This article is about the capital city of England and the United Kingdom. For early uses, see London ( disambiguation )
capital city and megacity in England
Reading: London – Wikipedia
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom. It stands on the River Thames in southeast England at the head of a 50-mile ( 80 kilometer ) estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major colony for two millennium. [ 9 ] The City of London, its ancient core and fiscal center, was founded by the Romans as Londinium and retains boundaries close to its medieval ones. [ note 1 ] [ 10 ] Since the nineteenth century, [ 11 ] “ London ” has besides referred to the city around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, [ 12 ] which largely comprises Greater London, [ 13 ] governed by the Greater London Authority. [ note 2 ] [ 14 ] The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries held the national government and fantan. London, as one of the world ‘s global cities, [ 15 ] exerts impregnable charm on its arts, department of commerce, education, entertainment, fashion, finance, health worry, media, tourism, and communications. [ 16 ] Its GDP ( €801.66 billion in 2017 ) makes it the biggest urban economy in Europe [ 17 ] and one of the major fiscal centres in the world. In 2019 it had the irregular highest number of extremist high-net-worth individuals in Europe after Paris [ 18 ] and the second-highest number of billionaires of any city in Europe after Moscow. [ 19 ] With Europe ‘s largest concentration of higher education institutions, [ 20 ] it includes Imperial College London in natural and apply sciences, the London School of Economics in social sciences, and the comprehensive examination University College London. [ 21 ] The city is home to the most 5-star hotels of any city in the earth. [ 22 ] In 2012, London became the first gear city to host three Summer Olympic Games. [ 23 ] Over holocene decades, as a result of increased immigration, London has become one of the most ethnically divers cities in the worldly concern, [ 24 ] and over 300 languages are now spoken in the city. [ 25 ] The mid-2018 population of Greater London of about 9 million, [ 5 ] made it Europe ‘s third-most populous city. [ 26 ] It accounts for 13.4 per penny of the UK population. [ 27 ] Greater London Built-up Area is the fourth-most populous in Europe, after Istanbul, Moscow and Paris, with 9,787,426 inhabitants at the 2011 census. [ 28 ] [ 29 ] The London metropolitan area is the third-most populous in Europe after Istanbul ‘s and Moscow ‘s, with 14,040,163 inhabitants in 2016. [ note 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 30 ] London has four World Heritage Sites : the Tower of London ; Kew Gardens ; the Palace of Westminster, along with Westminster Abbey, and St Margaret ‘s Church ; and the historic settlement in Greenwich, where the Royal Observatory, Greenwich defines the Prime Meridian ( 0° longitude ) and Greenwich Mean Time. [ 31 ] other landmarks include Buckingham Palace, the London Eye, Piccadilly Circus, St Paul ‘s Cathedral, Tower Bridge and Trafalgar Square. It has numerous museums, galleries, libraries and sporting venues, including the british Museum, National Gallery, Natural History Museum, Tate Modern, British Library and West End theatres. [ 32 ] The London Underground is the oldest rapid transit system in the universe .
toponymy
London is an ancient name, already attested in the first hundred AD, normally in the romanize kind Londinium ; [ 33 ] for case, handwritten Roman tablets recovered in the city originating from AD 65/70–80 include the word Londinio ( ‘in London ‘ ). [ 34 ] Over the years, the name has attracted many mythicising explanations. The earliest attested appears in Geoffrey of Monmouth ‘s Historia Regum Britanniae, written around 1136. [ 33 ] [ 35 ] Modern scientific analyses of the name must account for the origins of the different forms found in early sources : Latin ( normally Londinium ), Old English ( normally Lunden ), and Welsh ( normally Llundein ), with address to the known developments over meter of sounds in those different languages. It is agreed that the list came into these languages from Common Brythonic ; recent work tends to reconstruct the lose Celtic form of the name as * Londonjon or something similar. This was adapted into Latin as Londinium and borrowed into Old English. [ 36 ] The toponymy of the Common Brythonic form is debated. Prominent was Richard Coates ‘s 1998 argument that it derived from pre-Celtic Old European * (p)lowonida, meaning “ river excessively wide to ford ”. Coates suggested this was a name given to the separate of the River Thames that flows through London, from which the village gained the celtic imprint of its name, * Lowonidonjon. [ 37 ] however, most exploit has accepted a plain celtic origin. holocene studies favour an explanation of a Celtic derivative of a Proto-Indo-European root * lendh- ( ‘sink, cause to sink ‘ ), combined with the Celtic suffix * -injo- or * -onjo- ( used to form place-names ). Peter Schrijver has specifically suggested that the identify originally meant “ place that floods ( sporadically, tidally ) ”. [ 38 ] [ 36 ] Until 1889, the name “ London ” applied officially only to the City of London, but since then it has besides referred to the County of London and to Greater London. [ 39 ] In write, “ London ” is occasionally contracted to “ LDN ”. [ 40 ] [ clarification needed ] such use originated in SMS language and frequently appears in a social media user profile, suffixing an alias or handle .
