This article is about the nation in western Asia. For other uses, see Iraq ( disambiguation ) Coordinates :
Iraq ( Arabic : الْعِرَاق, romanized : al-ʿIrāq ; Kurdish : عێراق, romanized : Êraq ), formally the Republic of Iraq ( Arabic : جُمْهُورِيَّة ٱلْعِرَاق ; Kurdish : کۆماری عێراق, romanized : Komarî Êraq ), is a country in western Asia, bordered by Turkey to the union, Iran to the east, Jordan to the southwest, Syria to the west, Kuwait to the southeasterly and Saudi Arabia to the south. The capital and largest city is Baghdad. Iraq is home to diverse heathen groups including Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians/Chaldeans, Yazidis, Persians, Shabakis, Armenians, Sabian-Mandaeans, Circassians, and Kawliya. Around 95 % of the nation ‘s 40 million citizens are Muslims, [ 2 ] with minorities of Christians, Yarsans, Yezidis and Mandaeans besides present. The official languages of Iraq are Arabic and Kurdish while other recoginzed regional languages include english, Neo-Aramaic, Turkish and armenian language.
Reading: Wikipedia
The “ Cradle of Civilization “ is a common terminus for the area comprising modern Iraq as it was home to the earliest know refinement, the sumerian civilization. [ 11 ] Iraq has a coastline measuring 58 kilometer ( 36 miles ) on the northern Persian Gulf and encompasses the Mesopotamian Alluvial Plain, the northwestern end of the Zagros batch range and the eastern part of the syrian Desert. [ 12 ] Two major rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates, run confederacy through Iraq and into the Shatt al-Arab near the Persian Gulf. These rivers provide Iraq with significant amounts of fat land. The area between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, historically known as Mesopotamia. It was here that mankind first began to read, write, create laws and live in cities under an organised government—notably Uruk, from which “ Iraq ” is derived. The area has been home to successive civilisations since the 6th millennium BC. Iraq was the center of the Akkadian, Sumerian, Assyrian and babylonian empires. It was besides part of the Median, Achaemenid, Hellenistic, Parthian, Sassanid, Roman, Rashidun, Umayyad, Abbasid, Ayyubid, Seljuk, Mongol, Timurid, Safavid, Afsharid and Ottoman empires. [ 13 ] During the Ottoman occupation of Iraq until the partition of the Ottoman Empire in the twentieth hundred, Iraq was made up of three provinces, called vilayets in the Ottoman turkish language : Mosul Vilayet, Baghdad Vilayet, and Basra Vilayet. In April 1920 the british Mandate of Mesopotamia was created under the authority of the League of Nations. A British-backed monarchy joining these vilayets into one Kingdom was established in 1921 under Faisal I of Iraq. The Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq gained independence from the UK in 1932. In 1958, the monarchy was overthrown and the Iraqi Republic created. Iraq was controlled by the arabian Socialist Ba’ath Party from 1968 until 2003. In 1980, Iraq invaded Iran, sparking a prolong war which would stopping point for about eight years, and end in a stalemate with lay waste to losses for both countries. After an invasion by the United States and its allies in 2003, Saddam Hussein ‘s Ba’ath Party was removed from world power, and multi-party parliamentary elections were held in 2005. The US presence in Iraq ended in 2011, [ 14 ] but the Iraqi insurgency continued and intensified as fighters from the syrian civil war spilled into the nation. On 9 December 2017, then- Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi declared victory over ISIL and announced fully liberation of borders with Syria from Islamic State militants. [ 15 ] Iraq is a union parliamentary democracy consist of 19 governorates, four of which make up the autonomous Kurdistan Region. The country ‘s official religion is Islam while other recognize religions include Christianity, Yazidism and Mandaeism. Culturally, Iraq has a very rich inheritance and celebrates the achievements of its past in both pre-Islamic ampere well as post-Islamic times and is known for its poets, its painters and sculptors s among the best in the arabian universe, some of them being first equally well as producing fine handicrafts, including rugs and carpets. Iraq is a initiation member of the United Nations, the OPEC arsenic well as of the Arab League, OIC, Non-Aligned Movement and the IMF .
identify
The Arabic name al-ʿIrāq ( العراق ) has been in use since before the sixth century CE. There are several suggest origins for the list. One dates to the sumerian city of Uruk ( Biblical Hebrew Erech ) and is frankincense ultimately of sumerian beginning, as Uruk was the akkadian mention for the sumerian city of Urug, containing the sumerian give voice for “ city ”, UR. [ 16 ] [ 17 ] Another potential etymology for the mention is from the Middle Persian word erāq, meaning “ lowlands. ” [ 18 ] An “ Aramaic incantation bowl ” excavated in Nippur features the son ’yrg ( אירג ) next to myšyn ( Mesene ) that suggests that it refers to the region of southern Mesopotamia. [ 19 ] An Arabic tribe etymology for the identify is “ deeply rooted, well-watered ; fat “. [ 20 ] During the medieval time period, there was a region called ʿIrāq ʿArabī ( “ arab Iraq ” ) for Lower Mesopotamia and ʿIrāq ʿAjamī ( “ irani Iraq ” ), for the region nowadays situated in Central and Western Iran. The term historically included the obviously south of the Hamrin Mountains and did not include the northernmost and westernmost parts of the modern territory of Iraq. [ 22 ] Prior to the in-between of the nineteenth hundred, the term Eyraca Arabica was normally used to describe Iraq. [ 23 ] [ 24 ] The condition Sawad was besides used in early Islamic times for the region of the alluvial plain of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, contrasting it with the arid Arabian defect. As an Arabic discussion, عراق means “ hem ”, “ land ”, “ trust ”, or “ boundary ”, so that the list by tribe etymology came to be interpreted as “ the escarpment “, viz. at the south and east of the Jazira Plateau, which forms the northerly and western edge of the “ iraq arabi ” area. [ 25 ] The Arabic pronunciation is [ ʕiˈrɑːq ]. In English, it is either ( the lone pronunciation listed in the Oxford English Dictionary and the first one in Merriam-Webster’s Online Dictionary [ 26 ] ) or ( listed foremost by MQD ), the American Heritage Dictionary, [ 27 ] and the Random House Dictionary. [ 28 ] The pronunciation is occasionally heard in US media. [ citation needed ] Since January 1992, the official name of the express is “ Republic of Iraq ” ( Jumhūrīyyat al-‘Irāq ), reaffirmed in the 2005 Constitution. [ 1 ] [ 29 ] [ 30 ]
history
Prehistoric era
 [31][32] Inside the Shanidar Cave, where the remains of eight adults and two baby Neanderthals, dating from around 65,000–35,000 years ago where line up. Between 65,000 BC and 35,000 BC, northerly Iraq was home to a boorish culture, archaeological remains of which have been discovered at Shanidar Cave [ 33 ] This lapp region is besides the placement of a number of pre-Neolithic cemeteries, dating from approximately 11,000 BC. [ 34 ] Since approximately 10,000 BC, Iraq, together with a big contribution of the Fertile Crescent besides comprising Asia Minor and the Levant, was one of centres of a neolithic culture known as Pre-Pottery Neolithic A ( PPNA ), where department of agriculture and cattle breeding appeared for the first clock time in the earth. The follow neolithic age period, PPNB, is represented by orthogonal houses. At the time of the pre-pottery Neolithic, people used vessels made of rock, gypsum and burn lime ( Vaisselle blanche ). Finds of obsidian tools from Anatolia are evidences of early trade relations. Further crucial sites of homo advancement were Jarmo ( circa 7100 BC ), [ 34 ] a issue of sites belonging to the Halaf polish, and Tell al-‘Ubaid, the type locate of the Ubaid period ( between 6500 BC and 3800 BC ). [ 35 ] The respective periods show ever-increasing levels of progress in agribusiness, tool-making and architecture .
[31][32] Inside the Shanidar Cave, where the remains of eight adults and two baby Neanderthals, dating from around 65,000–35,000 years ago where line up. Between 65,000 BC and 35,000 BC, northerly Iraq was home to a boorish culture, archaeological remains of which have been discovered at Shanidar Cave [ 33 ] This lapp region is besides the placement of a number of pre-Neolithic cemeteries, dating from approximately 11,000 BC. [ 34 ] Since approximately 10,000 BC, Iraq, together with a big contribution of the Fertile Crescent besides comprising Asia Minor and the Levant, was one of centres of a neolithic culture known as Pre-Pottery Neolithic A ( PPNA ), where department of agriculture and cattle breeding appeared for the first clock time in the earth. The follow neolithic age period, PPNB, is represented by orthogonal houses. At the time of the pre-pottery Neolithic, people used vessels made of rock, gypsum and burn lime ( Vaisselle blanche ). Finds of obsidian tools from Anatolia are evidences of early trade relations. Further crucial sites of homo advancement were Jarmo ( circa 7100 BC ), [ 34 ] a issue of sites belonging to the Halaf polish, and Tell al-‘Ubaid, the type locate of the Ubaid period ( between 6500 BC and 3800 BC ). [ 35 ] The respective periods show ever-increasing levels of progress in agribusiness, tool-making and architecture .
Ancient Iraq
 Area of the Fertile Crescent, circa 7500 BC, with main archaeological sites of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic menstruation. At that time, the area of Mesopotamia proper was not so far settled by humans. The “ Cradle of Civilization “ is frankincense a common term for the area comprising advanced Iraq as it was home to the earliest know civilization, the sumerian civilization, which arose in the fertile Tigris-Euphrates river valley of southern Iraq in the Chalcolithic ( Ubaid period ). [ 36 ] It was here, in the late fourth millennium BC, that the populace ‘s first write arrangement and recorded history itself were born. The Sumerians were besides the first to harness the bicycle and create City States, and whose writings record the beginning attest of Mathematics, Astronomy, Astrology, Written Law, Medicine and Organised religion. [ 36 ] The speech of the Sumerians is a linguistic process sequester. The major city states of the early sumerian menstruation were ; Eridu, Bad-tibira, Larsa, Sippar, Shuruppak, Uruk, Kish, Ur, Nippur, Lagash, Girsu, Umma, Hamazi, Adab, Mari, Isin, Kutha, Der and Akshak .. [ 36 ] The cities to the north like Ashur, Arbela ( advanced Erbil ) and Arrapha ( modern Kirkuk ) were besides extant in what was to be called Assyria from the twenty-fifth century BC ; however, at this early stage, they were Sumerian ruled administrative centres .
Area of the Fertile Crescent, circa 7500 BC, with main archaeological sites of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic menstruation. At that time, the area of Mesopotamia proper was not so far settled by humans. The “ Cradle of Civilization “ is frankincense a common term for the area comprising advanced Iraq as it was home to the earliest know civilization, the sumerian civilization, which arose in the fertile Tigris-Euphrates river valley of southern Iraq in the Chalcolithic ( Ubaid period ). [ 36 ] It was here, in the late fourth millennium BC, that the populace ‘s first write arrangement and recorded history itself were born. The Sumerians were besides the first to harness the bicycle and create City States, and whose writings record the beginning attest of Mathematics, Astronomy, Astrology, Written Law, Medicine and Organised religion. [ 36 ] The speech of the Sumerians is a linguistic process sequester. The major city states of the early sumerian menstruation were ; Eridu, Bad-tibira, Larsa, Sippar, Shuruppak, Uruk, Kish, Ur, Nippur, Lagash, Girsu, Umma, Hamazi, Adab, Mari, Isin, Kutha, Der and Akshak .. [ 36 ] The cities to the north like Ashur, Arbela ( advanced Erbil ) and Arrapha ( modern Kirkuk ) were besides extant in what was to be called Assyria from the twenty-fifth century BC ; however, at this early stage, they were Sumerian ruled administrative centres .
Bronze Age
In the twenty-sixth hundred BC, Eannatum of Lagash created what was possibly the beginning conglomerate in history, though this was short-lived. Later, Lugal-Zage-Si, the priest-king of Umma, overthrew the primacy of the Lagash dynasty in the area, then conquered Uruk, making it his capital, and claimed an empire extending from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean. [ 37 ] It was during this period that the Epic of Gilgamesh originates, which includes the narrative of The Great Flood. From the twenty-ninth century BC, Akkadian Semitic names began to appear on king lists and administrative documents of respective city states. It remains nameless as to the origin of Akkad, where it was precisely situated and how it rose to prominence. Its people spoke Akkadian, an East semite lyric. [ 38 ] Between the 29th and 24th centuries BC, a number of kingdoms and city states within Iraq began to have akkadian speak dynasties ; including Assyria, Ekallatum, Isin and Larsa. however, the Sumerians remained broadly dominant allele until the lift of the akkadian Empire ( 2335–2124 BC ), based in the city of Akkad in cardinal Iraq. Sargon of Akkad, originally a Rabshakeh to a sumerian king, founded the conglomerate, he conquered all of the city states of southern and cardinal Iraq, and subjugated the kings of Assyria, therefore uniting the Sumerians and Akkadians in one state of matter. He then set about expanding his empire, conquering Gutium, Elam and had victories that did not result into a full seduction against the Amorites and Eblaites of Ancient Syria .
