4 (93.9) |
34.6 (94.3) |
34.4 (93.9) |
33.8 (92.8) |
36.0 (96.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 30.6 (87.1) |
31.5 (88.7) |
32.2 (90.0) |
32.4 (90.3) |
32.3 (90.1) |
31.9 (89.4) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.8 (89.2) |
31.2 (88.2) |
30.5 (86.9) |
31.6 (88.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.8 (80.2) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.8 (82.0) |
28.2 (82.8) |
28.6 (83.5) |
28.5 (83.3) |
28.2 (82.8) |
28.1 (82.6) |
28.0 (82.4) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.2 (81.0) |
26.8 (80.2) |
27.8 (82.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 24.3 (75.7) |
24.6 (76.3) |
24.9 (76.8) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.0 (77.0) |
24.6 (76.3) |
24.3 (75.7) |
25.0 (77.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 19.4 (66.9) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.2 (68.4) |
20.7 (69.3) |
21.2 (70.2) |
20.8 (69.4) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.2 (68.4) |
20.7 (69.3) |
20.6 (69.1) |
21.1 (70.0) |
20.6 (69.1) |
19.4 (66.9) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 221.6 (8.72) |
105.1 (4.14) |
151.7 (5.97) |
164.3 (6.47) |
164.3 (6.47) |
135.3 (5.33) |
146.6 (5.77) |
146.9 (5.78) |
124.9 (4.92) |
168.3 (6.63) |
252.3 (9.93) |
331.9 (13.07) |
2,113.2 (83.20) |
| Average rainy days ( ≥ 0.2 millimeter ) | 13 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 15 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 15 | 19 | 19 | 171 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 83.5 | 81.2 | 81.7 | 82.6 | 82.3 | 80.9 | 80.9 | 80.7 | 80.7 | 81.5 | 84.9 | 85.5 | 82.2 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 172.4 | 183.2 | 192.7 | 173.6 | 179.8 | 177.7 | 187.9 | 180.6 | 156.2 | 155.2 | 129.6 | 133.5 | 2,022.4 |
| Source 1: National Environment Agency[234][235] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (sun only, 1961–1990)[236] | |||||||||||||
economy
 A proportional representation of Singapore exports, 2019 Singapore has a highly explicate market economy, based historically on extended entrepôt trade. Along with Hong Kong, South Korea, and Taiwan, Singapore is one of the Four asian Tigers, and has surpassed its peers in terms of Gross Domestic Product ( GDP ) per caput. between 1965 and 1995, emergence rates averaged around 6 per cent per annum, transforming the exist standards of the population. [ 237 ] The Singaporean economy is regarded as exempt, [ 238 ] innovative, [ 239 ] dynamic [ 240 ] and business-friendly. [ 241 ] For respective years, Singapore has been one of the few [ 242 ] countries with an AAA credit rat from the big three, and the only asian nation to achieve this rate. [ 243 ] Singapore attracts a large come of foreign investing as a resultant role of its localization, skilled work force, low tax rates, advanced infrastructure and zero-tolerance against putrescence. [ 244 ] It is the populace ‘s most competitive economy, according to the World Economic Forum ‘s ranking of 141 countries, [ 245 ] with the 2nd highest GDP per head. [ 246 ] [ 247 ] There are more than 7,000 multinational corporations from the United States, Japan, and Europe in Singapore. [ citation needed ] [ 248 ] Roughly 44 percentage of the Singaporean work force is made up of non-Singaporeans. [ 249 ] Despite commercialize exemption, Singapore ‘s government operations have a significant stake in the economy, contributing 22 % of the GDP. [ 250 ] The city is a popular placement for conferences and events. [ 251 ] The currency of Singapore is the Singapore dollar ( SGD or S $ ), issued by the Monetary Authority of Singapore ( MAS ). [ 252 ] It is exchangeable with the Brunei dollar at par value since 1967. [ 253 ] MAS manages its monetary policy by allowing the Singapore dollar rally rate to rise or fall within an undisclosed deal band. This is different from most central banks, which use matter to rates to manage policy. [ 254 ] Singapore has the worldly concern ‘s eleventh largest foreign reserves, [ 255 ] and one of the highest net international investment position per caput. [ 256 ] [ 257 ] In late years, the country has been identified as an increasingly popular tax haven [ 258 ] for the affluent due to the low tax rate on personal income and tax exemptions on foreign-based income and das kapital gains. australian millionaire retailer Brett Blundy and multi-billionaire Facebook co-founder Eduardo Saverin are two examples of affluent individuals who have settled in Singapore ( Blundy in 2013 and Saverin in 2012 ). [ 259 ] In 2009, Singapore was removed from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development ( OECD ) “ liste grise ” of tax havens, [ 260 ] and ranked fourth on the Tax Justice Network ‘s 2015 Financial Secrecy Index of the world ‘s off-shore fiscal overhaul providers, banking one-eighth of the global ‘s offshore capital, while “ providing numerous tax avoidance and evasion opportunities ”. [ 261 ] In August 2016, The Straits Times reported that Indonesia had decided to create tax havens on two islands near Singapore to bring indonesian capital back into the tax base. [ 262 ] In October 2016, the Monetary Authority of Singapore admonished and fined UBS and DBS and withdrew Falcon Private Bank ‘s bank license for their alleged function in the malaysian Sovereign Fund scandal. [ 263 ] [ 264 ]
A proportional representation of Singapore exports, 2019 Singapore has a highly explicate market economy, based historically on extended entrepôt trade. Along with Hong Kong, South Korea, and Taiwan, Singapore is one of the Four asian Tigers, and has surpassed its peers in terms of Gross Domestic Product ( GDP ) per caput. between 1965 and 1995, emergence rates averaged around 6 per cent per annum, transforming the exist standards of the population. [ 237 ] The Singaporean economy is regarded as exempt, [ 238 ] innovative, [ 239 ] dynamic [ 240 ] and business-friendly. [ 241 ] For respective years, Singapore has been one of the few [ 242 ] countries with an AAA credit rat from the big three, and the only asian nation to achieve this rate. [ 243 ] Singapore attracts a large come of foreign investing as a resultant role of its localization, skilled work force, low tax rates, advanced infrastructure and zero-tolerance against putrescence. [ 244 ] It is the populace ‘s most competitive economy, according to the World Economic Forum ‘s ranking of 141 countries, [ 245 ] with the 2nd highest GDP per head. [ 246 ] [ 247 ] There are more than 7,000 multinational corporations from the United States, Japan, and Europe in Singapore. [ citation needed ] [ 248 ] Roughly 44 percentage of the Singaporean work force is made up of non-Singaporeans. [ 249 ] Despite commercialize exemption, Singapore ‘s government operations have a significant stake in the economy, contributing 22 % of the GDP. [ 250 ] The city is a popular placement for conferences and events. [ 251 ] The currency of Singapore is the Singapore dollar ( SGD or S $ ), issued by the Monetary Authority of Singapore ( MAS ). [ 252 ] It is exchangeable with the Brunei dollar at par value since 1967. [ 253 ] MAS manages its monetary policy by allowing the Singapore dollar