history
prehistory
In 1993, remains of a Bronze Age bridge were found on the south foreshore upriver from Vauxhall Bridge. [ 41 ] This either crossed the Thames or reached a now-lost island in it. Two of the timbers were radiocarbon dated to 1750–1285 BCE. [ 41 ] In 2010, foundations of a large timber social organization, dated to 4800–4500 BCE, [ 42 ] were found on the Thames ‘s south foreshore downriver from Vauxhall Bridge. [ 43 ] The function of the mesolithic age structure is ill-defined. Both structures are on the south bank of the Thames, where the now-underground River Effra flows into the Thames. [ 43 ]
Roman London
Despite the testify of disperse Brythonic settlements in the area, the first base major settlement was founded by the Romans about four years [ 2 ] after the invasion of 43 CE. [ 44 ] This only lasted until about 61 CE, when the Iceni kin led by Queen Boudica stormed it and burnt it to the ground. [ 45 ] The future, plan embodiment of Londinium prospered, superseding Colchester as capital of the Roman state of Britannia in 100. At its acme in the second hundred, Roman London had a population of about 60,000. [ 46 ]
Anglo-Saxon and Viking menstruation London
With the early 5th-century collapse of Roman rule, London ceased to be a das kapital and the wall city of Londinium was efficaciously abandoned, although Roman refinement continued around St Martin-in-the-Fields until about 450. [ 47 ] From about 500, an anglo-saxon colonization known as Lundenwic developed slightly west of the old Roman city. [ 48 ] By about 680 the city had become a major port again, but there is small evidence of large-scale production. From the 820s repeated Viking assaults brought worsen. Three are recorded ; those in 851 and 886 succeeded, while the last, in 994, was rebuffed. [ 49 ]
 The lancastrian siege of London in 1471 is attacked by a Yorkist sally. The Vikings applied Danelaw over much of eastern and northerly England, its boundary running approximately from London to Chester as an area of political and geographic master imposed by the Viking incursions formally agreed by the Danish warlord, Guthrum and the West Saxon king Alfred the Great in 886. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle records that Alfred “ refounded ” London in 886. archaeological inquiry shows this involved abandonment of Lundenwic and a revival of life and trade within the old Roman walls. London then grew lento until a dramatic increase in about 950. [ 50 ] By the eleventh hundred, London was intelligibly the largest township in England. Westminster Abbey, rebuild in Romanesque expressive style by King Edward the Confessor, was one of the grandest churches in Europe. Winchester had been the das kapital of Anglo-Saxon England, but from this fourth dimension London became the independent forum for foreign traders and the base for defense in time of war. In the opinion of Frank Stenton : “ It had the resources, and it was quickly developing the dignity and the political self-consciousness allow to a national capital. ” [ 51 ] [ 52 ]
The lancastrian siege of London in 1471 is attacked by a Yorkist sally. The Vikings applied Danelaw over much of eastern and northerly England, its boundary running approximately from London to Chester as an area of political and geographic master imposed by the Viking incursions formally agreed by the Danish warlord, Guthrum and the West Saxon king Alfred the Great in 886. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle records that Alfred “ refounded ” London in 886. archaeological inquiry shows this involved abandonment of Lundenwic and a revival of life and trade within the old Roman walls. London then grew lento until a dramatic increase in about 950. [ 50 ] By the eleventh hundred, London was intelligibly the largest township in England. Westminster Abbey, rebuild in Romanesque expressive style by King Edward the Confessor, was one of the grandest churches in Europe. Winchester had been the das kapital of Anglo-Saxon England, but from this fourth dimension London became the independent forum for foreign traders and the base for defense in time of war. In the opinion of Frank Stenton : “ It had the resources, and it was quickly developing the dignity and the political self-consciousness allow to a national capital. ” [ 51 ] [ 52 ]
Middle Ages