After the collapse of the Akkadian Empire in the late twenty-second hundred BC, the Gutians occupied the south for a few decades, while Assyria reasserted its independence in the north. Most of southern Mesopotamia was again unite under one ruler during the Ur III time period, most notably during the principle of the fecund king Shulgi. An Elamite invasion in 2004 BC brought the Ur III kingdom to an end. By the mid twenty-first century BC, the akkadian speak kingdom of Assyria had risen to dominance in northern Iraq. Assyria expanded territorially into the north eastern Levant, central Iraq, and eastern Anatolia, forming the Old Assyrian Empire ( circa 2035–1750 BC ) under kings such as Puzur-Ashur I, Sargon I, Ilushuma and Erishum I, the latter of whom produced the most detail fixed of law so far written. [ citation needed ] The south broke up into a number of akkadian talk states, Isin, Larsa and Eshnunna being the major ones. During the twentieth hundred BC, the Canaanite speaking Amorites began to migrate into southern Mesopotamia. finally, they began to set up modest petit larceny kingdoms in the south, adenine well as usurping the thrones of extant city states such as Isin, Larsa and Eshnunna. One of these small Amorite kingdoms founded in 1894 BC contained the then little administrative town of Babylon within its borders. It remained insignificant for over a hundred, overshadowed by older and more potent states, such as Assyria, Elam, Isin, Ehnunna and Larsa. In 1792 BC, an Amorite ruler named Hammurabi came to world power in this country, and immediately set about building Babylon from a minor town into a major city, declaring himself its king. Hammurabi conquered the whole of southerly and cardinal Iraq, equally well as Elam to the east and Mari to the west, then engaged in a drawn-out war with the assyrian neo-aramaic king Ishme-Dagan for domination of the region, creating the ephemeral Babylonian Empire. He finally prevailed over the successor of Ishme-Dagan and subjected Assyria and its anatolian colonies. By the middle of the eighteenth century BC, the Sumerians had lost their cultural identity and ceased to exist as a discrete people. [ 39 ] [ 40 ] Genetic and cultural analysis indicates that the Marsh Arabs of southerly Iraq are probably their most direct modern descendants. [ 41 ] [ 42 ] [ 43 ] It is from the time period of Hammurabi that southern Iraq came to be known as Babylonia, while the north had already coalesced into Assyria hundreds of years before. however, his empire was ephemeral, and quickly collapsed after his end, with both Assyria and southern Iraq, in the form of the Sealand Dynasty, falling back into native akkadian hands. The extraneous Amorites cling on to ability in a once more fallible and small Babylonia until it was sacked by the indo-european speak Hittite Empire based in Anatolia in 1595 BC. After this, another foreign people, the Language Isolate talk Kassites, originating in the Zagros Mountains of Ancient Iran, seized control of Babylonia, where they were to rule for about 600 years, by far the longest dynasty ever to rule in Babylon. Iraq was from this degree divided into three polities : Assyria in the north, Kassite Babylonia in the south cardinal area, and the Sealand Dynasty in the far south. The Sealand Dynasty was ultimately conquered by Kassite Babylonia circa 1380 BC. The Middle Assyrian Empire ( 1365–1020 BC ) saw Assyria arise to be the most brawny nation in the know global. Beginning with the campaigns of Ashur-uballit I, Assyria destroyed the equal Hurrian – Mitanni Empire, annexed huge swathes of the Hittite Empire for itself, annexed northern Babylonia from the Kassites, forced the egyptian empire from the region, and defeated the Elamites, Phrygians, Canaanites, Phoenicians, Cilicians, Gutians, Dilmunites and Arameans. At its acme, the Middle Assyrian Empire stretched from The Caucasus to Dilmun ( modern Bahrain ), and from the Mediterranean coasts of Phoenicia to the Zagros Mountains of Iran. In 1235 BC, Tukulti-Ninurta I of Assyria took the throne of Babylon, therefore becoming the first base native Mesopotamian to rule the submit .
During the Bronze Age break down ( 1200–900 BC ), Babylonia was in a state of chaos, dominated for retentive periods by Assyria and Elam. The Kassites were driven from ability by Assyria and Elam, allowing native south Mesopotamian kings to rule Babylonia for the first time, although often subject to Assyrian or Elamite rulers. however, these East Semitic Akkadian kings, were unable to prevent new waves of West Semitic migrants entering southerly Iraq, and during the eleventh hundred BC Arameans and Suteans entered Babylonia from The Levant, and these were followed in the late 10th to early 9th hundred BC by the migrant Chaldeans who were closely related to the earlier Arameans .
Iron Age
After a period of comparative decline in Assyria, it once more began to expand with the Neo Assyrian Empire ( 935–605 BC ). This was to be the largest empire the region had even seen, and under rulers such as Adad-Nirari II, Ashurnasirpal, Shalmaneser III, Semiramis, Tiglath-pileser III, Sargon II, Sennacherib, Esarhaddon and Ashurbanipal, Iraq became the center of an conglomerate stretching from Persia, Parthia and Elam in the east, to Cyprus and Antioch in the west, and from The Caucasus in the north to Egypt, Nubia and Arabia in the south. The Arabs and the Chaldeans are first mentioned in written history ( circa 850 BC ) in the annals of Shalmaneser III. It was during this period that an akkadian influence phase of Eastern Aramaic was adopted by the Assyrians as the tongue franca of their huge empire, and Mesopotamian Aramaic began to supplant akkadian as the spoken lyric of the general populace of both Assyria and Babylonia. The descendant dialects of this natural language survive amongst the Mandaeans of southern Iraq and Assyrians of northerly Iraq to this day. In the late seventh hundred BC, the Assyrian Empire tore itself apart with a series of brutal civil wars, weakening itself to such a degree that a alliance of its erstwhile subjects ; the Babylonians, Chaldeans, Medes, Persians, Parthians, Scythians and Cimmerians, were able to attack Assyria, last bringing its empire down by 605 BC. [ 44 ]
babylonian and iranian periods
The ephemeral Neo-Babylonian Empire ( 620–539 BC ) succeeded that of Assyria. It failed to attain the size, power or longevity of its harbinger ; however, it came to dominate The Levant, Canaan, Arabia, Israel and Judah, and to defeat Egypt. Initially, Babylon was ruled by however another extraneous dynasty, that of the Chaldeans, who had migrated to the region in the former 10th or early 9th century BC. Its greatest king, Nebuchadnezzar II, rivalled another not native rule, the ethnically unrelated Amorite king Hammurabi, as the greatest king of Babylon. however, by 556 BC, the Chaldeans had been deposed from baron by the assyrian bear Nabonidus and his son and regent Belshazzar .
In the sixth century BC, Cyrus the Great of neighbouring Persia defeated the Neo-Babylonian conglomerate at the Battle of Opis and Iraq was subsumed into the Achaemenid Empire for closely two centuries. The Achaemenids made Babylon their chief capital. The Chaldeans and Chaldea disappeared at around this time, though both Assyria and Babylonia endured and thrived under Achaemenid rule ( see Achaemenid Assyria ). little changed under the Persians, having spent three centuries under assyrian neo-aramaic rule, their kings saw themselves as successors to Ashurbanipal, and they retained Assyrian Imperial Aramaic as the terminology of empire, together with the assyrian akkadian imperial infrastructure, and an assyrian neo-aramaic manner of art and architecture. [ citation needed ] In the late fourth hundred BC, Alexander the Great conquered the region, putting it under Hellenistic Seleucid rule for over two centuries. [ 45 ] The Seleucids introduced the Indo-Anatolian and greek condition Syria to the region. This mention had for many centuries been the indo-european son for Assyria and specifically and only mean Assyria ; however, the Seleucids besides applied it to The Levant ( Aramea, causing both the Assyria and the Assyrians of Iraq and the Arameans and The Levant to be called Syria and Syrians/Syriacs in the Greco-Roman earth. [ 46 ] The Parthians ( 247 BC – 224 AD ) from Persia conquered the region during the reign of Mithridates I of Parthia ( r. 171–138 BC ). From Syria, the Romans invaded western parts of the region several times, concisely founding Assyria Provincia in Assyria. Christianity began to take hold in Iraq ( particularly in Assyria ) between the 1st and 3rd centuries, and Assyria became a center of Syriac Christianity, the Church of the East and Syriac literature. A number of independent states evolved in the north during the Parthian era, such as Adiabene, Assur, Osroene and Hatra. The Sassanids of Persia under Ardashir I destroyed the parthian Empire and conquered the region in 224 AD. During the 240s and 250 ‘s AD, the Sassanids gradually conquered the freelancer states, culminating with Assur in 256 AD. The region was frankincense a province of the Sassanid Empire for over four centuries, and became the frontier and battle background between the Sassanid Empire and Byzantine Empire, with both empires weakening each early, paving the way for the Arab – Muslim seduction of Persia in the mid-7th century .