rally rate to rise or fall within an undisclosed deal band. This is different from most central banks, which use matter to rates to manage policy. [ 254 ] Singapore has the worldly concern ‘s eleventh largest foreign reserves, [ 255 ] and one of the highest net international investment position per caput. [ 256 ] [ 257 ] In late years, the country has been identified as an increasingly popular tax haven [ 258 ] for the affluent due to the low tax rate on personal income and tax exemptions on foreign-based income and das kapital gains. australian millionaire retailer Brett Blundy and multi-billionaire Facebook co-founder Eduardo Saverin are two examples of affluent individuals who have settled in Singapore ( Blundy in 2013 and Saverin in 2012 ). [ 259 ] In 2009, Singapore was removed from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development ( OECD ) “ liste grise ” of tax havens, [ 260 ] and ranked fourth on the Tax Justice Network ‘s 2015 Financial Secrecy Index of the world ‘s off-shore fiscal overhaul providers, banking one-eighth of the global ‘s offshore capital, while “ providing numerous tax avoidance and evasion opportunities ”. [ 261 ] In August 2016, The Straits Times reported that Indonesia had decided to create tax havens on two islands near Singapore to bring indonesian capital back into the tax base. [ 262 ] In October 2016, the Monetary Authority of Singapore admonished and fined UBS and DBS and withdrew Falcon Private Bank ‘s bank license for their alleged function in the malaysian Sovereign Fund scandal. [ 263 ] [ 264 ]
Singapore has the worldly concern ‘s highest share of millionaires, with one out of every six households having at least one million US dollars in disposable wealth. This excludes property, businesses, and luxury goods, which if included would increase the count of millionaires, particularly as property in Singapore is among the worldly concern ‘s most expensive. [ 265 ] In 2016, Singapore was rated the universe ‘s most expensive city for the one-third consecutive year by the Economist Intelligence Unit, [ 266 ] [ 267 ] and this remained true in 2018. [ 268 ] The government provides numerous aid programmes to the homeless and needy through the Ministry of Social and Family Development, so acuate poverty is rare. Some of the programmes include providing between S $ 400 and S $ 1000 of fiscal aid per calendar month to needy households, providing spare medical manage at government hospitals, and paying for children ‘s tutelage. [ 269 ] [ 270 ] [ 271 ] other benefits include compensation for gymnasium fees to encourage citizens to exercise, [ 272 ] up to S $ 166,000 as a baby bonus for each citizen, [ 273 ] heavily subsidised healthcare, fiscal care for the disable, the provision of reduced-cost laptops for poor people students, [ 274 ] rebates for costs such as populace transmit [ 275 ] and utility bills, and more. [ 276 ] [ 277 ] As of 2018 Singapore ‘s rank in the Human Development Index is 9th in the populace, with an HDI value of 0.935. [ 278 ]
use
Singapore has a low unemployment rate for a develop country, with the rate not exceeding 4 % from 2005 to 2014, and reaching highs of 3.1 % in 2005 and 3 % during the 2009 global fiscal crisis ; it fell to 1.8 % in the first gear quarter of 2015. [ 288 ] Singapore does not have a minimum wage, believing that it would lower its competitiveness. It besides has one of the highest income inequalities among grow countries. [ 289 ] [ 290 ] Although recognising that foreign workers are all-important to the nation ‘s economy, the politics has considered placing limits on inflows of these workers, [ 291 ] as alien workers make up 80 % of the structure industry and up to 50 % of the overhaul diligence. [ 292 ] [ 293 ]
diligence sectors
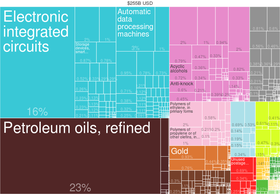 [294] singaporean exports by product ( 2014 ) Singapore is the worldly concern ‘s 3rd-largest foreign exchange concentrate, 6th-largest fiscal center, [ 295 ] 2nd-largest casino gambling market, [ 296 ] 3rd-largest oil-refining and trade center, largest oil-rig producer and hub for embark repair services, [ 297 ] [ 298 ] [ 299 ] and largest logistics hub. [ 300 ] The economy is diversify, with its top contributors being fiscal services, manufacture, and oil-refining. Its main exports are refined petroleum, integrated circuits, and computers, [ 301 ] which constituted 27 % of the nation ‘s GDP in 2010. other meaning sectors include electronics, chemicals, mechanical engineer, and biomedical sciences. Singapore was ranked 8th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, the lapp as 8th in 2019. [ 302 ] [ 303 ] [ 304 ] [ 305 ] In 2019, there were more than 60 semiconductor companies in Singapore, which together constituted 11 % of the global market partake. The semiconductor device industry entirely contributes around 7 % of Singapore ‘s GDP. [ 306 ] Singapore ‘s largest companies are in the telecommunications, bank, transportation, and manufacture sectors, many of which started as state-run statutory corporations and have since been publicly listed on the Singapore Exchange. such companies include Singapore Telecommunications ( Singtel ), Singapore Technologies Engineering, Keppel Corporation, Oversea-Chinese Banking Corporation ( OCBC ), Development Bank of Singapore ( DBS ), and United Overseas Bank ( UOB ). In 2011, amidst the global fiscal crisis, OCBC, DBS and UOB were ranked by Bloomberg Businessweek as the world ‘s 1st, 5th, and 6th strongest banks in the worldly concern, respectively. [ 307 ] It is home to the headquarters of 3 Fortune Global 500 companies, the highest in the region. [ 308 ] The nation ‘s best known ball-shaped companies include Singapore Airlines, Changi Airport, and the Port of Singapore, all of which are among the most-awarded in their respective fields. Singapore Airlines was ranked as Asia ‘s most-admired company, and the world ‘s 19th most-admired company in 2015 by Fortune ’ s annual “ 50 most admired companies in the global ” industry surveys. other awards it has received include the US-based Travel + Leisure ’ s Best International Airline prize, which it has won for 20 consecutive years. [ 309 ] [ 310 ] Changi Airport connects over 100 airlines to more than 300 cities. The strategic external air hub has more than 480 World ‘s Best airport awards as of 2015, and is known as the most-awarded airport in the world. [ 311 ] Over ten free-trade agreements have been signed with early countries and regions. [ 138 ] Singapore is the second-largest foreign investor in India. [ 312 ] It is the 14th largest exporter and the 15th largest importer in the world. [ 313 ] [ 314 ]