After winning the Battle of Hastings, William, Duke of Normandy was crowned King of England in newly completed Westminster Abbey on Christmas Day 1066. [ 53 ] William built the Tower of London, the first of many such in England rebuild in stone in the south-eastern corner of the city, to intimidate the inhabitants. [ 54 ] In 1097, William II began building Westminster Hall, close by the abbey of the like identify. It became the footing of a fresh Palace of Westminster. [ 55 ] [ 56 ] In the twelfth century, the institutions of cardinal government, which had so far followed the royal english court around the nation, grew in size and sophistication and became increasingly fixed, for most purposes at Westminster, although the royal treasury, having been moved from Winchester, came to rest in the Tower. While the City of Westminster developed into a dependable governmental capital, its clear-cut neighbor, the City of London, remained England ‘s largest city and star commercial center and flourished under its own alone presidency, the Corporation of London. In 1100, its population was some 18,000 ; by 1300 it had grown to closely 100,000. [ 57 ] Disaster fall in the shape of the Black Death in the mid-14th hundred, when London lost closely a one-third of its population. [ 58 ] London was the focus of the Peasants ‘ Revolt in 1381. [ 59 ] London was besides a center of England ‘s jewish population before their ejection by Edward I in 1290. ferocity against Jews occurred in 1190, when it was rumoured that the new king had ordered their massacre after they had presented themselves at his coronation. [ 60 ] In 1264 during the second Barons ‘ War, Simon de Montfort ‘s rebels killed 500 Jews while attempting to seize records of debts. [ 61 ]
early modern
 Map of London in 1593. There is only one bridge across the Thames, but parts of Southwark on the south bank of the river have been developed. During the Tudor period the Reformation produced a gradual switch to Protestantism. Much of London property passed from church to private ownership, which accelerated trade and business in the city. [ 62 ] In 1475, the Hanseatic League set up a chief trading floor ( kontor ) of England in London, called the Stalhof or Steelyard. It remained until 1853, when the Hanseatic cities of Lübeck, Bremen and Hamburg sold the property to South Eastern Railway. [ 63 ] Woollen fabric was shipped unbleached and strip from 14th/15th hundred London to the nearby shores of the Low Countries, where it was considered indispensable. [ 64 ] however english maritime enterprise hardly reached beyond the seas of northwest Europe. The commercial route to Italy and the Mediterranean was normally through Antwerp and over the Alps ; any ships passing through the Strait of Gibraltar to or from England were likely to be italian or Ragusan. The reopen of the Netherlands to English embark in January 1565 spurred a burst of commercial activeness. [ 65 ] The Royal Exchange was founded. [ 66 ] Mercantilism grew and monopoly traders such as the East India Company were founded as trade expanded to the New World. London became the main North Sea port, with migrants arriving from England and overseas. The population rose from about 50,000 in 1530 to about 225,000 in 1605. [ 62 ] In the sixteenth century William Shakespeare and his contemporaries lived in London at a time of hostility to the development of the field. By the end of the Tudor period in 1603, London was distillery compress. There was an assassination attempt on James I in Westminster, in the Gunpowder Plot of 5 November 1605. [ 67 ]
Map of London in 1593. There is only one bridge across the Thames, but parts of Southwark on the south bank of the river have been developed. During the Tudor period the Reformation produced a gradual switch to Protestantism. Much of London property passed from church to private ownership, which accelerated trade and business in the city. [ 62 ] In 1475, the Hanseatic League set up a chief trading floor ( kontor ) of England in London, called the Stalhof or Steelyard. It remained until 1853, when the Hanseatic cities of Lübeck, Bremen and Hamburg sold the property to South Eastern Railway. [ 63 ] Woollen fabric was shipped unbleached and strip from 14th/15th hundred London to the nearby shores of the Low Countries, where it was considered indispensable. [ 64 ] however english maritime enterprise hardly reached beyond the seas of northwest Europe. The commercial route to Italy and the Mediterranean was normally through Antwerp and over the Alps ; any ships passing through the Strait of Gibraltar to or from England were likely to be italian or Ragusan. The reopen of the Netherlands to English embark in January 1565 spurred a burst of commercial activeness. [ 65 ] The Royal Exchange was founded. [ 66 ] Mercantilism grew and monopoly traders such as the East India Company were founded as trade expanded to the New World. London became the main North Sea port, with migrants arriving from England and overseas. The population rose from about 50,000 in 1530 to about 225,000 in 1605. [ 62 ] In the sixteenth century William Shakespeare and his contemporaries lived in London at a time of hostility to the development of the field. By the end of the Tudor period in 1603, London was distillery compress. There was an assassination attempt on James I in Westminster, in the Gunpowder Plot of 5 November 1605. [ 67 ]