Middle Ages
The arab Islamic conquest in the mid-7th hundred AD established Islam in Iraq and saw a large inflow of Arabs. Under the Rashidun Caliphate, the prophet Muhammad ‘s cousin and son-in-law, Ali, moved his capital to Kufa when he became the fourth caliph. The Umayyad Caliphate ruled the province of Iraq from Damascus in the seventh hundred. ( however, finally there was a break, freelancer Caliphate of Córdoba in Iberia. ) The Abbasid Caliphate built the city of Baghdad along the Tigris in the eighth hundred as its capital, and the city became the leading city of the Arab and Muslim worldly concern for five centuries. Baghdad was the largest multicultural city of the Middle Ages, peaking at a population of more than a million, [ 47 ] and was the centre of learning during the Islamic Golden Age. The Mongols destroyed the city and burned its library during the siege of Baghdad in the thirteenth century. [ 48 ] In 1257, Hulagu Khan amassed an unusually boastfully united states army, a significant part of the Mongol Empire ‘s forces, for the purpose of conquering Baghdad. When they arrived at the Islamic das kapital, Hulagu Khan demanded its capitulation, but the last Abbasid Caliph Al-Musta’sim refused. This anger Hulagu, and, reproducible with Mongol strategy of discouraging resistance, he besieged Baghdad, sacked the city and massacred many of the inhabitants. [ 49 ] Estimates of the phone number of dead range from 200,000 to a million. [ 50 ]
The Mongols destroyed the Abbasid Caliphate and Baghdad ‘s House of Wisdom, which contained countless precious and historical documents. The city has never regained its former pre-eminence as a major concentrate of culture and influence. Some historians believe that the Mongol invasion destroyed much of the irrigation infrastructure that had sustained Mesopotamia for millennium. early historians point to soil salination as the perpetrator in the decay in department of agriculture. [ 51 ] The mid-14th-century Black Death ravaged much of the Islamic world. [ 52 ] The best appraisal for the Middle East is a death rate of approximately one-third. [ 53 ] In 1401, a warlord of Mongol origin, Tamerlane ( Timur Lenk ), invaded Iraq. After the capture of Baghdad, 20,000 of its citizens were massacred. [ 54 ] Timur ordered that every soldier should return with at least two sever human heads to show him ( many warriors were thus daunt they killed prisoners captured earlier in the campaign just to ensure they had heads to present to Timur ). [ 55 ] Timur besides conducted massacres of the autochthonal assyrian Christian population, so far hush the majority population in northern Mesopotamia, and it was during this time that the ancient assyrian city of Assur was last abandoned. [ 56 ]
Ottoman Iraq
During the late 14th and early fifteenth centuries, the Black Sheep Turkmen ruled the area now known as Iraq. In 1466, the White Sheep Turkmen defeated the Black Sheep and took manipulate. From the earliest sixteenth century, in 1508, as with all territories of the former White Sheep Turkmen, Iraq fell into the hands of the iranian Safavids. Owing to the hundred long Turco-Iranian competition between the Safavids and the neighbor Ottoman Turks, Iraq would be contested between the two for more than a hundred years during the patronize Ottoman-Persian Wars. With the Treaty of Zuhab in 1639, most of the territory of contemporary Iraq finally came under the control of Ottoman Empire as the eyalet of Baghdad as a result of wars with the neighbouring equal, Safavid Iran. Throughout most of the period of Ottoman convention ( 1533–1918 ), the district of contemporary Iraq was a battle zone between the rival regional empires and tribal alliances. By the seventeenth hundred, the frequent conflicts with the Safavids had sapped the lastingness of the Ottoman Empire and had weakened its control over its provinces. The mobile population swelled with the inflow of bedouins from Najd, in the arab Peninsula. Bedouin raids on settle areas became impossible to curb. [ 57 ]
During the years 1747–1831, Iraq was ruled by a Mamluk dynasty of Georgian [ 58 ] origin who succeeded in obtaining autonomy from the Ottoman Porte, suppressed tribal revolts, curbed the power of the Janissaries, restored order and introduced a program of modernization of economy and military. In 1831, the Ottomans managed to overthrow the Mamluk government and imposed their address control over Iraq. The population of Iraq, estimated at 30 million in 800 AD, was merely 5 million at the start of the twentieth century. [ 59 ] During World War I, the Ottomans sided with Germany and the Central Powers. In the Mesopotamian campaign against the Central Powers, british forces invaded the area and initially suffered a major get the better of at the hands of the turkish united states army during the Siege of Kut ( 1915–1916 ). however, subsequent to this the british began to gain the upper bridge player, and were far aided by the corroborate of local Arabs and Assyrians. In 1916, the british and french made a plan for the post-war division of western Asia under the Sykes-Picot Agreement. [ 60 ] british forces regrouped and captured Baghdad in 1917, and defeated the Ottomans. An armistice was signed in 1918. The british lost 92,000 soldiers in the Mesopotamian crusade. ottoman losses are unknown but the british captured a total of 45,000 prisoners of war. By the end of 1918, the british had deployed 410,000 men in the area, of which 112,000 were battle troops. [ citation needed ]
contemporary period
british administration and independent kingdom
 british troops in Baghdad, June 1941. The nation today known as Iraq was a region of the Ottoman Empire until the division of the Ottoman Empire in the twentieth century. It was made up of three provinces, called vilayets in the Ottoman terminology : Mosul Vilayet, Baghdad Vilayet, and Basra Vilayet. These three provinces were joined into one Kingdom by the british after the area became a League of Nations mandate, administered under british operate, with the name “ State of Iraq “. A fourth province ( Zor Sanjak ), which Iraqi nationalists considered part of Upper Mesopotamia was ultimately added to Syria. [ 61 ] [ 62 ] In line with their “ Sharifian Solution “ policy, the british established the Hashemite king, Faisal I of Iraq, who had been forced out of Syria by the french, as their client rule. Likewise, British authorities selected Sunni Arab elites from the region for appointments to politics and ministry offices. [ specify ] [ 63 ] [ page needed ] [ 64 ] Faced with corkscrew costs and influenced by the public protestations of the war hero T. E. Lawrence [ 65 ] in The Times, Britain replaced Arnold Wilson in October 1920 with a fresh Civil Commissioner, Sir Percy Cox. [ 66 ] Cox managed to quell a rebellion, yet was besides responsible for implementing the fatal policy of close co-operation with Iraq ‘s Sunni minority. [ 67 ] The institution of slavery was abolished in the 1920s. [ 68 ] Britain granted independence to the Kingdom of Iraq in 1932, [ 69 ] on the cheer of King Faisal, though the british retained military bases, local militia in the shape of assyrian Levies, and transportation system rights for their forces. King Ghazi ruled as a figurehead after King Faisal ‘s death in 1933, while undermined by try military coups, until his death in 1939. Ghazi was followed by his minor son, Faisal II. ‘Abd al-Ilah served as Regent during Faisal ‘s minority. On 1 April 1941, Rashid Ali al-Gaylani and members of the Golden Square staged a coup d’etat d’état and overthrew the government of ‘Abd al-Ilah. During the subsequent Anglo-Iraqi War, the United Kingdom ( which placid maintained air bases in Iraq ) invaded Iraq for fear that the Rashid Ali government might cut oil supplies to westerly nations because of his links to the Axis powers. The war started on 2 May, and the british, together with loyal assyrian Levies, [ 70 ] defeated the forces of Al-Gaylani, forcing an armistice on 31 May. A military occupation followed the restoration of the pre-coup government of the Hashemite monarchy. The occupation ended on 26 October 1947, although Britain was to retain military bases in Iraq until 1954, after which the assyrian militia were disbanded. The rulers during the occupation and the remainder of the Hashemite monarchy were Nuri as-Said, the autocratic Prime Minister, who besides ruled from 1930 to 1932, and ‘Abd al-Ilah, the former Regent who now served as an adviser to King Faisal II .
british troops in Baghdad, June 1941. The nation today known as Iraq was a region of the Ottoman Empire until the division of the Ottoman Empire in the twentieth century. It was made up of three provinces, called vilayets in the Ottoman terminology : Mosul Vilayet, Baghdad Vilayet, and Basra Vilayet. These three provinces were joined into one Kingdom by the british after the area became a League of Nations mandate, administered under british operate, with the name “ State of Iraq “. A fourth province ( Zor Sanjak ), which Iraqi nationalists considered part of Upper Mesopotamia was ultimately added to Syria. [ 61 ] [ 62 ] In line with their “ Sharifian Solution “ policy, the british established the Hashemite king, Faisal I of Iraq, who had been forced out of Syria by the french, as their client rule. Likewise, British authorities selected Sunni Arab elites from the region for appointments to politics and ministry offices. [ specify ] [ 63 ] [ page needed ] [ 64 ] Faced with corkscrew costs and influenced by the public protestations of the war hero T. E. Lawrence [ 65 ] in The Times, Britain replaced Arnold Wilson in October 1920 with a fresh Civil Commissioner, Sir Percy Cox. [ 66 ] Cox managed to quell a rebellion, yet was besides responsible for implementing the fatal policy of close co-operation with Iraq ‘s Sunni minority. [ 67 ] The institution of slavery was abolished in the 1920s. [ 68 ] Britain granted independence to the Kingdom of Iraq in 1932, [ 69 ] on the cheer of King Faisal, though the british retained military bases, local militia in the shape of assyrian Levies, and transportation system rights for their forces. King Ghazi ruled as a figurehead after King Faisal ‘s death in 1933, while undermined by try military coups, until his death in 1939. Ghazi was followed by his minor son, Faisal II. ‘Abd al-Ilah served as Regent during Faisal ‘s minority. On 1 April 1941, Rashid Ali al-Gaylani and members of the Golden Square staged a coup d’etat d’état and overthrew the government of ‘Abd al-Ilah. During the subsequent Anglo-Iraqi War, the United Kingdom ( which placid maintained air bases in Iraq ) invaded Iraq for fear that the Rashid Ali government might cut oil supplies to westerly nations because of his links to the Axis powers. The war started on 2 May, and the british, together with loyal assyrian Levies, [ 70 ] defeated the forces of Al-Gaylani, forcing an armistice on 31 May. A military occupation followed the restoration of the pre-coup government of the Hashemite monarchy. The occupation ended on 26 October 1947, although Britain was to retain military bases in Iraq until 1954, after which the assyrian militia were disbanded. The rulers during the occupation and the remainder of the Hashemite monarchy were Nuri as-Said, the autocratic Prime Minister, who besides ruled from 1930 to 1932, and ‘Abd al-Ilah, the former Regent who now served as an adviser to King Faisal II .
Republic and Ba’athist Iraq
In 1958, a coup d’etat d’état known as the 14 July Revolution was led by the Brigadier General Abd al-Karim Qasim. This disgust was strongly anti-imperial and anti-monarchical in nature and had potent socialist elements. numerous people were killed in the coup, including King Faysal II, Prince Abd al-Ilah, and Nuri al-Sa’id. [ 71 ] Qasim controlled Iraq through military rule and in 1958 he began a process of forcibly reducing the excess amounts of estate owned by a few citizens and having the state redistribute the state. He was overthrown by Colonel Abdul Salam Arif in a February 1963 coup. After the latter ‘s death in 1966, he was succeeded by his brother, Abdul Rahman Arif, who was overthrown by the Ba’ath Party in 1968. Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr became the first Ba’ath President of Iraq but then the movement gradually came under the control of Saddam Hussein, who acceded to the presidency and control of the Revolutionary Command Council ( RCC ), then Iraq ‘s supreme administrator soundbox, in July 1979. In 1979, the irani Revolution took put. Following months of cross-border raids between the two countries, Saddam declared war on Iran in September 1980, initiating the Iran–Iraq War ( or First Persian Gulf War ). Taking advantage of the post-revolution chaos in Iran, Iraq captured some territories in southwest of Iran, but Iran recaptured all of the helpless territories within two years, and for the next six years Iran was on the dysphemistic. [ 72 ] [ page needed ] The war, which ended in stalemate in 1988, had cost the lives of between half a million and 1.5 million people. [ 73 ] In 1981, Israeli aircraft bombed an Iraqi nuclear materials testing reactor at Osirak and was wide criticised at the United Nations. [ 74 ] [ 75 ] During the eight-year war with Iran, Saddam Hussein extensively used chemical weapons against Iranians. [ 76 ] In the final stages of the Iran–Iraq War, the Ba’athist Iraqi government led the Al-Anfal Campaign, a genocidal [ 77 ] campaign that targeted Iraqi Kurds, [ 78 ] [ 79 ] [ 80 ] and led to the kill of 50,000–100,000 civilians. [ 81 ] Ba’athist earned run average presidents Hassan al-Bakr ( right ) and Saddam Hussein in 1978 .
Ba’athist earned run average presidents Hassan al-Bakr ( right ) and Saddam Hussein in 1978 . Saddam Hussein ‘s family, mid-late 1980s In August 1990, Iraq invaded and annex Kuwait. This subsequently led to military intervention by United States -led forces in the First Gulf War. The coalition forces proceeded with a bombing campaign targeting military targets [ 82 ] [ 83 ] [ 84 ] and then launched a 100-hour-long establish assault against Iraqi forces in Southern Iraq and those occupying Kuwait. Iraq ‘s arm forces were devastated during the war. shortly after it ended in 1991, Kurdish Iraqis led respective uprisings against Saddam Hussein ‘s regimen, but these were successfully repressed using the Iraqi security forces and chemical weapons. It is estimated that vitamin a many as 100,000 people, including many civilians were killed. [ 85 ] During the uprisings the US, UK, France and Turkey, claiming authority under UNSCR 688, established the Iraqi no-fly zones to protect Kurdish population from attacks by the Saddam regimen ‘s fixed-wing aircraft ( but not helicopters ). Iraq was ordered to destroy its chemical and biological weapons and the UN attempted to compel Saddam ‘s government to disarm and agree to a ceasefire by imposing extra sanctions on the area in addition to the initial sanctions imposed following Iraq ‘s invasion of Kuwait. The Iraqi Government ‘s failure to disarm and agree to a ceasefire resulted in sanctions which remained in rate until 2003. The effects of the sanctions on the civilian population of Iraq have been disputed. [ 86 ] [ 87 ] Whereas it was widely believed that the sanctions caused a major rise in child deathrate, recent research has shown that normally cited data were fabricated by the Iraqi politics and that “ there was no major rise in child deathrate in Iraq after 1990 and during the period of the sanctions. ” [ 88 ] [ 89 ] [ 90 ] An oil for food course of study was established in 1996 to ease the effects of sanctions. Following the September 11 attacks, the George W. Bush administration began planning the overthrow of Saddam ‘s politics and in October 2002, the US Congress passed the Joint Resolution to Authorize the Use of United States Armed Forces Against Iraq. In November 2002, the UN Security Council passed UNSCR 1441 and in March 2003 the US and its allies invaded Iraq .