[294] singaporean exports by product ( 2014 ) Singapore is the worldly concern ‘s 3rd-largest foreign exchange concentrate, 6th-largest fiscal center, [ 295 ] 2nd-largest casino gambling market, [ 296 ] 3rd-largest oil-refining and trade center, largest oil-rig producer and hub for embark repair services, [ 297 ] [ 298 ] [ 299 ] and largest logistics hub. [ 300 ] The economy is diversify, with its top contributors being fiscal services, manufacture, and oil-refining. Its main exports are refined petroleum, integrated circuits, and computers, [ 301 ] which constituted 27 % of the nation ‘s GDP in 2010. other meaning sectors include electronics, chemicals, mechanical engineer, and biomedical sciences. Singapore was ranked 8th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, the lapp as 8th in 2019. [ 302 ] [ 303 ] [ 304 ] [ 305 ] In 2019, there were more than 60 semiconductor companies in Singapore, which together constituted 11 % of the global market partake. The semiconductor device industry entirely contributes around 7 % of Singapore ‘s GDP. [ 306 ] Singapore ‘s largest companies are in the telecommunications, bank, transportation, and manufacture sectors, many of which started as state-run statutory corporations and have since been publicly listed on the Singapore Exchange. such companies include Singapore Telecommunications ( Singtel ), Singapore Technologies Engineering, Keppel Corporation, Oversea-Chinese Banking Corporation ( OCBC ), Development Bank of Singapore ( DBS ), and United Overseas Bank ( UOB ). In 2011, amidst the global fiscal crisis, OCBC, DBS and UOB were ranked by Bloomberg Businessweek as the world ‘s 1st, 5th, and 6th strongest banks in the worldly concern, respectively. [ 307 ] It is home to the headquarters of 3 Fortune Global 500 companies, the highest in the region. [ 308 ] The nation ‘s best known ball-shaped companies include Singapore Airlines, Changi Airport, and the Port of Singapore, all of which are among the most-awarded in their respective fields. Singapore Airlines was ranked as Asia ‘s most-admired company, and the world ‘s 19th most-admired company in 2015 by Fortune ’ s annual “ 50 most admired companies in the global ” industry surveys. other awards it has received include the US-based Travel + Leisure ’ s Best International Airline prize, which it has won for 20 consecutive years. [ 309 ] [ 310 ] Changi Airport connects over 100 airlines to more than 300 cities. The strategic external air hub has more than 480 World ‘s Best airport awards as of 2015, and is known as the most-awarded airport in the world. [ 311 ] Over ten free-trade agreements have been signed with early countries and regions. [ 138 ] Singapore is the second-largest foreign investor in India. [ 312 ] It is the 14th largest exporter and the 15th largest importer in the world. [ 313 ] [ 314 ]
tourism
 The merlion, the official mascot of Singapore tourism is a major industry and contributor to the Singaporean economy, attracting 18.5 million external tourists in 2018, more than three times Singapore ‘s sum population. [ 315 ] Singapore is the fifth most inflict city in the universe, and 2nd in the Asia-Pacific. [ 316 ] In 2019 tourism contributed directly to about 4 % of Singapore ‘s GDP, [ 317 ] down from 2016, when tourism contributed, directly and indirectly, to around 9.9 % of Singapore ‘s GDP. [ 318 ] Altogether, the sector generated approximately 8.6 % of Singapore ‘s employment in 2016. [ 318 ]
The merlion, the official mascot of Singapore tourism is a major industry and contributor to the Singaporean economy, attracting 18.5 million external tourists in 2018, more than three times Singapore ‘s sum population. [ 315 ] Singapore is the fifth most inflict city in the universe, and 2nd in the Asia-Pacific. [ 316 ] In 2019 tourism contributed directly to about 4 % of Singapore ‘s GDP, [ 317 ] down from 2016, when tourism contributed, directly and indirectly, to around 9.9 % of Singapore ‘s GDP. [ 318 ] Altogether, the sector generated approximately 8.6 % of Singapore ‘s employment in 2016. [ 318 ]
Read more: Clint Barton (Marvel Cinematic Universe)
The Singapore Tourism Board ( STB ) is the statutory board under the Ministry of Trade and Industry which is tasked with the promotion of the area ‘s tourism industry. In August 2017 the STB and the Economic Development Board ( EDB ) unveiled a coordinated mark, Singapore – Passion Made Possible, to marketplace Singapore internationally for tourism and business purposes. [ 319 ] The Orchard Road district, which contains multi-storey denounce centres and hotels, can be considered the center of patronize and tourism in Singapore. [ 320 ] other popular tourist attractions include the Singapore Zoo, River Wonders and Night Safari. The Singapore Zoo has embraced the receptive menagerie concept whereby animals are kept in enclosures, separated from visitors by hide dry or wet moats, alternatively of caging the animals, and the river Wonders has 300 species of animals, including numerous endanger species. [ 321 ] Singapore promotes itself as a medical tourism hub, with about 200,000 foreigners seeking medical care there each year. Singapore medical services bearing to serve at least one million foreign patients annually and generate US $ 3 billion in tax income. [ 322 ] In 2015, Lonely Planet and The New York Times list Singapore as their top and 6th-best earth destinations to visit, respectively. [ 323 ] long-familiar landmarks include the Merlion, [ 324 ] Marina Bay Sands, [ 325 ] Gardens by the Bay, [ 326 ] the Jewel, [ 327 ] the Orchard Road denounce knock, [ 320 ] the recourse island of Sentosa, [ 328 ] and the Singapore Botanic Gardens, Singapore ‘s first UNESCO World Heritage Site. [ 329 ]
infrastructure
transportation
Singapore has a road system covering 3,356 kilometres ( 2,085 mi ), which includes 161 kilometres ( 100 secret intelligence service ) of expressways. [ 330 ] [ 331 ] The Singapore Area Licensing Scheme, implemented in 1975, became the universe ‘s first congestion price outline, and included other complementary measures such as rigorous car ownership quotas and improvements in aggregate transit. [ 332 ] [ 333 ] Upgraded in 1998 and renamed Electronic Road Pricing, the system introduced electronic bell collection, electronic detection, and video recording surveillance technology. [ 334 ] A Global Navigation Satellite System will replace the physical gantries by 2020. [ 335 ] As Singapore is a belittled island with a high population density, the number of private cars on the road is restricted to curb befoulment and congestion. car buyers must pay for duties one-and-a-half times the fomite ‘s grocery store respect, and bid for a singaporean Certificate of Entitlement ( COE ), which allows the cable car to run on the road for a ten. cable car prices are by and large significantly higher in Singapore than in other english-speaking countries. [ 336 ] As with most Commonwealth countries, vehicles on the road and people walking on the streets keep to the entrust. [ 337 ] common alternatives to secret vehicles include bicycles, bus topology, taxis and aim ( MRT or LRT ). Two companies run the educate ecstasy system— SBS Transit and SMRT Corporation. Four companies, green light, Tower-Transit, SBS Transit and SMRT Corporation run the public buses under a ‘Bus Contracting Model ‘ where operators bid for routes. There are six cab companies, who together put out over 28,000 taxis on the road. [ 338 ] Taxis are a popular shape of conveyance as the fares are relatively cheap compared to many early evolve countries. [ 339 ] Singapore is a major external transportation hub in Asia, serving some of the busiest ocean and atmosphere deal routes. Changi Airport is an aviation center for Southeast