In 1637, the politics of Charles I attempted to reform administration in the London area. This called for the Corporation of the city to extend its jurisdiction and administration over expanding areas around the city. Fearing an attack by the Crown to diminish the Liberties of London, coupled with a miss of interest in administering these extra areas or concern by city guilds of having to share office, caused the Corporation ‘s “ The Great Refusal ”, a decision which largely continues to account for the singular governmental status of the City. [ 68 ] In the English Civil War the majority of Londoners supported the Parliamentary induce. After an initial progress by the Royalists in 1642, culminating in the battles of Brentford and Turnham Green, London was surrounded by a defensive perimeter wall known as the Lines of Communication. The lines were built by up to 20,000 people, and were completed in under two months. [ 69 ] The fortifications failed their entirely screen when the New Model Army entered London in 1647, [ 70 ] and they were levelled by Parliament the lapp year. [ 71 ] London was plagued by disease in the early on seventeenth hundred, [ 72 ] culminate in the Great Plague of 1665–1666, which killed up to 100,000 people, or a fifth of the population. [ 73 ]
The Great Fire of London broke out in 1666 in Pudding Lane in the city and quickly swept through the wooden buildings. [ 74 ] Rebuilding took over ten-spot years and was supervised by Robert Hooke [ 75 ] [ 76 ] [ 77 ] as Surveyor of London. [ 78 ] In 1708 Christopher Wren ‘s masterpiece, St Paul ‘s Cathedral, was completed. During the Georgian earned run average, new districts such as Mayfair were formed in the west ; newfangled bridges over the Thames encouraged development in South London. In the east, the Port of London expanded downstream. London ‘s exploitation as an international fiscal center matured for much of the eighteenth hundred. In 1762, George III acquired Buckingham House, which was enlarged over the future 75 years. During the eighteenth century, London was said to be dogged by crime, [ 79 ] and the Bow Street Runners were established in 1750 as a professional patrol force. [ 80 ] A full of more than 200 offences were punishable by death, [ 81 ] including fiddling larceny. [ 82 ] Most children born in the city died before reaching their third birthday. [ 83 ]
 horizon to the Royal Exchange in the City of London in 1886 Coffee-houses became a popular place to debate ideas, as growing literacy and development of the printing imperativeness made news widely available, with Fleet Street becoming the center of the british compress. The invasion of Amsterdam by Napoleonic armies led many financiers to relocate to London and the first London international issue was arranged in 1817. Around the lapp time, the Royal Navy became the worldly concern leading war fleet, acting as a major hindrance to potential economic adversaries. The abrogation of the Corn Laws in 1846 was specifically aimed at weakening Dutch economic office. London then overtook Amsterdam as the leading international fiscal center. [ 84 ] [ 85 ] According to Samuel Johnson :
horizon to the Royal Exchange in the City of London in 1886 Coffee-houses became a popular place to debate ideas, as growing literacy and development of the printing imperativeness made news widely available, with Fleet Street becoming the center of the british compress. The invasion of Amsterdam by Napoleonic armies led many financiers to relocate to London and the first London international issue was arranged in 1817. Around the lapp time, the Royal Navy became the worldly concern leading war fleet, acting as a major hindrance to potential economic adversaries. The abrogation of the Corn Laws in 1846 was specifically aimed at weakening Dutch economic office. London then overtook Amsterdam as the leading international fiscal center. [ 84 ] [ 85 ] According to Samuel Johnson :
You find no man, at all intellectual, who is volition to leave London. No, Sir, when a man is tired of London, he is tired of liveliness ; for there is in London all that biography can afford .Samuel Johnson, 1777[86]
late modern and contemporaneous
London was the global ‘s largest city from about 1831 to 1925, [ 87 ] with a population density of 325 per hectare. [ 88 ] London ‘s overcrowd conditions led to cholera epidemics, [ 89 ] claiming 14,000 lives in 1848, and 6,000 in 1866. [ 90 ] Rising traffic congestion led to the initiation of the world ‘s beginning local urban rail network. The Metropolitan Board of Works oversaw infrastructure expansion in the capital and some encompassing counties ; it was abolished in 1889 when the London County Council was created out of county areas surrounding the capital. The city was the target of many attacks during an early on terrorist campaign, the suffragette bombing and arson campaign, between 1912 and 1914, which saw historic landmarks such as Westminster Abbey and St Paul ‘s Cathedral bombard. [ 91 ]