Saddam Hussein ‘s family, mid-late 1980s In August 1990, Iraq invaded and annex Kuwait. This subsequently led to military intervention by United States -led forces in the First Gulf War. The coalition forces proceeded with a bombing campaign targeting military targets [ 82 ] [ 83 ] [ 84 ] and then launched a 100-hour-long establish assault against Iraqi forces in Southern Iraq and those occupying Kuwait. Iraq ‘s arm forces were devastated during the war. shortly after it ended in 1991, Kurdish Iraqis led respective uprisings against Saddam Hussein ‘s regimen, but these were successfully repressed using the Iraqi security forces and chemical weapons. It is estimated that vitamin a many as 100,000 people, including many civilians were killed. [ 85 ] During the uprisings the US, UK, France and Turkey, claiming authority under UNSCR 688, established the Iraqi no-fly zones to protect Kurdish population from attacks by the Saddam regimen ‘s fixed-wing aircraft ( but not helicopters ). Iraq was ordered to destroy its chemical and biological weapons and the UN attempted to compel Saddam ‘s government to disarm and agree to a ceasefire by imposing extra sanctions on the area in addition to the initial sanctions imposed following Iraq ‘s invasion of Kuwait. The Iraqi Government ‘s failure to disarm and agree to a ceasefire resulted in sanctions which remained in rate until 2003. The effects of the sanctions on the civilian population of Iraq have been disputed. [ 86 ] [ 87 ] Whereas it was widely believed that the sanctions caused a major rise in child deathrate, recent research has shown that normally cited data were fabricated by the Iraqi politics and that “ there was no major rise in child deathrate in Iraq after 1990 and during the period of the sanctions. ” [ 88 ] [ 89 ] [ 90 ] An oil for food course of study was established in 1996 to ease the effects of sanctions. Following the September 11 attacks, the George W. Bush administration began planning the overthrow of Saddam ‘s politics and in October 2002, the US Congress passed the Joint Resolution to Authorize the Use of United States Armed Forces Against Iraq. In November 2002, the UN Security Council passed UNSCR 1441 and in March 2003 the US and its allies invaded Iraq .
twenty-first century
2003–2007 : invasion and occupation
On 20 March 2003, a United States-organized alliance invaded Iraq, under the pretext that Iraq had failed to abandon its weapons of batch destruction course of study in irreverence of UN Resolution 687. This claim was based on documents provided by the CIA and the british politics that were late found to be unreliable. [ 91 ] [ 92 ] [ 93 ] Following the invasion, the United States established the Coalition Provisional Authority to govern Iraq. In May 2003 L. Paul Bremer, the head executive of the CPA, issued orders to exclude Baath Party members from the modern Iraqi politics ( CPA Order 1 ) and to disband the Iraqi Army ( CPA Order 2 ). [ 94 ] The decision dissolved the largely Sunni Iraqi Army and excluded many of the nation ‘s former politics officials from participating in the state ‘s administration, [ 95 ] including 40,000 school teachers who had joined the Baath Party just to keep their jobs, [ 96 ] helping to bring about a chaotic post-invasion environment. [ 97 ] An insurgency against the US-led coalescence -rule of Iraq began in summer 2003 within elements of the early Iraqi secret patrol and army, who formed guerrilla units. In fall 2003, self-entitled ‘ jihadist ‘ groups began targeting alliance forces. assorted Sunni militia were created in 2003, for exercise Jama’at al-tawhid wal-Jihad led by Abu Musab al-Zarqawi. The insurgency included intense inter-ethnic ferocity between Sunnis and Shias. [ 98 ] The Abu Ghraib torture and prisoner abuse scandal came to lighter, late 2003 in reports by Amnesty International and Associated Press .
The Mahdi Army —a Shia militia created in the summer of 2003 by Muqtada al-Sadr —began to fight Coalition forces in April 2004. [ 99 ] 2004 learn Sunni and Shia militants fighting against each early and against the modern Iraqi Interim Government installed in June 2004, and against Coalition forces, a well as the First Battle of Fallujah in April and Second Battle of Fallujah in November. The Mahdi army would kidnap Sunni civilians as contribution of a genocide that occurred against them. [ 100 ] In January 2005, the first elections since the invasion took place and in October a new Constitution was approved, [ 1 ] which was followed by parliamentary elections in December. however, insurgent attacks were common and increased to 34,131 in 2005 from 26,496 in 2004. [ 101 ] During 2006, fighting continued and reached its highest levels of violence, more war crimes scandals were made populace, Abu Musab al-Zarqawi the leader of Al-Qaeda in Iraq was killed by US forces and Iraq ‘s erstwhile dictator Saddam Hussein was sentenced to end for crimes against world and hanged. [ 102 ] [ 103 ] [ 104 ] In recently 2006, the US government ‘s Iraq Study Group recommended that the US begin focusing on training Iraqi military personnel and in January 2007 US President George W. Bush announced a “ tide ” in the number of US troops deployed to the state. [ 105 ] In May 2007, Iraq ‘s Parliament called on the United States to set a timetable for withdrawal and US coalescence partners such as the UK and Denmark began withdrawing their forces from the country. [ 106 ] [ 107 ] [ 108 ] The war in Iraq has resulted in between 151,000 and 1.2 million Iraqis being killed. [ 109 ] [ 110 ]
2008–2018 : instability and ISIS
In 2008, fighting continued and Iraq ‘s newly trained armed forces launched attacks against militants. The iraqi government signed the US–Iraq Status of Forces Agreement, which required US forces to withdraw from Iraqi cities by 30 June 2009 and to withdraw completely from Iraq by 31 December 2011. US troops handed over security duties to Iraqi forces in June 2009, though they continued to work with Iraqi forces after the disengagement. [ 111 ] On the dawn of 18 December 2011, the final contingent of US troops to be withdrawn ceremoniously exited over the border to Kuwait. [ 14 ] Crime and ferocity initially spiked in the months following the US withdrawal from cities in mid-2009 [ 112 ] [ 113 ] but despite the initial increase in ferocity, in November 2009, Iraqi Interior Ministry officials reported that the civilian death toll in Iraq fell to its lowest grade since the 2003 invasion. [ 114 ]
 military situation in 2015 Following the withdrawal of US troops in 2011, the insurgency continued and Iraq suffered from political imbalance. In February 2011, the arab form protests spread to Iraq ; [ 115 ] but the initial protests did not topple the politics. The Iraqi National Movement, reportedly representing the majority of Iraqi Sunnis, boycotted Parliament for respective weeks in late 2011 and early 2012, claiming that the Shiite-dominated government was striving to sideline Sunnis. In 2012 and 2013, levels of ferocity increased and armed groups inside Iraq were increasingly galvanised by the syrian Civil War. Both Sunnis and Shias crossed the surround to fight in Syria. [ 116 ] In December 2012, Sunni Arabs protested against the government, whom they claimed marginalised them. [ 117 ] [ 118 ] During 2013, Sunni militant groups stepped up attacks targeting the Iraq ‘s population in an undertake to undermine confidence in the Nouri al-Maliki -led government. [ 119 ] In 2014, Sunni insurgents belonging to the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant ( ISIL ) terrorist group seized restraint of big swathes of kingdom including several major Iraqi cities, like Tikrit, Fallujah and Mosul creating hundreds of thousands of internally displaced persons amid reports of atrocities by ISIL fighters. [ 120 ] After an inconclusive election in April 2014, Nouri al-Maliki served as caretaker-Prime-Minister. [ 121 ] On 11 August, Iraq ‘s highest court ruled that PM Maliki ‘s bloc was the largest in parliament, meaning Maliki could stay Prime Minister. [ 121 ] By 13 August, however, the Iraqi president had tasked Haider al-Abadi with forming a new government, and the United Nations, the United States, the European Union, Saudi Arabia, Iran, and some Iraqi politicians expressed their wish for a new leadership in Iraq, for case from Haider al-Abadi. [ 122 ] On 14 August, Maliki stepped down a PM to support Mr al-Abadi and to “ safeguard the high interests of the state ”. The u government welcomed this as “ another major step ahead ” in union Iraq. [ 123 ] [ 124 ] On 9 September 2014, Haider al-Abadi had formed a new government and became the modern prime minister. [ citation needed ] Intermittent conflict between Sunni, Shiite and Kurdish factions has led to increasing argue about the cleave of Iraq into three autonomous regions, including Sunni Kurdistan in the northeast, a Sunnistan in the west and a Shiastan in the southeast. [ 125 ] In response to rapid territorial gains made by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant ( ISIL ) during the first half of 2014, and its universally-condemned executions and reported human rights abuses, many states began to intervene against it in the Iraqi Civil War ( 2014–2017 ). Since the airstrikes started, ISIL has been losing ground in both Iraq and Syria. [ 126 ] Tens of thousands of civilians have been killed in Iraq in ISIL-linked violence. [ 127 ] [ 128 ] The genocide of Yazidis by ISIL has led to the expulsion, flight and effective exile of the Yazidis from their ancestral lands in northern Iraq. [ 129 ] The 2016 Karrada bombing killed about 400 civilians and injure hundreds more. [ 130 ] On 17 March 2017, a US-led coalescence airstrike in Mosul killed more than 200 civilians. [ 131 ] Since 2015, ISIL lost district in Iraq, including Tikrit in March and April 2015, [ 132 ] Baiji in October 2015, [ 133 ] Sinjar in November 2015, [ 134 ] Ramadi in December 2015, [ 135 ] Fallujah in June 2016 [ 136 ] and Mosul in July 2017. By December 2017, ISIL had no remaining territory in Iraq, following the 2017 Western Iraq campaign. [ 137 ] In September 2017, a referendum was held regarding kurdish independence in Iraq. 92 % of Iraqi Kurds voted in favor of independence. [ 138 ] The referendum was regarded as illegal by the federal government in Baghdad. [ 139 ] In March 2018, Turkey launched military operations to eliminate the Kurdish separatist fighters in northern Iraq. [ 140 ] anti-american cleric Muqtada al-Sadr ‘s political alliance won Iraq ‘s parliamentary election in May 2018. [ 141 ]
military situation in 2015 Following the withdrawal of US troops in 2011, the insurgency continued and Iraq suffered from political imbalance. In February 2011, the arab form protests spread to Iraq ; [ 115 ] but the initial protests did not topple the politics. The Iraqi National Movement, reportedly representing the majority of Iraqi Sunnis, boycotted Parliament for respective weeks in late 2011 and early 2012, claiming that the Shiite-dominated government was striving to sideline Sunnis. In 2012 and 2013, levels of ferocity increased and armed groups inside Iraq were increasingly galvanised by the syrian Civil War. Both Sunnis and Shias crossed the surround to fight in Syria. [ 116 ] In December 2012, Sunni Arabs protested against the government, whom they claimed marginalised them. [ 117 ] [ 118 ] During 2013, Sunni militant groups stepped up attacks targeting the Iraq ‘s population in an undertake to undermine confidence in the Nouri al-Maliki -led government. [ 119 ] In 2014, Sunni insurgents belonging to the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant ( ISIL ) terrorist group seized restraint of big swathes of kingdom including several major Iraqi cities, like Tikrit, Fallujah and Mosul creating hundreds of thousands of internally displaced persons amid reports of atrocities by ISIL fighters. [ 120 ] After an inconclusive election in April 2014, Nouri al-Maliki served as caretaker-Prime-Minister. [ 121 ] On 11 August, Iraq ‘s highest court ruled that PM Maliki ‘s bloc was the largest in parliament, meaning Maliki could stay Prime Minister. [ 121 ] By 13 August, however, the Iraqi president had tasked Haider al-Abadi with forming a new government, and the United Nations, the United States, the European Union, Saudi Arabia, Iran, and some Iraqi politicians expressed their wish for a new leadership in Iraq, for case from Haider al-Abadi. [ 122 ] On 14 August, Maliki stepped down a PM to support Mr al-Abadi and to “ safeguard the high interests of the state ”. The u government welcomed this as “ another major step ahead ” in union Iraq. [ 123 ] [ 124 ] On 9 September 2014, Haider al-Abadi had formed a new government and became the modern prime minister. [ citation needed ] Intermittent conflict between Sunni, Shiite and Kurdish factions has led to increasing argue about the cleave of Iraq into three autonomous regions, including Sunni Kurdistan in the northeast, a Sunnistan in the west and a Shiastan in the southeast. [ 125 ] In response to rapid territorial gains made by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant ( ISIL ) during the first half of 2014, and its universally-condemned executions and reported human rights abuses, many states began to intervene against it in the Iraqi Civil War ( 2014–2017 ). Since the airstrikes started, ISIL has been losing ground in both Iraq and Syria. [ 126 ] Tens of thousands of civilians have been killed in Iraq in ISIL-linked violence. [ 127 ] [ 128 ] The genocide of Yazidis by ISIL has led to the expulsion, flight and effective exile of the Yazidis from their ancestral lands in northern Iraq. [ 129 ] The 2016 Karrada bombing killed about 400 civilians and injure hundreds more. [ 130 ] On 17 March 2017, a US-led coalescence airstrike in Mosul killed more than 200 civilians. [ 131 ] Since 2015, ISIL lost district in Iraq, including Tikrit in March and April 2015, [ 132 ] Baiji in October 2015, [ 133 ] Sinjar in November 2015, [ 134 ] Ramadi in December 2015, [ 135 ] Fallujah in June 2016 [ 136 ] and Mosul in July 2017. By December 2017, ISIL had no remaining territory in Iraq, following the 2017 Western Iraq campaign. [ 137 ] In September 2017, a referendum was held regarding kurdish independence in Iraq. 92 % of Iraqi Kurds voted in favor of independence. [ 138 ] The referendum was regarded as illegal by the federal government in Baghdad. [ 139 ] In March 2018, Turkey launched military operations to eliminate the Kurdish separatist fighters in northern Iraq. [ 140 ] anti-american cleric Muqtada al-Sadr ‘s political alliance won Iraq ‘s parliamentary election in May 2018. [ 141 ]