Asia and a stopover on the Kangaroo Route between Sydney and London. [ 340 ] There are three civilian airports in Singapore, Singapore Changi Airport, Seletar Airport [ 341 ] [ 342 ] and Kallang Airport ( which is not open to public ). Singapore Changi Airport hosts a network of over 100 airlines connecting Singapore to some 300 cities in about 70 countries and territories worldwide. [ 343 ] It has been rated one of the best international airports by international travel magazines, including being rated as the universe ‘s best airport for the first clock time in 2006 by Skytrax. [ 344 ] The national airline is Singapore Airlines. [ 345 ] The Port of Singapore, managed by interface operators PSA International and Jurong Port, was the world ‘s second-busiest port in 2019 in terms of shipping tonnage handled, at 2.85 billion gross tons ( GT ), and in terms of containerize traffic, at 37.2 million twenty-foot equivalent units ( TEUs ). [ 346 ] It is besides the world ‘s second-busiest, behind Shanghai, in terms of cargo tonnage with 626 million tons handled. In addition, the port is the world ‘s interfering for transshipment traffic and the world ‘s biggest transport refuelling center. [ 347 ]
fresh water
Singapore considers water a national security issue and the government has sought to emphasise conservation. [ 348 ] Water access is universal and of high quality, though the nation is projected to face meaning water-stress by 2040. [ 349 ] [ 350 ] To circumvent this, the Public Utilities Board has implemented the “ four national taps ” scheme – water imported from neighbouring Malaysia, urban rain catchments, reclaimed water ( NEWater ) and seawater desalination. [ 351 ] Singapore ‘s approach does not rely only on physical infrastructure ; it besides emphasises proper legislation and enforcement, water pricing, public education deoxyadenosine monophosphate well as inquiry and exploitation. [ 352 ] Singapore has declared that it will be water self-sufficient by the clock time its 1961 long-run body of water supply agreement with Malaysia expires in 2061. however, according to official forecasts, water necessitate in Singapore is expected to double from 380 to 760 million US gallons ( 1.4 to 2.8 billion litres ; 1.4 to 2.8 million cubic meters ) per day between 2010 and 2060. The increase is expected to come primarily from non-domestic water consumption, which accounted for 55 % of water demand in 2010 and is expected to account for 70 % of necessitate in 2060. By that clock time, water requirement is expected to be met by domesticate body of water at the tune of 50 % and by desalination accounting for 30 %, compared to merely 20 % supplied by inner catchments. [ 353 ] [ 354 ] Singapore is expanding its recycle system and intends to spend $ 7.4 billion ( Sg $ 10 billion ) in water discussion infrastructure upgrades. [ 355 ] The Ula Pandan effluent treatment was particularly built to test advanced practice water system treatment processes before full deployment and won the Water/Wastewater Project of the Year Award at the 2018 Global Water Awards in Paris, France. [ 356 ] Operation started in 2017 and was jointly developed by PUB and the Black & Veatch + AECOM Joint Venture. [ 357 ]
Demographics
As of mid-2018, the calculate population of Singapore was 5,638,700 people, 3,471,900 ( 61.6 % ) of whom were citizens, while the remaining 2,166,800 ( 38.4 % ) were permanent residents ( 522,300 ) or external students, extraneous workers, or dependants ( 1,644,500 ). [ 3 ] According to the state ‘s most late census in 2010, closely 23 % of singaporean residents ( i.e. citizens and permanent residents ) were foreign born ; if non-residents were counted, closely 43 % of the sum population were foreign born. [ 358 ] [ 359 ] The like census besides reports that about 74.1 % of residents were of taiwanese lineage, 13.4 % of Malay origin, 9.2 % of indian descent, and 3.3 % of early ( including Eurasian ) descent. [ 358 ] Prior to 2010, each person could register as a penis of entirely one subspecies, by default that of his or her church father, therefore mixed-race persons were entirely grouped under their father ‘s race in politics censuses. From 2010 ahead, people may register using a multi-racial classification, in which they may choose one elementary raceway and one secondary subspecies, but no more than two. [ 360 ] The median age of singaporean residents was 40.5 in 2017, [ 361 ] and the total richness rate is estimated to be 0.80 children per woman in 2014, the lowest in the world and well below the 2.1 needed to replace the population. [ 362 ] The politics has attempted to increase richness with limited success, arsenic well as adjusting immigration policy to maintain its working-age population. [ 363 ] [ 364 ] 91 % of house physician households ( i.e. households headed by a Singapore citizen or permanent nonmigratory ) own the homes they live in, and the average family size is 3.43 persons ( which include dependants who are neither citizens nor permanent residents ). [ 365 ] [ 366 ] however, due to scarcity of bring, 78.7 % of resident households live in subsidize, high-rise, public housing apartments developed by the Housing and Development Board ( HDB ). besides, 75.9 % of resident households live in properties that are equal to, or larger than, a four-room ( i.e. three bedrooms plus one living room ) HDB flat or in private housing. [ 367 ] [ 368 ] Live-in alien domestic workers are quite common in Singapore, with about 224,500 foreign domestic workers there, as of December 2013. [ 369 ]
religion
buddhism is the most widely practised religion in Singapore : 31 % of the resident population declared themselves adherents at the most recent census. The next-most practiced religion is Christianity, followed by Islam, Taoism, and Hinduism. 20 % of the population did not have a religious affiliation. The proportion of Christians, Taoists, and non-religious people increased between 2000 and 2010 by about 3 percentage points each, while the proportion of Buddhists decreased. other faiths remained largely stable in their share of the population. [ 370 ] There are monasteries and Dharma centres from all three major traditions of Buddhism in Singapore : Theravada, Mahayana, and Vajrayana. Most Buddhists in Singapore are taiwanese and are of the Mahayana custom, [ 371 ] missionaries having come into the country from China for several decades. however, Thailand ‘s Theravada Buddhism has seen growing popularity among the populace ( not only the Chinese ) during the past decade. The religion of Soka Gakkai International, a japanese Buddhist constitution, is practised by many people in Singapore, and largely by those of chinese descent. Tibetan Buddhism has besides made dense inroads into the nation in recent years. [ 372 ]
Languages
Singapore has four official languages : English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil. [ 373 ]
| Language used most frequently at home[1] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Percent | |||
| English | 48.3% | |||
| Mandarin | 29.9% | |||
| Malay | 9.2% | |||
| Chinese dialects | 8.7% | |||
| Tamil | 2.5% | |||
| Others | 1.4% | |||
English is the tongue franca [ 374 ] [ 375 ] [ 376 ] [ 377 ] and the main language used in business, government, law and department of education. [ 378 ] [ 379 ] The Constitution of Singapore and all government legislations are written in English, and interpreters are required if a speech early than English is used in the singaporean courts. [ 380 ] [ 381 ] Statutory corporations conduct their businesses in English, while any official documents written in a non-English official speech such as Malay, Mandarin, or Tamil are typically translated into English to be accepted for manipulation. [ 382 ] [ 375 ] [ 383 ] Malay was designated as a national speech by the singaporean politics after independence from Britain in the 1960s to avoid clash with Singapore ‘s Malay-speaking neighbours of Malaysia and Indonesia. [ 7 ] It has a symbolic, rather than running purpose. [ 373 ] [ 384 ] [ 385 ] It is used in the national hymn Majulah Singapura, [ 386 ] in citations of singaporean orders and decorations and in military commands. [ 387 ] [ 388 ] Singaporean Malay is officially written in the Latin-based Rumi handwriting, though some Singaporean Malays besides learn the Arabic-based Jawi script. [ 389 ] Jawi is considered an ethnic handwriting for use on Singaporean identity cards. [ 390 ] Singaporeans are by and large bilingual, typically with English as their common lyric and their mother-tongue as a second gear terminology teach in schools, in order to preserve each person ‘s cultural identity and values. English is the most speak terminology at dwelling at 48.3 % of the population ; Mandarin is following, at 29.9 % according to the 2020 census. [ 388 ] [ 391 ] Nearly half a million talk other varieties of Chinese, chiefly Hokkien, Teochew, and Cantonese, as their home speech, although the consumption of these is declining in privilege of Mandarin or equitable english. [ 392 ] Singapore chinese characters are written using simplified chinese characters. [ 393 ] Singaporean English is largely based on british English, owing to the country ‘s status as a early crown colony. [ 394 ] [ 395 ] however, forms of English speak in Singapore crop from Standard Singapore English to a colloquial imprint known as Singlish, which is discouraged by the politics as it claims it to be a deficient English creole that handicaps Singaporeans, presenting an obstacle to learning standard English and rendering the speaker inexplicable to everyone except to another Singlish speaker. [ 396 ]
education
education for primary, secondary, and third levels is largely supported by the state. All institutions, private and public, must be registered with the Ministry of Education. [ 397 ] English is the terminology of instruction in all public schools, [ 398 ] and all subjects are teach and examined in English except for the “ mother tongue “ terminology paper. [ 399 ] While the term “ mother tongue ” in general refers to the beginning language internationally, in Singapore ‘s department of education system, it is used to refer to the second language, as English is the first terminology. [ 400 ] [ 401 ] Students who have been abroad for a while, or who struggle with their “ Mother Tongue ” language, are allowed to take a elementary course of study or drop the subject. [ 402 ] [ 403 ] department of education takes invest in three stages : basal, secondary, and pre-university education. merely the primary level is compulsory. Students begin with six years of primary school, which is made up of a four-year basis course and a biennial orientation stage. The course of study is focused on the development of English, the mother tongue, mathematics, and skill. [ 404 ] [ 405 ] Secondary school lasts from four to five years, and is divided between Special, Express, Normal ( Academic ), and Normal ( Technical ) streams in each school, depending on a scholar ‘s ability grade. [ 406 ] The basic coursework breakdown is the same as in the primary level, although classes are much more specialized. [ 407 ] Pre-university education takes rate over two to three years at elder schools, largely called Junior Colleges. [ 408 ] As alternatives to Pre-U education, however, courses are offered in other post-secondary education institutions, including 5 polytechnics and the Institutes of Technical Education ( ITEs ). Singapore has six public universities [ 409 ] of which the National University of Singapore and Nanyang Technological University are among the top 20 universities in the world. [ 410 ] National examinations are standardised across all schools, with a test taken after each stage. After the foremost six years of education, students take the Primary School Leaving Examination ( PSLE ), [ 404 ] which determines their placement at secondary school. At the end of the secondary stage, GCE O-Level or N-level exams are taken ; [ 411 ] at the end of the following pre-university stage, the GCE A-Level exams are taken. [ 412 ] Some schools have a degree of freedom in their course of study and are known as autonomous schools, for secondary education level and above. [ 406 ] Singapore is besides an education hub, with more than 80,000 international students in 2006. [ 413 ] 5,000 malaysian students cross the Johor–Singapore Causeway casual to attend schools in Singapore. [ 414 ] In 2009, 20 % of all students in singaporean universities were international students—the utmost cap allowed, a majority from ASEAN, China and India. [ 415 ] Singapore students have excelled in many of the world education benchmarks in maths, skill and take. In 2015, both its primary coil and secondary students rank beginning in OECD ‘s global school performance rankings across 76 countries—described as the most comprehensive map of education standards. [ 416 ] [ 417 ] In 2016, Singapore students topped both the Program International Student Assessment ( PISA ) [ 418 ] [ 419 ] [ 420 ] [ 421 ] and the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study ( TIMSS ). [ 422 ] [ 423 ] [ 424 ] In the 2016 EF English Proficiency Index taken in 72 countries, Singapore position 6th and has been the merely asian nation in the top ten-spot. [ 425 ] [ 426 ] [ 427 ] [ 428 ]
healthcare
Singapore has a generally efficient healthcare organization, even though health expenditures are relatively low for develop countries. [ 429 ] The World Health Organisation ranks Singapore ‘s healthcare system as 6th overall in the world in its World Health Report. [ 430 ] In general, Singapore has had the lowest baby mortality rates in the universe for the past two decades. [ 431 ] In 2019, Singaporeans have the longest life anticipation of any state at 84.8 years. Women can expect to live an average of 87.6 years with 75.8 years in good health. The averages are lower for men. [ 432 ] Singapore is ranked 1st on the Global Food Security Index. [ 433 ] As of December 2011 and January 2013, 8,800 foreigners and 5,400 Singaporeans were respectively diagnosed with HIV, [ 434 ] but there are fewer than 10 annual deaths from HIV per 100,000 people. There is a high level of immunization. [ 435 ] Adult fleshiness is below 10 %. [ 436 ] The Economist Intelligence Unit, in its 2013 Where-to-be-born Index, ranked Singapore as having the best quality of biography in Asia and sixth overall in the world. [ 437 ] The government ‘s healthcare arrangement is based upon the “ 3M ” framework. This has three components : Medifund, which provides a guard net income for those not able to otherwise yield healthcare, Medisave, a compulsory national medical savings explanation system covering about 85 % of the population, and Medishield, a government-funded health insurance broadcast. public hospitals in Singapore have a considerable autonomy in their management decisions, and notionally compete for patients, however they remain in politics ownership ; the politics appoints their boards, and Chief Executive Officers and management reports are responsible to these boards. [ 438 ] A subsidy scheme exists for those on low income. [ 439 ] In 2008, 32 % of healthcare was funded by the politics. It accounts for approximately 3.5 % of Singapore ‘s GDP. [ 440 ]