2019–present : civil agitation and proxy war
serious civil agitation rocked the nation beginning in Baghdad and Najaf in July 2018 and spreading to other provinces in belated September 2019 as rallies to protest corruption, unemployment, and public serve failures turned violent. [ 142 ] Protests and demonstrations started again on 1 October 2019, against 16 years of corruptness, unemployment and inefficient populace services, before they escalated into calls to overthrow the administration and to stop iranian intervention in Iraq. The iraqi government at times reacted gratingly, resulting in over 500 deaths by 12 December 2019. On 27 December 2019, the K-1 Air Base in Iraq was attacked by more than 30 rockets, killing a U.S. civilian contractor and injuring others. The U.S. blamed the Iranian-backed Kata’ib Hezbollah militia. belated that month, the United States bombed five Kata’ib Hezbollah militia ‘s positions in Iraq and Syria, in retaliation for the presume Kata’ib attack of 27 December. According to Iraqi sources, at least 25 militia fighters were killed. On 31 December 2019, after a funeral for Kata’ib Hezbollah militiamen killed by U.S. airstrikes, dozens of Iraqi Shia militiamen and their supporters marched into the Green Zone of Baghdad and surrounded the U.S. embassy colonial ( see article : attack on the United States embassy in Baghdad ). Demonstrators smashed a doorway of the checkpoint, set burn to the reception area, left anti-american posters and sprayed anti-american graffito. U.S. president Trump accused Iran of orchestrating the attack. On 3 January 2020, amid rising tensions between the United States and Iran, the U.S. launched a drone strike on a convoy traveling near Baghdad International Airport, killing Qasem Soleimani, Iranian major general and Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps ( IRGC ) and Quds Force commanding officer, the moment most knock-down person of Iran ; [ 143 ] Abu Mahdi al-Muhandis, deputy commander of Iraq ‘s democratic mobilization Forces ( PMF or PMU ), four senior irani officers ; and four Iraqi officers. Following months of protests that broke out across Iraq in October 2019 and the resignation of Prime Minister Adel Abdul Mahdi and his cabinet, Mustafa Al Kadhimi became a leading rival for the Premiership. [ 144 ] On 9 April 2020, he was named by President Barham Salih as prime minister-designate, the third base person tapped to lead the area in good 10 weeks as it struggled to replace a politics that fell the year anterior after months of protests. Kadhimi was nominated by President Barham Salih, state television receiver reported, curtly after the previous delegate prime minister, Adnan al-Zurfi, announced he was withdrawing having failed to secure enough support to pass a government. [ 145 ]
geography
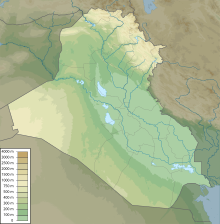 topography of Iraq. Iraq lies between latitudes 29° and 38° N, and longitudes 39° and 49° E ( a small sphere lies west of 39° ). Spanning 437,072 km2 ( 168,754 sq secret intelligence service ), it is the 58th-largest nation in the universe. It is comparable in size to the US express of California, and slightly larger than Paraguay. Near the two major rivers ( Euphrates and Tigris ) are fecund alluvial plains, as the rivers carry about 60,000,000 m3 ( 78,477,037 copper yd ) of silt per annum to the delta. rough deserts cover about 40 percentage of the kingdom. much of the south is boggy and damp. Another 30 percentage is mountainous with piercingly cold winters. The north of the country is by and large composed of mountains ; the highest point being at 3,611 thousand ( 11,847 foot ) distributor point, unnamed on the map opposite, but known locally as Cheekah Dar ( black camp ). Iraq has a small coastline measuring 58 kilometer ( 36 mi ) along the Persian Gulf. Close to the slide and along the Shatt al-Arab ( known as arvandrūd : اروندرود among Iranians ) there used to be marshlands, but many were drained in the 1990s. Iraq is home to seven terrestrial ecoregions : Zagros Mountains forest steppe, syrian xeric grasslands and shrublands, Tigris-Euphrates alluvial salt marsh, easterly Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests, Arabian Desert, Mesopotamian shrub desert, and South Iran Nubo-Sindian abandon and semi-desert. [ 146 ]
topography of Iraq. Iraq lies between latitudes 29° and 38° N, and longitudes 39° and 49° E ( a small sphere lies west of 39° ). Spanning 437,072 km2 ( 168,754 sq secret intelligence service ), it is the 58th-largest nation in the universe. It is comparable in size to the US express of California, and slightly larger than Paraguay. Near the two major rivers ( Euphrates and Tigris ) are fecund alluvial plains, as the rivers carry about 60,000,000 m3 ( 78,477,037 copper yd ) of silt per annum to the delta. rough deserts cover about 40 percentage of the kingdom. much of the south is boggy and damp. Another 30 percentage is mountainous with piercingly cold winters. The north of the country is by and large composed of mountains ; the highest point being at 3,611 thousand ( 11,847 foot ) distributor point, unnamed on the map opposite, but known locally as Cheekah Dar ( black camp ). Iraq has a small coastline measuring 58 kilometer ( 36 mi ) along the Persian Gulf. Close to the slide and along the Shatt al-Arab ( known as arvandrūd : اروندرود among Iranians ) there used to be marshlands, but many were drained in the 1990s. Iraq is home to seven terrestrial ecoregions : Zagros Mountains forest steppe, syrian xeric grasslands and shrublands, Tigris-Euphrates alluvial salt marsh, easterly Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests, Arabian Desert, Mesopotamian shrub desert, and South Iran Nubo-Sindian abandon and semi-desert. [ 146 ]
climate
Most of Iraq has a hot arid climate with subtropical influence. Summer temperatures average above 40 °C ( 104 °F ) for most of the area and frequently exceed 48 °C ( 118.4 °F ). Winter temperatures infrequently exceed 21 °C ( 69.8 °F ) with utmost approximately 15 to 19 °C ( 59.0 to 66.2 °F ) and night-time lows 2 to 5 °C ( 35.6 to 41.0 °F ). typically, haste is low ; most places receive less than 250 millimeter ( 9.8 in ) per annum, with maximum rain occurring during the winter months. Rainfall during the summer is highly rare, except in the army for the liberation of rwanda north of the area. The northern cragged regions have cold winters with casual heavy snows, sometimes causing across-the-board flood. Climate change in Iraq is leading to increasing temperatures, reduced precipitation, and increasing water scarcity which will likely have serious implications for the area for years to come. [ 147 ]
Read more: S.S. Lazio
Government and politics
The union politics of Iraq is defined under the current Constitution as a democratic, federal parliamentary democracy. The federal government is composed of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, angstrom well as numerous independent commissions. away from the federal politics, there are regions ( made of one or more governorates ), governorates, and districts within Iraq with legal power over assorted matters as defined by law. [ 1 ] The National Alliance is the main Shia parliamentary bloc, and was established as a result of a fusion of Prime Minister Nouri Maliki ‘s State of Law Coalition and the Iraqi National Alliance. [ 148 ] The Iraqi National Movement is led by Iyad Allawi, a profane Shia widely supported by Sunnis. The party has a more consistent anti-sectarian position than most of its rivals. [ 148 ] The Kurdistan List is dominated by two parties, the Kurdistan Democratic Party led by Masood Barzani and the Patriotic Union of Kurdistan headed by Jalal Talabani. Both parties are layman and delight close ties with the West. [ 148 ]
 see over Green Zone, which contains govermental headquarter and the united states army, in addition to containing the headquarters of the american embassy and the headquarters of foreign organizations and agencies for early countries. In 2008, according to the Failed States Index, Iraq was the earth ‘s eleventh most politically fluid nation. [ 149 ] [ 150 ] The concentration of office in the hands of Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki and growing atmospheric pressure on the opposition led to growing concern about the future of political rights in Iraq. [ 151 ] Nevertheless, advance was made and the country had risen to 11th identify by 2013. [ 152 ] In August 2014, al-Maliki ‘s reign came to an end. He announced on 14 August 2014 that he would stand aside sol that Haider Al-Abadi, who had been nominated just days early by newly installed President Fuad Masum, could take over. Until that point, al-Maliki had cling to might even asking the federal court to veto the president ‘s nomination describing it as a violation of the constitution. [ 153 ] Transparency International ranks Iraq ‘s government as the eighth-most-corrupt politics in the world. Government payroll have increased from 1 million employees under Saddam Hussein to around 7 million employees in 2016. In combination with decreased oil prices, the government budget deficit is near 25 % of GDP as of 2016. [ 154 ] Since the establishment of the no–fly zones following the Gulf War of 1990–1991, the Kurds established their own autonomous region. [ citation needed ]
see over Green Zone, which contains govermental headquarter and the united states army, in addition to containing the headquarters of the american embassy and the headquarters of foreign organizations and agencies for early countries. In 2008, according to the Failed States Index, Iraq was the earth ‘s eleventh most politically fluid nation. [ 149 ] [ 150 ] The concentration of office in the hands of Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki and growing atmospheric pressure on the opposition led to growing concern about the future of political rights in Iraq. [ 151 ] Nevertheless, advance was made and the country had risen to 11th identify by 2013. [ 152 ] In August 2014, al-Maliki ‘s reign came to an end. He announced on 14 August 2014 that he would stand aside sol that Haider Al-Abadi, who had been nominated just days early by newly installed President Fuad Masum, could take over. Until that point, al-Maliki had cling to might even asking the federal court to veto the president ‘s nomination describing it as a violation of the constitution. [ 153 ] Transparency International ranks Iraq ‘s government as the eighth-most-corrupt politics in the world. Government payroll have increased from 1 million employees under Saddam Hussein to around 7 million employees in 2016. In combination with decreased oil prices, the government budget deficit is near 25 % of GDP as of 2016. [ 154 ] Since the establishment of the no–fly zones following the Gulf War of 1990–1991, the Kurds established their own autonomous region. [ citation needed ]
law
In October 2005, the new Constitution of Iraq was approved in a referendum with a 78 % overall majority, although the share of support varying wide between the nation ‘s territories. [ 155 ] The new fundamental law was backed by the Shia and Kurdish communities, but was rejected by Arab Sunnis. Under the terms of the constitution, the nation conducted fresh nationally parliamentary elections on 15 December 2005. All three major heathen groups in Iraq voted along ethnic lines, as did Assyrian and Turcoman minorities. Law no. 188 of the year 1959 ( Personal Status Law ) [ 156 ] made polygamy extremely unmanageable, granted child custody to the mother in case of disassociate, prohibited repudiation and marriage under the historic period of 16. [ 157 ] Article 1 of Civil Code besides identifies Islamic law as a formal source of law. [ 158 ] Iraq had no Sharia courts but civil courts used Sharia for issues of personal status including marriage and divorce. In 1995 Iraq introduced Sharia punishment for certain types of condemnable offences. [ 159 ] The code is based on French civil law vitamin a well as Sunni and Jafari ( Shi’ite ) interpretations of Sharia. [ 160 ] In 2004, the CPA head executive L. Paul Bremer said he would veto any built-in conscription stating that shariah is the chief basis of law. [ 161 ] The announcement enraged many local anesthetic Shia clerics, [ 162 ] and by 2005 the United States had relented, allowing a character for shariah in the fundamental law to help end a stalemate on the gulp constitution. [ 163 ] The Iraqi Penal Code is the statutory law of Iraq .