culture
 Ornate details on crown of Sri Mariamman Temple in Chinatown district, Singapore ‘s oldest Hindu temple since 1827 Despite its belittled size, Singapore has a diversity of languages, religions, and cultures. [ 441 ] Former prime ministers of Singapore, Lee Kuan Yew and Goh Chok Tong, have stated that Singapore does not fit the traditional description of a nation, calling it a society-in-transition, pointing out the fact that Singaporeans do not all speak the lapp terminology, share the same religion, or have the like customs. [ 441 ] [ 442 ] Each Singaporean ‘s demeanor and attitudes are influenced by, among other things, his or her home speech and his religion. Singaporeans who speak English as their native linguistic process tend to lean toward western culture and christian culture, [ 443 ] while those who speak chinese as their native linguistic process tend to lean toward chinese culture and Confucianism. Malay-speaking Singaporeans tend to lean toward Malay culture, which itself is close linked to Islamic acculturation. [ 444 ] [ 445 ] Racial and religious harmony is regarded by Singaporeans as a crucial part of Singapore ‘s success, and played a part in building a singaporean identity. [ 446 ] [ 447 ] When Singapore became mugwump from the United Kingdom in 1963, most singaporean citizens were ephemeral labourers who had no purpose of staying permanently. [ 448 ] There was besides a ample minority of middle-class, locally born people—known as Peranakans or Baba-Nyonya—descendants of 15th- and 16th-century chinese immigrants. With the exception of the Peranakans who pledged their loyalties to Singapore, most of the labourers ‘ loyalties lay with their respective homelands of Malaysia, China and India. After independence, the politics began a careful process of crafting a singaporean identity and culture. [ 448 ] Singapore has a reputation as a nanny express. [ 449 ] [ 450 ] The government besides places heavy emphasis on meritocracy, where one is judged based on one ‘s ability. [ 451 ] The national flower of Singapore is the hybrid orchid, Vanda ‘Miss Joaquim ‘, named in memory of a Singapore-born armenian woman, who crossbred the bloom in her garden at Tanjong Pagar in 1893. [ 452 ] Many national symbols such as the Coat of arms of Singapore and the Lion head symbol of Singapore make use of the lion, as Singapore is known as the Lion City. Major religious festivals are public holidays. [ 453 ]
Ornate details on crown of Sri Mariamman Temple in Chinatown district, Singapore ‘s oldest Hindu temple since 1827 Despite its belittled size, Singapore has a diversity of languages, religions, and cultures. [ 441 ] Former prime ministers of Singapore, Lee Kuan Yew and Goh Chok Tong, have stated that Singapore does not fit the traditional description of a nation, calling it a society-in-transition, pointing out the fact that Singaporeans do not all speak the lapp terminology, share the same religion, or have the like customs. [ 441 ] [ 442 ] Each Singaporean ‘s demeanor and attitudes are influenced by, among other things, his or her home speech and his religion. Singaporeans who speak English as their native linguistic process tend to lean toward western culture and christian culture, [ 443 ] while those who speak chinese as their native linguistic process tend to lean toward chinese culture and Confucianism. Malay-speaking Singaporeans tend to lean toward Malay culture, which itself is close linked to Islamic acculturation. [ 444 ] [ 445 ] Racial and religious harmony is regarded by Singaporeans as a crucial part of Singapore ‘s success, and played a part in building a singaporean identity. [ 446 ] [ 447 ] When Singapore became mugwump from the United Kingdom in 1963, most singaporean citizens were ephemeral labourers who had no purpose of staying permanently. [ 448 ] There was besides a ample minority of middle-class, locally born people—known as Peranakans or Baba-Nyonya—descendants of 15th- and 16th-century chinese immigrants. With the exception of the Peranakans who pledged their loyalties to Singapore, most of the labourers ‘ loyalties lay with their respective homelands of Malaysia, China and India. After independence, the politics began a careful process of crafting a singaporean identity and culture. [ 448 ] Singapore has a reputation as a nanny express. [ 449 ] [ 450 ] The government besides places heavy emphasis on meritocracy, where one is judged based on one ‘s ability. [ 451 ] The national flower of Singapore is the hybrid orchid, Vanda ‘Miss Joaquim ‘, named in memory of a Singapore-born armenian woman, who crossbred the bloom in her garden at Tanjong Pagar in 1893. [ 452 ] Many national symbols such as the Coat of arms of Singapore and the Lion head symbol of Singapore make use of the lion, as Singapore is known as the Lion City. Major religious festivals are public holidays. [ 453 ]
Arts
 The National Gallery Singapore oversees the populace ‘s largest public solicitation of Singapore and Southeast Asian art During the 1990s when the National Arts Council was created to spearhead the development of performing arts, along with ocular and literary art forms. [ 454 ] The National Gallery Singapore is the state ‘s flagship museum with some 8,000 works from Singaporean and other Southeast asian artists. The Singapore Art Museum focuses on contemporary art. The Red Dot Design Museum celebrates especial art and design of objects for casual life, hosting more than 1,000 items from 50 countries. The lotus-shaped ArtScience Museum hosts touring exhibitions that combine art with the sciences. other major museums include the asian Civilisations Museum, the Peranakan Museum, and The Arts House. [ 455 ] The Esplanade is Singapore ‘s largest do arts kernel. In 2016 alone, it was the web site of 5,900 barren art and polish events. [ 456 ] [ 457 ] literature of Singapore, or “ SingLit ”, comprises a collection of literary works by Singaporeans written chiefly in the nation ‘s four official languages : English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil. Singapore is increasingly regarded as having four sub-literatures alternatively of one. many significant works have been translated and showcased in publications such as the literary diary Singa, published in the 1980s and 1990s with editors including Edwin Thumboo and Koh Buck Song, american samoa well as in multilingual anthologies such as Rhythms: A Singaporean Millennial Anthology Of Poetry ( 2000 ), in which the poems were all translated three times each. A count of singaporean writers such as Tan Swie Hian and Kuo Pao Kun have contributed make in more than one terminology. [ 458 ] [ 459 ] Singapore has a diverse music culture that ranges from pop music and rock, to folk and classical. western classical music plays a significant function in the cultural life in Singapore, with the Singapore Symphony Orchestra ( SSO ) instituted in 1979. other celebrated westerly orchestras in Singapore include Singapore National Youth Orchestra which is funded by the Ministry of Education [ 460 ] and the community-based Braddell Heights Symphony Orchestra. [ 461 ] many orchestras and ensembles are besides found in secondary schools and junior colleges. assorted communities have their own discrete heathen musical traditions : chinese, Malays, Indians, and Eurasians. With their traditional forms of music and respective modern melodious styles, the fusion of different forms account for the musical diverseness in the area. [ 462 ] The state ‘s lively urban musical scene has made it a centre for international performances and festivals in the area. Some of Singapore ‘s best known pop singers includes Stefanie Sun, JJ Lin, Liang Wern Fook, Taufik Batisah and Dick Lee, who is celebrated for composing National Day theme songs, including Home. [ 463 ] [ 464 ]
The National Gallery Singapore oversees the populace ‘s largest public solicitation of Singapore and Southeast Asian art During the 1990s when the National Arts Council was created to spearhead the development of performing arts, along with ocular and literary art forms. [ 454 ] The National Gallery Singapore is the state ‘s flagship museum with some 8,000 works from Singaporean and other Southeast asian artists. The Singapore Art Museum focuses on contemporary art. The Red Dot Design Museum celebrates especial art and design of objects for casual life, hosting more than 1,000 items from 50 countries. The lotus-shaped ArtScience Museum hosts touring exhibitions that combine art with the sciences. other major museums include the asian Civilisations Museum, the Peranakan Museum, and The Arts House. [ 455 ] The Esplanade is Singapore ‘s largest do arts kernel. In 2016 alone, it was the web site of 5,900 barren art and polish events. [ 456 ] [ 457 ] literature of Singapore, or “ SingLit ”, comprises a collection of literary works by Singaporeans written chiefly in the nation ‘s four official languages : English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil. Singapore is increasingly regarded as having four sub-literatures alternatively of one. many significant works have been translated and showcased in publications such as the literary diary Singa, published in the 1980s and 1990s with editors including Edwin Thumboo and Koh Buck Song, american samoa well as in multilingual anthologies such as Rhythms: A Singaporean Millennial Anthology Of Poetry ( 2000 ), in which the poems were all translated three times each. A count of singaporean writers such as Tan Swie Hian and Kuo Pao Kun have contributed make in more than one terminology. [ 458 ] [ 459 ] Singapore has a diverse music culture that ranges from pop music and rock, to folk and classical. western classical music plays a significant function in the cultural life in Singapore, with the Singapore Symphony Orchestra ( SSO ) instituted in 1979. other celebrated westerly orchestras in Singapore include Singapore National Youth Orchestra which is funded by the Ministry of Education [ 460 ] and the community-based Braddell Heights Symphony Orchestra. [ 461 ] many orchestras and ensembles are besides found in secondary schools and junior colleges. assorted communities have their own discrete heathen musical traditions : chinese, Malays, Indians, and Eurasians. With their traditional forms of music and respective modern melodious styles, the fusion of different forms account for the musical diverseness in the area. [ 462 ] The state ‘s lively urban musical scene has made it a centre for international performances and festivals in the area. Some of Singapore ‘s best known pop singers includes Stefanie Sun, JJ Lin, Liang Wern Fook, Taufik Batisah and Dick Lee, who is celebrated for composing National Day theme songs, including Home. [ 463 ] [ 464 ]
cuisine
Singapore ‘s diverseness of cuisine is touted as a reason to visit the country, due to its combination of convenience, variety show, choice, and price. [ 465 ] Local food items by and large relate to a particular ethnicity – Chinese, Malay and Indian ; but the diversity of cuisine has increased far by the hybridization of unlike styles ( for example, the Peranakan cuisine, a mix of Chinese and Malay cuisine ). In peddler centres, cultural diffusion is exemplified by traditionally Malay peddler stalls besides selling Tamil food. taiwanese stalls may introduce Malay ingredients, cooking techniques, or integral dishes into their range of cater. [ 465 ] Hainanese chicken rice, based on the Hainanese cup of tea Wenchang chicken, is considered Singapore ‘s national dish. [ 466 ] [ 467 ] The city state has a burgeoning food scene ranging from falconer centres ( alfresco ), food courts ( air-condition ), chocolate shops ( alfresco with up to a twelve falconer stalls ), cafes, fast food, elementary kitchens, free-and-easy, fame and high-end restaurants. [ 468 ] Cloud kitchens and food delivery are besides on the upgrade, with 70 % of residents ordering from delivery apps at least once a month. [ 469 ] [ 470 ] Many international fame chef restaurants are located within the integrate resorts. [ 471 ] Religious dietary strictures exist ( Muslims do not eat pork and Hindus do not eat gripe ), and there is besides a significant group of vegetarians. The Singapore Food Festival which celebrates Singapore ‘s cuisine is held annually in July. [ 472 ] anterior to the 1980s, street food was sold chiefly by immigrants from China, India, and Malaysia to other immigrants seeking a familiar taste. In Singapore, street food has long been associated with falconer centres with communal seating areas. typically, these centres have a few twelve to hundreds of food stalls, with each specialising in one or more related dishes. [ 473 ] [ 468 ] While street food can be found in many countries, the variety and range of centralize peddler centres that serve inheritance street food in Singapore is alone. [ 474 ] In 2018, there were 114 falconer centres spread across the city center and heartland house estates. They are maintained by the National Environment Agency, which besides grade each food stall for hygiene. The largest peddler center is located on the second gear floor of Chinatown Complex, and contains over 200 stalls. [ 474 ] The building complex is besides home to the cheapest Michelin-starred meal in the global – a home plate of soya-sauce wimp rice or noodles for S $ 2 ( US $ 1.50 ). Two street food stalls in the city are the first in the earth to be awarded a Michelin star, obtaining a single leading each. [ 475 ]
fun and refreshment