military
Iraqi security forces are composed of forces serving under the Ministry of Interior ( which controls the Police and Popular Mobilization Forces ) and the Ministry of Defense, angstrom well as the Iraqi Counter Terrorism Bureau, reporting immediately to the Prime Minister of Iraq, which oversees the Iraqi Special Operations Forces. Ministry of Defense forces include the Iraqi Army, the Iraqi Air Force and the Iraqi Navy. The Peshmerga are a separate armed push firm to the Kurdistan Regional Government. The regional government and the cardinal government disagree as to whether they are under Baghdad ‘s authority and to what extent. [ 164 ] The Iraqi Army is an objective counter-insurgency force that as of November 2009 includes 14 divisions, each division consisting of 4 brigades. [ 165 ] It is described as the most significant component of the counter-insurgency fight. [ 166 ] Light infantry brigades are equipped with small arms, machine guns, RPGs, body armor and light armor vehicles. Mechanized infantry brigades are equipped with T-54/55 main conflict tanks and BMP-1 infantry fighting vehicles. [ 166 ] As of mid-2008, logistic problems included a maintenance crisis and ongoing issue problems. [ 167 ] The Iraqi Air Force is designed to support ground forces with surveillance, reconnaissance and troop lift. Two reconnaissance squadrons use light aircraft, three helicopter squadrons are used to move troops and one air department of transportation squadron uses C-130 transport aircraft to move troops, equipment, and supplies. It presently has 3,000 personnel. It is planned to increase to 18,000 personnel, with 550 aircraft by 2018. [ 166 ] The Iraqi Navy is a small force with 1,500 sailors and officers, including 800 Marines, designed to protect shoreline and inland waterways from insurgent percolation. The united states navy is besides creditworthy for the security of offshore anoint platforms. The united states navy will have coastal patrol squadrons, assault boat squadrons and a marine battalion. [ 166 ] The pull will consist of 2,000 to 2,500 sailors by year 2010. [ 168 ] On 4 November 2019, more than 100 australian Defence Force personnel left Darwin for the tenth rotation of Task Group Taji basis in north of Baghdad. The australian contingent mentors the Iraqi School of Infantry, where the Iraqi Security Forces are trained. however, Australia ‘s contribution was reduced from 250 to 120 ADF personnel, which along with New Zealand had trained over 45,000 ISF members before that. [ 169 ]
foreign relations
On 17 November 2008, the US and Iraq agreed to a Status of Forces Agreement, [ 170 ] as part of the broader Strategic Framework Agreement. [ 171 ] This agreement states “ the Government of Iraq requests ” US forces to temporarily remain in Iraq to “ maintain security and constancy ” and that Iraq has jurisdiction over military contractors, and US personnel when not on US bases or on–duty. On 12 February 2009, Iraq officially became the 186th State Party to the Chemical Weapons Convention. Under the provisions of this treaty, Iraq is considered a party with declare stockpiles of chemical weapons. Because of their recently accession, Iraq is the only State Party exempt from the existing timeline for end of their chemical weapons. specific criteria are in development to address the singular nature of Iraqi accession. [ 172 ] Iran–Iraq relations have flourished since 2005 by the exchange of high flat visits : Iraqi PM Nouri al-Maliki made frequent visits to Iran, along with Jalal Talabani visiting numerous times, to help boost bilateral co-operation in all fields. [ citation needed ] A conflict occurred in December 2009, when Iraq accused Iran of seizing an oil well on the border. [ 173 ] Relationships with Turkey are tense, largely because of the Kurdistan Regional Government, as clashes between Turkey and the PKK continue. [ 174 ] In October 2011, the Turkish parliament renewed a law that gives turkish forces the ability to pursue rebels over the boundary line in Iraq. ” [ 175 ] On 5 January 2020, the Iraqi parliament voted for a resolving power that urges the politics to work on expelling U.S. troops from Iraq. The resolution was passed two days after a U.S. drone strike that killed iranian Major General Qasem Soleimani of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps and commanding officer of the Quds Force. The resolution specifically calls for ending of a 2014 agreement allowing Washington to help Iraq against Islamic State groups by sending troops. [ 176 ] This resolution will besides signify ending an agreement with Washington to station troops in Iraq as Iran vows to retaliate after the kill. [ 177 ] On 28 September 2020, Washington made preparations to withdraw diplomats from Iraq, as a result of Iranian-backed militias firing rockets at the american Embassy in Baghdad. The officials said that the motion was seen as an escalation of US ’ confrontation with Iran. [ 178 ]
Human rights
Relations between Iraq and its kurdish population have been sour in holocene history, particularly with Saddam Hussein ‘s genocidal crusade against them in the 1980s. After uprisings during the early 90s, many Kurds fled their fatherland and no-fly zones were established in northerly Iraq to prevent more conflicts. Despite historically poor relations, some progress has been made, and Iraq elected its first Kurdish president of the united states, Jalal Talabani, in 2005. Furthermore, Kurdish is now an official linguistic process of Iraq alongside Arabic according to Article 4 of the Constitution. [ 1 ] LGBT rights in Iraq remain circumscribed. Although legalize, homosexuality remains stigmatised in Iraqi society. [ 179 ]
administrative divisions
 administrative districts of Iraq Iraq is composed of nineteen governorates ( or provinces ) ( arabic : muhafadhat ( singular muhafadhah ) ; kurdish : پارێزگا Pârizgah ). The governorates are subdivided into districts ( or qadhas ), which are further divided into sub-districts ( or nawāḥī ). Kurdistan Region ( Erbil, Dohuk, Sulaymaniyah and Halabja ) is the merely legally defined region within Iraq, with its own politics and quasi-official army Peshmerga .
administrative districts of Iraq Iraq is composed of nineteen governorates ( or provinces ) ( arabic : muhafadhat ( singular muhafadhah ) ; kurdish : پارێزگا Pârizgah ). The governorates are subdivided into districts ( or qadhas ), which are further divided into sub-districts ( or nawāḥī ). Kurdistan Region ( Erbil, Dohuk, Sulaymaniyah and Halabja ) is the merely legally defined region within Iraq, with its own politics and quasi-official army Peshmerga .
economy
 agribusiness is the independent occupation of the people. Iraq ‘s economy is dominated by the oil sector, which has traditionally provided about 95 % of foreign switch over earnings. The lack of exploitation in other sectors has resulted in 18 % –30 % unemployed and a per head GDP of $ 4,000. [ 2 ] Public sector use accounted for about 60 % of full-time employment in 2011. [ 180 ] The anoint export diligence, which dominates the Iraqi economy, generates very fiddling use. [ 180 ] Currently only a modest share of women ( the highest estimate for 2011 was 22 % ) enter in the labor pull. [ 180 ] anterior to US occupation, Iraq ‘s centrally planned economy prohibited extraneous ownership of Iraqi businesses, ran most large industries as state-owned enterprises, and imposed bombastic tariffs to keep out alien goods. [ 181 ] After the 2003 invasion of Iraq, the Coalition Provisional Authority quickly began issuing many binding orders privatising Iraq ‘s economy and opening it up to foreign investing. On 20 November 2004, the Paris Club of creditor nations agreed to write off 80 % ( $ 33 billion ) of Iraq ‘s $ 42 billion debt to Club members. Iraq ‘s full external debt was around $ 120 billion at the time of the 2003 invasion, and had grown another $ 5 billion by 2004. The debt relief will be implemented in three stages : two of 30 % each and one of 20 %. [ 182 ] The official currency in Iraq is the Iraqi tunisian dinar. The Coalition Provisional Authority issued new iraqi dinar coins and notes, with the notes printed by De La Rue using advanced anti-forgery techniques. [ 183 ] Jim Cramer ‘s 20 October 2009 endorsement of the Iraqi algerian dinar on CNBC has far piqued interest in the investment. [ 184 ] Five years after the invasion, an estimated 2.4 million people were internally displaced ( with a far two million refugees outside Iraq ), four million Iraqis were considered food-insecure ( a quarter of children were chronically malnourished ) and lone a third base of Iraqi children had access to safe drink water. [ 185 ] According to the Overseas Development Institute, international NGOs face challenges in carrying out their mission, leaving their aid “ piecemeal and largely conducted clandestine, hindered by insecurity, a miss of organize fund, express operational capacity and patchy information ”. [ 185 ] International NGOs have been targeted and during the first 5 years, 94 aid workers were killed, 248 hurt, 24 arrested or detained and 89 kidnapped or abducted. [ 185 ]
agribusiness is the independent occupation of the people. Iraq ‘s economy is dominated by the oil sector, which has traditionally provided about 95 % of foreign switch over earnings. The lack of exploitation in other sectors has resulted in 18 % –30 % unemployed and a per head GDP of $ 4,000. [ 2 ] Public sector use accounted for about 60 % of full-time employment in 2011. [ 180 ] The anoint export diligence, which dominates the Iraqi economy, generates very fiddling use. [ 180 ] Currently only a modest share of women ( the highest estimate for 2011 was 22 % ) enter in the labor pull. [ 180 ] anterior to US occupation, Iraq ‘s centrally planned economy prohibited extraneous ownership of Iraqi businesses, ran most large industries as state-owned enterprises, and imposed bombastic tariffs to keep out alien goods. [ 181 ] After the 2003 invasion of Iraq, the Coalition Provisional Authority quickly began issuing many binding orders privatising Iraq ‘s economy and opening it up to foreign investing. On 20 November 2004, the Paris Club of creditor nations agreed to write off 80 % ( $ 33 billion ) of Iraq ‘s $ 42 billion debt to Club members. Iraq ‘s full external debt was around $ 120 billion at the time of the 2003 invasion, and had grown another $ 5 billion by 2004. The debt relief will be implemented in three stages : two of 30 % each and one of 20 %. [ 182 ] The official currency in Iraq is the Iraqi tunisian dinar. The Coalition Provisional Authority issued new iraqi dinar coins and notes, with the notes printed by De La Rue using advanced anti-forgery techniques. [ 183 ] Jim Cramer ‘s 20 October 2009 endorsement of the Iraqi algerian dinar on CNBC has far piqued interest in the investment. [ 184 ] Five years after the invasion, an estimated 2.4 million people were internally displaced ( with a far two million refugees outside Iraq ), four million Iraqis were considered food-insecure ( a quarter of children were chronically malnourished ) and lone a third base of Iraqi children had access to safe drink water. [ 185 ] According to the Overseas Development Institute, international NGOs face challenges in carrying out their mission, leaving their aid “ piecemeal and largely conducted clandestine, hindered by insecurity, a miss of organize fund, express operational capacity and patchy information ”. [ 185 ] International NGOs have been targeted and during the first 5 years, 94 aid workers were killed, 248 hurt, 24 arrested or detained and 89 kidnapped or abducted. [ 185 ]
vegetable oil and energy
With its 143.1 billion barrels ( 2.275×1010 m3 ) of proved oil reserves, Iraq ranks third base in the world behind Venezuela and Saudi Arabia in the sum of anoint reserves. [ 186 ] [ 187 ] Oil production levels reached 3.4 million barrels per sidereal day by December 2012. [ 188 ] only about 2,000 vegetable oil wells have been drilled in Iraq, compared with approximately 1 million wells in Texas alone. [ 189 ] Iraq was one of the founding members of OPEC. [ 190 ] [ 191 ] During the 1970s Iraq produced up to 3.5 million barrels per day, but sanctions imposed against Iraq after its invasion of Kuwait in 1990 crippled the nation ‘s petroleum sector. The sanctions prohibited Iraq from exporting petroleum until 1996 and Iraq ‘s output declined by 85 % in the years following the First Gulf War. The sanctions were lifted in 2003 after the US-led invasion removed Saddam Hussein from baron, but development of Iraq ‘s petroleum resources has been hampered by the ongoing dispute. [ 192 ] As of 2010, despite improved security and billions of dollars in oil tax income, Iraq even generates about half the electricity that customers demand, leading to protests during the hot summer months. [ 193 ] The Iraq anoint jurisprudence, a proposed patch of legislation submitted to the Council of Representatives of Iraq in 2007, has failed to gain blessing due to disagreements among Iraq ‘s versatile political bloc. [ 194 ] [ 195 ] According to a US Study from May 2007, between 100,000 barrels per day ( 16,000 m3/d ) and 300,000 barrels per day ( 48,000 m3/d ) of Iraq ‘s declare petroleum production over the past four years could have been siphoned off through corruption or smuggling. [ 196 ] In 2008, Al Jazeera reported $ 13 billion of Iraqi oil revenues in US care was improperly accounted for, of which $ 2.6 billion is wholly unaccounted for. [ 197 ] Some reports that the government has reduced corruption in public procurement of petroleum ; however, reliable reports of bribery and kickbacks to government officials persist. [ 198 ] In June 2008, the Iraqi Oil Ministry announced plans to go ahead with humble one- or biennial no-bid contracts to ExxonMobil, Shell, Total and BP —once partners in the Iraq Petroleum Company —along with Chevron and smaller firms to service Iraq ‘s largest fields. [ 199 ] These plans were cancelled in September because negotiations had stalled for indeed long that the oeuvre could not be completed within the fourth dimension frame, according to Iraqi petroleum minister Hussain al-Shahristani. several United States senators had besides criticised the conduct, arguing it was hindering efforts to pass the hydrocarbon law. [ 200 ] On 30 June and 11 December 2009, the Iraqi ministry of anoint awarded service contracts to external vegetable oil companies for some of Iraq ‘s many oil fields. [ 201 ] [ 202 ] Oil fields contracted include the “ super-giant ” Majnoon oil battlefield, Halfaya Field, West Qurna Field and Rumaila Field. [ 202 ] BP and China National Petroleum Corporation won a bargain to develop Rumaila, the largest iraqi vegetable oil plain. [ 203 ] [ 204 ] On 14 March 2014, the International Energy Agency said Iraq ‘s vegetable oil end product jumped by half a million barrels a day in February to average 3.6 million barrels a day. The country had not pumped that much oil since 1979, when Saddam Hussein rose to power. [ 205 ] however, on 14 July 2014, as sectarian strife had taken hold, Kurdistan Regional Government forces seized manipulate of the Bai Hassan and Kirkuk oilfields in the north of the area, taking them from Iraq ‘s control. Baghdad condemned the seizure and threatened “ awful consequences ” if the fields were not returned. [ 206 ] The UN estimates that petroleum accounts for 99 % of Iraq ‘s gross. [ 192 ]