The development of secret sports and refreshment clubs began in the nineteenth century colonial Singapore, with clubs founded during this clock including the Cricket Club, the Singapore Recreation Club, the Singapore Swimming Club, and the Hollandse Club. [ 477 ] Water sports are some of the most popular in Singapore. At the 2016 Rio Olympics, Joseph Schooling won Singapore ‘s first Olympic gold decoration, claiming the 100-metre butterfly in a new Olympic record time of 50.39 seconds. [ 476 ] Singapore sailors have had success on the international stage, with their optimist team being considered among the best in the world. [ 478 ] [ 479 ] Despite its size, the state has dominated swim meets in the Southeast Asia Games. Its men ‘s urine polo team won the SEA Games amber decoration for the twenty-seventh time in 2017, continuing Singapore frolic ‘s longest gain mottle. [ 480 ] Singapore hosted the inaugural 2010 Summer Youth Olympics, in which 3,600 athletes from 204 nations competed in 26 sports. [ 481 ] The island is home to ONE Championship, the biggest interracial Martial Arts forwarding in Asia. [ 482 ] Singapore ‘s women ‘s mesa tennis team were silver medalists at the 2008 Beijing Olympics. [ 483 ] [ 484 ] They became world champions in 2010 when they beat China at the World Team Table Tennis Championships in Russia, breaking China ‘s 19-year victorious streak. [ 485 ] Weightlifter Tan Howe Liang was Singapore ‘s first Olympic medalist, winning a silver at the 1960 Rome Games. [ 486 ] Singapore ‘s football league, the Singapore Premier League, was launched in 1996 as the S.League and comprises nine clubs, including two extraneous teams. [ 487 ] [ 488 ] The Singapore Slingers, once the Hunter Pirates in the australian National Basketball League, is one of the inaugural teams in the ASEAN Basketball League, which was founded in October 2009. [ 489 ] Kranji Racecourse is run by the Singapore Turf Club and hosts respective meetings per week, including external races—notably the Singapore Airlines International Cup. [ 490 ] Singapore began hosting a rung of the Formula One World Championship, the Singapore Grand Prix at the Marina Bay Street Circuit in 2008. It was the inauguration F1 night rush, [ 491 ] and the first F1 street race in Asia. [ 492 ] It is considered a touch event on the F1 calendar. [ 493 ]
Media
Companies linked to the politics control much of the domestic media in Singapore. [ 494 ] MediaCorp operates most free-to-air television receiver channels and free-to-air radio stations in Singapore. There are a total of seven free-to-air television channels offered by Mediacorp. [ 495 ] [ 496 ] Starhub Cable Vision ( SCV ) besides offers cable television with channels from all around the populace, [ 497 ] and Singtel ‘s Mio TV provides an IPTV overhaul. [ 498 ] Singapore Press Holdings, a soundbox with conclusion links to the government, controls most of the newspaper diligence in Singapore. [ 499 ] Singapore ‘s media industry has sometimes been criticised for being excessively regulated and lacking in exemption by human rights groups such as Freedom House. [ 494 ] Self-censorship among journalists is said to be coarse. [ 499 ] In 2014, Singapore dipped to its lowest ranking ever ( 153rd of 180 nations ) on the Press Freedom Index published by Reporters Without Borders. [ 500 ] In 2020, Singapore was ranked 160 on the Press Freedom Index. [ 501 ] The Media Development Authority regulates singaporean media, claiming to balance the demand for choice and protective covering against offensive and harmful material. [ 502 ] Private possession of television satellite dishes is banned. [ 499 ] Internet in Singapore is provided by country owned Singtel, partially express owned Starhub and M1 Limited ampere well as some other business internet service providers ( ISPs ) that offer residential military service plans of speeds up to 2 Gbit/s as of spring 2015. [ 503 ] Equinix ( 332 participants ) and besides its smaller brother Singapore Internet Exchange ( 70 participants ) are Internet exchange points where Internet service providers and Content pitch networks exchange Internet traffic between their networks ( autonomous systems ) in versatile locations in Singapore. [ 504 ] [ 505 ] In the mid-1980s to 1990s, Singaporeans could besides use the locally based videotext military service Singapore Teleview to communicate with one another. [ 506 ] The idiom Intelligent Island rebel in the 1990s in reference book to the island state ‘s early adaptive relationship with the internet. [ 506 ] [ 507 ] In 2016, there were an estimated 4.7 million internet users in Singapore, representing 82.5 % of the population. [ 508 ] The Singapore government does not engage in far-flung censor of the internet, [ 509 ] but it maintains a list of one hundred websites—mostly pornographic—that it blocks as a “ emblematic instruction of the Singaporean community ‘s stand on harmful and undesirable content on the Internet ”. [ 510 ] As the block covers alone base internet access, users may calm visit the obstruct websites from their office computers. [ 511 ] Singapore has the world ‘s highest smartphone penetration rates, in surveys by Deloitte [ 512 ] [ 513 ] and Google Consumer Barometer – at 89 % and 85 % of the population respectively in 2014. [ 514 ] Overall mobile phone penetration pace is at 148 mobile earphone subscribers per 100 people. [ 515 ]
See besides
Notes
- ^[3] Of which 3,498,200 are citizens .
- ^ The unwrap down of british Empire losses included 38,496 United Kingdom, 18,490 australian, 67,340 indian and 14,382 local volunteer troops. total australian casualties included 1,789 killed and 1,306 wounded .
References
Citations
- Attribution
Works cited
promote reading
- Abshire, Jean. The History of Singapore (ABC-CLIO, 2011).
- Barr, Michael D. Singapore: A Modern History (2019)
- Corfield, Justin J. Historical dictionary of Singapore (2011) online
- Ghesquière, Henri C. Singapore’s success: engineering economic growth (2007)
- Heng, Chye Kiang. 50 Years of Urban Planning in Singapore (2016)
- Hill, Michael (1995). Kwen Fee Lian (ed.). The Politics of Nation Building and Citizenship in Singapore. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-12025-8.
- Huff, W. G. The Economic Growth of Singapore: Trade and Development in the Twentieth Century (1995)
- King, Rodney (2008). The Singapore Miracle, Myth and Reality. Insight Press. ISBN 978-0-9775567-0-0.
- Mauzy, Diane K.; Milne, R.S. (2002). Singapore Politics: Under the People’s Action Party. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-24653-8.
- Mun, Chia Wai. Singapore and Asia in a Globalized World: Contemporary Economic Issues and Policies (2008)
- Perry, John Curtis. Singapore: Unlikely Power (Oxford University Press, 2017).
- Singh, Bilveer. Understanding Singapore Politics (2017)
- Tan, Kenneth Paul (2007). Renaissance Singapore? Economy, Culture, and Politics. NUS Press. ISBN 978-9971-69-377-0.
- Worthington, Ross (2002). Governance in Singapore. Routledge/Curzon. ISBN 978-0-7007-1474-2.
- Yew, Lee Kuan. From Third World To First: The Singapore Story: 1965–2000. New York: HarperCollins, 2000. ISBN 0-06-019776-5.
Read more: Ex on the Beach (British series 6)