Water provide and sanitation
Water issue and sanitation in Iraq is characterized by poor water and service quality. Three decades of war, combined with specify environmental awareness, have destroyed Iraq ‘s body of water resources management system. Access to potable water differs significantly among governorates and between urban and rural areas. 91 % of the integral population has access to drinkable body of water. But in rural areas, merely 77 % of the population has access to improved drink in water sources compared to 98 % in urban areas. [ 207 ] Large amounts of water are wasted during product. [ 207 ]
infrastructure
Although many infrastructure projects are afoot, Iraq remains in deep house crisis, with the war-ravaged country probably to complete only 5 percentage of the 2.5 million homes it needs to build by 2016 to keep up with demand, the Minister for Construction and Housing said in September 2013. [ 208 ]
Demographics
The 2018 estimate of the full Iraqi population is 38,433,600. [ 209 ] [ 210 ] Iraq ‘s population was estimated to be 2 million in 1878. [ 211 ] In 2013 Iraq ‘s population reached 35 million amid a post-war population boom. [ 212 ]
heathen groups

Sunni Arabs
Shiite Arabs
Sunni Kurds
Assyrians
Yazidi Kurds
Turkmen Iraq ‘s native population is predominantly arab, but besides includes other heathen groups such as Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Yazidis, Shabaks, Armenians, Sabian-Mandaeans, Circassians, and Kawliya. A report by the European Parliamentary Research Service suggests that, in 2015, there were 24 million Arabs ( 14 million Shia and 9 million Sunni ) ; 4.7 million Sunni Kurds ( plus 500,000 Faili Kurds and 200,000 Kaka’i ) ; 3 million ( by and large Sunni ) Iraqi Turkmens ; 1 million Black Iraqis ; 500,000 Christians ( including Chaldeans, Syriacs, Assyrians and Armenians ) ; 500,000 Yazidis ; 250,000 Shabaks ; 50,000 Roma ; 3,000 Sabian-Mandaeans ; 2,000 Circassians ; 1,000 of the Baháʼí Faith ; and a few twelve Jews. [ 213 ] According to the CIA World Factbook, citing a 1987 Iraqi government estimate, [ 2 ] the population of Iraq is 75–80 % Arab followed by 15 % Kurds. [ 2 ] In addition, the estimate claims that other minorities form 5 % of the country ‘s population, including the Turkmen/Turcoman, Assyrians, Yezidis, Shabak, Kaka’i, Bedouins, Roma, Circassians, Sabian-Mandaeans, and Persians. [ 2 ] however, the International Crisis Group points out that figures from the 1987 census, angstrom well as the 1967, 1977, and 1997 censuses, “ are all considered highly baffling, due to suspicions of government handling ” because Iraqi citizens were lone allowed to indicate belong to either the arab or Kurdish ethnic groups ; [ 214 ] consequently, this skewed the numeral of other heathen minorities, such as Iraq ‘s third largest ethnic group – the Turkmens. [ 214 ] Around 20,000 Marsh Arabs live in southern Iraq. [ 215 ] Iraq has a community of 2,500 Chechens, [ 216 ] and some 20,000 Armenians. [ 217 ] In southerly Iraq, there is a community of Iraqis of African origin, a bequest of the slavery practised in the Islamic Caliphate beginning before the Zanj Rebellion of the ninth hundred, and Basra ‘s character as a key larboard. [ 68 ] It is the most populous state in the arabian Plate. [ 218 ]
Languages
The independent languages spoken in Iraq are Mesopotamian Arabic and Kurdish, followed by the Iraqi Turkmen/Turkoman dialect of Turkish, and the Neo-Aramaic languages ( specifically Chaldean and Assyrian ). [ 219 ] Arabic and Kurdish are written with versions of the Arabic script. Since 2005, the Turkmen/Turkoman have switched from the Arabic script to the turkish alphabet. [ 220 ] In addition, the Neo-Aramaic languages use the Syriac script. other smaller minority languages include Mandaic, Shabaki, Armenian, Circassian and Persian. prior to the invasion in 2003, Arabic was the exclusive official speech. Since the new Constitution of Iraq was approved in 2005, both Arabic and Kurdish are recognized ( Article 4 ) as official languages of Iraq, while three other languages : Turkmen, Syriac and Armenian, are besides recognized as minority languages. In addition, any area or state may declare other languages official if a majority of the population approves in a cosmopolitan referendum. [ 1 ] According to the Constitution of Iraq ( Article 4 ) :
- The Arabic language and the Kurdish language are the two official languages of Iraq. The right of Iraqis to educate their children in their mother tongue, such as Turkmen, Syriac, and Armenian shall be guaranteed in government educational institutions in accordance with educational guidelines, or in any other language in private educational institutions.[1]
Urban areas
religion
Religions in Iraq are dominantly Abrahamic religions with the CIA World Factbook ( 2021 ) stating ; that 95–98 % were Muslim ( Shia 64–69 %, Sunni 29–34 % ), christian < 0.1 %, Yazidi < 0.1 %, Sabian-Mandaean < 0.1 %, Baháʼí < 0.1 %, zoroastrian < 0.1 %, Hindu < 0.1 %, Buddhist < 0.1 %, Jewish < 0.1 %, tribe religion < 0.1, unaffiliated 0.1 %, other < 0.1 % [ 2 ] It has a assorted Shia and Sunni population. An older 2011 Pew Research Center estimates that 47~51 % of Muslims in Iraq see themselves as Shia, 42 % are Sunni, while 5 % identify themselves as `` Just a Muslim ''. [ 223 ] The Sunni population complains of facing discrimination in about all aspects of life by the government. however, former Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki denied that such discrimination occurs. [ 224 ] christendom in Iraq has its roots from the concept of the Church of the East in the fifth century AD, predating the universe of Islam in the region. Christians in Iraq are predominantly native Assyrians belonging to the Ancient Church of the East, Assyrian Church of the East, Chaldean Catholic Church, Syriac Catholic Church and Syriac Orthodox Church. There is besides a significant population of armenian Christians in Iraq who had fled Turkey during the armenian genocide. Christians numbered over 1.4 million in 1987 or 8 % of the calculate population of 16.3 million and 550,000 in 1947 or 12 % of the population of 4.6 millions. [ 225 ] After the 2003 invasion of Iraq, violence against Christians rose, with reports of abduction, torture, bombings, and killings. [ 226 ] The post-2003 Iraq War have displaced much of the remaining Christian community from their fatherland as a consequence of cultural and religious persecution at the hands of Islamic extremists. [ 227 ] [ 228 ] [ 229 ] [ 230 ] [ 231 ] [ 232 ] There are besides small ethno-religious minority populations of Sabian-Mandaeans, Shabaks, Yarsan and Yezidis remaining. Prior to 2003 their numbers together may have been 2 million, the majority Yarsan, a non-Islamic religion with roots in pre-Islamic and pre-christian religion. The Iraqi Jewish community, numbering about 150,000 in 1941, has about wholly left the country. [ 233 ] Iraq is home to two of the universe 's holy places among Shi'as : Najaf and Karbala. [ 234 ]
Diaspora and refugees
The distribution of native Iraqis to other countries is known as the Iraqi diaspora. The UN High Commission for Refugees has estimated that about two million Iraqis fled the country after the multinational invasion of Iraq in 2003. [ 235 ] The UN Refugee agency estimated in 2021 that an 1.1 million were displaced within the area. [ 236 ] In 2007, the UN said that about 40 % of Iraq ‘s center class was believed to have fled and that most had fled taxonomic persecution and had no desire to return. [ 237 ] Refugees are mired in poverty as they are generally barred from working in their horde countries. [ 238 ] [ 239 ] Subsequently, the diaspora seemed to be returning, as security improved ; the Iraqi government claimed that 46,000 refugees returned to their homes in October 2007 alone. [ 240 ] As of 2011, about 3 million Iraqis had been displaced, with 1.3 million within Iraq and 1.6 million in neighbouring countries, chiefly Jordan and Syria. [ 241 ] More than half of Iraqi Christians had fled the country since the 2003 US-led invasion. [ 242 ] [ 243 ] According to official United States Citizenship and Immigration Services statistics, 58,811 Iraqis had been granted refugee-status citizenship as of 25 May 2011. [ 244 ] After the start of the syrian Civil War in 2011, numerous Iraqi refugees in Syria returned to their native country. [ 245 ] To escape the civil war, over 160,000 syrian refugees of varying ethnicities have fled to Iraq since 2012. [ 246 ]
Health
In 2010, spending on healthcare accounted for 6.84 % of the nation ‘s GDP. In 2008, there were 6.96 physicians and 13.92 nurses per 10,000 inhabitants. [ 247 ] The life anticipation at parturition was 68.49 years in 2010, or 65.13 years for males and 72.01 years for females. [ 248 ] This is down from a bill life anticipation of 71.31 years in 1996. [ 249 ] Iraq had developed a centralized free health care system in the 1970s using a hospital based, capital-intensive model of remedy manage. The state depended on large-scale imports of medicines, aesculapian equipment and even nurses, paid for with oil export income, according to a “ determine brief ” report issued jointly by the United Nations Children ‘s Fund ( UNICEF ) and the World Health Organization ( WHO ) in July 2003. Unlike early poor countries, which focused on mass health care using primary coil wish practitioners, Iraq developed a Westernized system of sophisticate hospitals with advance medical procedures, provided by specialist physicians. The UNICEF/WHO report noted that prior to 1990, 97 % of the urban dwellers and 71 % of the rural population had access to free primary health concern ; equitable 2 % of hospital beds were privately managed. [ 250 ]
education
Before Iraq faced economic sanctions from the UN, it already had an advanced and successful Arab department of education system. [ 251 ] however, it has immediately been “ de-developing ” in its educational success. [ 251 ] Some say that the sanctions, whether intentionally or not, hurt the education arrangement because of how it affected the children. [ 251 ] Whether or not this is true, UNICEF ‘s statistics and numbers show how Iraq ‘s education system has room for improvement. [ 252 ] At the turn of the millennium, many countries, including Iraq, attempted to take part in the Millennium Development Goals as a way to help underdeveloped countries prosper. In Iraq, one of the goals was for education to be universally available for both boys and girls at the basal flat. UNICEF collected several pieces of data that indicate whether or not, Iraq has been accomplishing
this goal. [ 252 ] In general, the department of education of Iraq has been improving since the MDGs were implemented. [ 252 ] For model, registration numbers closely doubled from 2000 to 2012. [ 252 ] It went from 3.6 million to six million. [ 252 ] The latest statistic from 2015 to 2016 showed that about 9.2 million children were in school. [ 252 ] Enrollment rates continue to be on a sweetheart increase at about 4.1 % each year. [ 252 ] The bluff addition in numbers shows that there are distinctly improvements of children in Iraq having access to education. however, the dramatic increase of the number of students in basal department of education has had some negative and distortion effects for the department of education system. [ 252 ] The budget for education makes up about only 5.7 % of politics spending and continues to stay at or below this share. [ 252 ] Investments for schools has besides been on the descent. [ 252 ] As a resultant role, the country now ranks at the bottom of Middle East countries in terms of education. [ 252 ] The little fund for department of education makes it more unmanageable to improve the timbre and resources for department of education. [ 252 ] At the same time, UNICEF investigated portions of spending for education and found that some of the money has gone to waste. [ 252 ] They found that dropout rates are increasing deoxyadenosine monophosphate well as repetition rates for children. [ 252 ] In both Iraq Centre and KRI, the rates for dropouts are about 1.5 % to 2.5 %. [ 252 ] Within these dropout rates, there is besides an spotty number among boys and girls who dropout. [ 252 ] While the pace for dropouts for male child was around 16.5 %, girls were at 20.1 % where it could be due to economic or family reasons. [ 252 ] For repeat rates, percentages have about reached 17 % among all students. [ 252 ] To put the money passing in perspective, about $ 1,100 is spent on each scholar. [ 252 ] For each student who drops out or repeats a grade, $ 1,100 is lost. [ 252 ] As a leave, about 20 % of the fund for education was lost to dropouts and repeat for the class 2014–2015. [ 252 ] many of those people who dropout or have to repeat a grade do not see the economic price for long term results. [ 252 ] UNICEF takes note of how quell in school can in fact, increase wealth for the person and their family. [ 252 ] While it may put a tenor on the education system, it will besides hinder the chances of a person receiving higher earnings in whatever career they go into. [ 252 ] early statistics show that regional differences can attribute to lower or higher registration rates for children in primary education. [ 252 ] For exemplar, UNICEF found that areas with conflict like Salah al-Din have “ more than 90 % of school-age children ” not in the education system. [ 252 ] In addition, some schools were converted into refugee shelters or military bases in 2014 as conflict began to increase. [ 253 ] The resources for education become more strain and make it harder for children to go to educate and finish receiving their education. [ 253 ] however, in 2017, there were efforts being made to open up 47 schools that had previously been closed. [ 254 ] There has been more success in Mosul where over 380,000 are going to school again. [ 254 ] Depending on where children live, they may or may not have the same access to education as other children. There are besides the differing registration rates between boys and girls. [ 252 ] UNICEF found that in 2013–2014, registration numbers for male child was at about five million while girls were at about 4.2 million. [ 252 ] While the out-of-school rate for girl is at about 11 %, boys are at less than half of that. [ 252 ] There is distillery a opening between boys and girls in terms of educational opportunities. [ 252 ] however, the rate of enrollments for girl has been increasing at a higher rate than for boys. [ 252 ] In 2015–2016, the registration numbers for girls increased by 400,000 from the former year where a big total of them were located in Iraq Centre. [ 252 ] not only that, UNICEF found that the increase of girls going to school was across all levels of education. [ 252 ] Therefore, the inadequate registration numbers between boys and girls could potentially change so that universal education can be achieved by all at equal rates. Although the numbers suggest a dramatic increase of registration rates for primary education in total, a large number of children still remain out of the education organization. [ 252 ] Many of these children drop under the category of internally preempt children due to the conflict in Syria and the takeover by ISIL. [ 252 ] This causes a disturbance for children who are attempting to go to school and holds them back from completing their education, no matter what level they are at. [ 252 ] Internally displaced children are specifically recorded to track children who have been forced to move within their state due to these types of conflicts. About 355,000 of internally displaced children are not in the department of education system. [ 252 ] 330,000 of those children live in Iraq Centre. [ 252 ] The rates among internally displaced children continue to remain higher in Iraq Centre than other areas such as the KRI. [ 252 ]
 University students in Iraq, 2016 With the overall increase of registration rates, there continues to be a boastfully puree on the resources for education. [ 252 ] UNICEF notes that without an increase on expenditures for education, the quality of department of education will continue to decrease. [ 252 ] early in the 2000s, the UNESCO International Bureau of Education found that the education system in Iraq had issues with standard-built school buildings, having adequate teachers, implementing a standardized course of study, textbooks and technologies that are needed to help reach its educational goals. [ 251 ] Teachers are significant resources that are starting to become more and more tense with the rising phone number of students. [ 252 ] Iraq Centre has a faster registration growth rate than teacher growth. [ 252 ] Teachers begin to have to take in more and more students which can produce a bigger strain on the teacher and quality of education the children receive. [ 252 ] Another large resource for department of education is libraries that can increase literacy and create a read culture. [ 255 ] however, this can merely be improved through a restructure of the education organization. [ 255 ] UNICEF provides more details, regarding the actions needed to help Iraq reach its MDG goal of department of education being attainable by all children at the chief level. [ 252 ] much of it has to do with the restructure of the education system, research into improving the quality of education, and discovering ways on how to better become the needs of girls and children with disabilities in the education system. [ 252 ] The CIA World Factbook estimates that, in 2000, the adult literacy rate was 84 % for males and 64 % for females, with UN figures suggesting a small fall in literacy of Iraqis aged 15–24 between 2000 and 2008, from 84.8 % to 82.4 %. [ 256 ]
University students in Iraq, 2016 With the overall increase of registration rates, there continues to be a boastfully puree on the resources for education. [ 252 ] UNICEF notes that without an increase on expenditures for education, the quality of department of education will continue to decrease. [ 252 ] early in the 2000s, the UNESCO International Bureau of Education found that the education system in Iraq had issues with standard-built school buildings, having adequate teachers, implementing a standardized course of study, textbooks and technologies that are needed to help reach its educational goals. [ 251 ] Teachers are significant resources that are starting to become more and more tense with the rising phone number of students. [ 252 ] Iraq Centre has a faster registration growth rate than teacher growth. [ 252 ] Teachers begin to have to take in more and more students which can produce a bigger strain on the teacher and quality of education the children receive. [ 252 ] Another large resource for department of education is libraries that can increase literacy and create a read culture. [ 255 ] however, this can merely be improved through a restructure of the education organization. [ 255 ] UNICEF provides more details, regarding the actions needed to help Iraq reach its MDG goal of department of education being attainable by all children at the chief level. [ 252 ] much of it has to do with the restructure of the education system, research into improving the quality of education, and discovering ways on how to better become the needs of girls and children with disabilities in the education system. [ 252 ] The CIA World Factbook estimates that, in 2000, the adult literacy rate was 84 % for males and 64 % for females, with UN figures suggesting a small fall in literacy of Iraqis aged 15–24 between 2000 and 2008, from 84.8 % to 82.4 %. [ 256 ]
culture
 Al-Mutanabi, regarded as one of the greatest, most prominent and influential poets in the Arabic language, much of his work has been translated into over 20 languages worldwide Iraq ‘s art has a deep inheritance that extends second in time to ancient Mesopotamian art. Iraq has one of the longest written traditions in the world including architecture, literature, music, dance, painting, weaving, pottery, calligraphy, stonemasonry and metalworking. For centuries, the capital, Baghdad was the Medieval kernel of the literary and artistic Arab universe, but its artistic traditions suffered at the hands of the Mongol invaders in the thirteenth century. Baghdad evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in summation to house several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, ampere well as hosting a multiethnic and multireligious environment, garnered the city a global repute as the “ Centre of Learning ”. [ 257 ]
Al-Mutanabi, regarded as one of the greatest, most prominent and influential poets in the Arabic language, much of his work has been translated into over 20 languages worldwide Iraq ‘s art has a deep inheritance that extends second in time to ancient Mesopotamian art. Iraq has one of the longest written traditions in the world including architecture, literature, music, dance, painting, weaving, pottery, calligraphy, stonemasonry and metalworking. For centuries, the capital, Baghdad was the Medieval kernel of the literary and artistic Arab universe, but its artistic traditions suffered at the hands of the Mongol invaders in the thirteenth century. Baghdad evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in summation to house several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, ampere well as hosting a multiethnic and multireligious environment, garnered the city a global repute as the “ Centre of Learning ”. [ 257 ]
music
Iraq is known primarily for its rich people maqam inheritance which has been passed down orally by the masters of the maqam in an unbroken chain of transmission leading up to the present. The maqam al-Iraqi is considered to be the most baronial and perfect form of maqam. Al-maqam al-Iraqi is the collection of sing poems written either in one of the sixteen meters of classical Arabic or in Iraqi dialect ( Zuhayri ). [ 258 ] This form of artwork is recognised by UNESCO as “ an intangible inheritance of world ”. [ 259 ] early in the twentieth hundred, many of the most outstanding musicians in Iraq were Jewish. [ 260 ] In 1936, Iraq Radio was established with an ensemble made up entirely of Jews, with the exception of the percussion player. At the cabaret of Baghdad, ensembles consisted of oud, qanun and two percussionists, while the like format with a ney and cello were used on the radio. [ 260 ] The most celebrated singer of the 1930s–1940s was possibly the Jew Salima Pasha ( late Salima Murad ). [ 260 ] [ 261 ] The obedience and adoration for Pasha were unusual at the time since populace performance by women was considered black, and most female singers were recruited from brothels. [ 260 ] The most celebrated early composer from Iraq was Ezra Aharon, an oud player, while the most outstanding musician was Daoud Al-Kuwaiti. [ citation needed ] Daoud and his brother Saleh formed the official ensemble for the Iraqi radio station and were creditworthy for introducing the cello and ney into the traditional ensemble. [ 260 ]
art and architecture
important cultural institutions in the capital include the Iraqi National Symphony Orchestra – rehearsals and performances were briefly interrupted during the Occupation of Iraq but have since returned to normal. The National Theatre of Iraq was looted during the 2003 invasion, but efforts are afoot to restore it. The hot field scene received a promote during the 1990s when UN sanctions limited the consequence of alien films. deoxyadenosine monophosphate many as 30 film were reported to have been converted to survive stages, producing a wide range of comedies and dramatic productions. Institutions offering cultural education in Baghdad include the Academy of Music, Institute of Fine Arts and the Music and Ballet school Baghdad. Baghdad besides features a number of museums including the National Museum of Iraq – which houses the world ‘s largest and finest collection of artefacts and relics of Ancient Iraqi civilisations ; some of which were stolen during the Occupation of Iraq .
 Zaha Hadid was an Iraqi architect, artist and designer, recognised as a major figure in architecture of the late 20th and early 21st centuries. She is known for being influenced by Sumerian ancient cities. The capital, Ninus or Nineveh, was taken by the Medes under Cyaxares, and some 200 years after xenophon passed over its site, then mere mounds of ground. It remained buried until 1845, when Botta and Layard discovered the ruins of the assyrian akkadian cities. The principal remains are those of Khorsabad, 16 kilometer ( 10 nautical mile ) N.E. of Mosul ; of Nimroud, supposed to be the ancient Calah ; and of Kouyunjik, in all probability the ancient Nineveh. In these cities are found fragments of several great buildings which seem to have been palace-temples. They were constructed chiefly of sun-dried bricks, and all that remains of them is the lower separate of the walls, decorated with sculpt and paintings, portions of the pavements, a few indications of the acme, and some concern works connected with the drain .
Zaha Hadid was an Iraqi architect, artist and designer, recognised as a major figure in architecture of the late 20th and early 21st centuries. She is known for being influenced by Sumerian ancient cities. The capital, Ninus or Nineveh, was taken by the Medes under Cyaxares, and some 200 years after xenophon passed over its site, then mere mounds of ground. It remained buried until 1845, when Botta and Layard discovered the ruins of the assyrian akkadian cities. The principal remains are those of Khorsabad, 16 kilometer ( 10 nautical mile ) N.E. of Mosul ; of Nimroud, supposed to be the ancient Calah ; and of Kouyunjik, in all probability the ancient Nineveh. In these cities are found fragments of several great buildings which seem to have been palace-temples. They were constructed chiefly of sun-dried bricks, and all that remains of them is the lower separate of the walls, decorated with sculpt and paintings, portions of the pavements, a few indications of the acme, and some concern works connected with the drain .
Media
After the end of the entire state control in 2003, there were a period of significant emergence in the broadcast media in Iraq. immediately, and the ban on satellite dishes is no longer in put, and by mid-2003, according to a BBC report, there were 20 radio receiver stations from 0.15 to 17 television stations owned by Iraqis, and 200 Iraqi newspapers owned and operated. significantly, there have been many of these newspapers in numbers disproportionate to the population of their locations. For case, in Najaf, which has a population of 300,000, is being published more than 30 newspapers and distributed. Iraqi media adept and author of a number of reports on this topic, Ibrahim Al Marashi, identifies four stages of the US invasion of Iraq in 2003 where they had been taking the steps that have meaning effects on the manner for the later of the Iraqi media since then. Stages are : pre-invasion training, and the war and the actual option of targets, the inaugural post-war period, and a growing insurgency and hand over ability to the Iraqi Interim Government ( IIG ) and Prime Minister Iyad Allawi. [ 262 ] [ page needed ]
cuisine
Iraqi cuisine can be traced back some 10,000 years – to the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, Assyrians and Ancient Persians. [ 263 ] Tablets found in ancient ruins in Iraq show recipes prepared in the temples during religious festivals – the first cookbook in the global. [ 263 ] Ancient Iraq, or Mesopotamia, was home to many sophisticated and highly advance civilisations, in all fields of cognition – including the culinary arts. [ 263 ] however, it was in the medieval era when Baghdad was the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate that the Iraqi kitchen reached its zenith. [ 263 ] Today the cuisine of Iraq reflects this rich inheritance angstrom well as hard influences from the culinary traditions of neighbouring Turkey, Iran and the Greater Syria area. [ 263 ] Some characteristic ingredients of Iraqi cuisine include – vegetables such as eggplant, tomato, okra, onion, potato, zucchini, garlic, peppers and chili, cereals such as rice, bulgur pale yellow and barley, pulses and legumes such as lentils, chickpeas and cannellini, fruits such as dates, raisins, apricots, figs, grapes, melon, pomegranate and citrus fruits, specially gamboge and lime. [ 263 ] similarly with other countries of western Asia, chicken and specially lamb are the favored meats. Most dishes are served with rice – normally Basmati, grown in the marshes of southern Iraq. [ 263 ] Bulgur pale yellow is used in many dishes – having been a staple in the country since the days of the Ancient Assyrians. [ 263 ]
sport
football is the most popular sport in Iraq. Football is a considerable union gene in Iraq following years of war and agitation. basketball, naiant, weight-lift, bodybuilding, box, kick box and tennis are besides popular sports. The Iraqi Football Association is the governing consistency of football in Iraq, controlling the Iraq national football team and the Iraqi Premier League. It was founded in 1948, and has been a member of FIFA since 1950 and the Asian Football Confederation since 1971. Iraq were the 2007 AFC asian Cup champions after defeating Saudi Arabia in the final examination by 1–0 thanks to a goal by captain Younis Mahmoud and they have participated in two FIFA competitions ( the 1986 FIFA World Cup and the 2009 FIFA Confederations Cup ) .
See besides
References
bibliography
farther understand
Government
General information
Read more: Real Sociedad