London was bombed by the Germans in the First World War, [ 92 ] and during the second World War, the Blitz and other bombings by the german Luftwaffe killed complete 30,000 Londoners, destroying bombastic tracts of housing and other buildings across the city. [ 93 ] The 1948 Summer Olympics were held at the original Wembley Stadium, while London was still recovering from the war. [ 94 ] From the 1940s, London became home to many immigrants, chiefly from Commonwealth countries such as Jamaica, India, Bangladesh and Pakistan, [ 95 ] making London one of the most divers cities in the world. In 1951, the Festival of Britain was held on the South Bank. [ 96 ] The Great Smog of 1952 led to the Clean Air Act 1956, which ended the “ pea soup fogs “ for which London had been ill-famed. [ 97 ] Starting chiefly in the mid-1960s, London became a center for global youth polish, exemplified by the Swinging London sub-culture [ 98 ] associated with the King ‘s Road, Chelsea [ 99 ] and Carnaby Street. [ 100 ] The function of trendsetter revived in the hood era. [ 101 ] In 1965 London ‘s political boundaries were expanded in response to the increase of the urban area and a modern Greater London Council was created. [ 102 ] During The Troubles in Northern Ireland, London was hit in 1973 to bomb attacks by the Provisional irish Republican Army, [ 103 ] for two decades, starting with the Old Bailey fail. [ 104 ] [ 105 ] Racial inequality was highlighted by the 1981 Brixton rioting. [ 106 ] Greater London ‘s population declined in the decades after the second World War, from an estimated flower of 8.6 million in 1939 to around 6.8 million in the 1980s. [ 107 ] The principal ports for London moved downriver to Felixstowe and Tilbury, with the London Docklands sphere becoming a focus for regeneration, including the Canary Wharf growth. This was borne out of London ‘s increasing function as an external fiscal center in the 1980s. [ 108 ] The Thames Barrier was completed in the 1980s to protect London against tidal surges from the North Sea. [ 109 ] The Greater London Council was abolished in 1986, leaving London with no central administration until 2000 and the creation of the Greater London Authority. [ 110 ] To mark the twenty-first hundred, the Millennium Dome, London Eye and Millennium Bridge were constructed. [ 111 ] On 6 July 2005 London was awarded the 2012 Summer Olympics, as the first gear city to stage the Olympic Games three times. [ 112 ] On 7 July 2005, three London Underground trains and a bus bus were bombed in a serial of terrorist attacks. [ 113 ] In 2008, Time named London alongside New York City and Hong Kong as Nylonkong, hailing them as the world ‘s three most influential ball-shaped cities. [ 114 ] In January 2015, Greater London ‘s population was estimated to be 8.63 million, its highest since 1939. [ 115 ] During the Brexit referendum in 2016, the UK as a whole decided to leave the European Union, but most London constituencies voted for remaining. [ 116 ]
administration
local government
The presidency of London is formed of two tiers : a citywide, strategic tier and a local tier. Citywide administration is coordinated by the Greater London Authority ( GLA ), while local administration is carried out by 33 smaller authorities. [ 118 ] The GLA consists of two elect components : the mayor of London, who has administrator powers, and the London Assembly, which scrutinises the mayor ‘s decisions and can accept or reject the mayor ‘s budget proposals each class. The headquarter of the GLA is City Hall, Southwark. The mayor since 2016 has been Sadiq Khan, the first Muslim mayor of a major western capital. [ 119 ] [ 120 ] The mayor ‘s statutory plan strategy is published as the London Plan, which was most recently revised in 2011. [ 121 ] The local authorities are the councils of the 32 London boroughs and the City of London Corporation. [ 122 ] They are responsible for most local services, such as local planning, schools, social services, local roads and refuse solicitation. Certain functions, such as waste management, are provided through joint arrangements. In 2009–2010 the combined tax income consumption by London councils and the GLA amounted to good over £22 billion ( £14.7 billion for the boroughs and £7.4 billion for the GLA ). [ 123 ] The London Fire Brigade is the statutory fuel and rescue service for Greater London, run by the London Fire and Emergency Planning Authority. It is the third base largest arouse avail in the world. [ 124 ] National Health Service ambulance services are provided by the London Ambulance Service ( LAS ) NHS Trust, the largest free-at-the-point-of-use emergency ambulance service in the universe. [ 125 ] The London Air Ambulance charity operates in conjunction with the LAS where required. Her Majesty ‘s Coastguard and the Royal National Lifeboat Institution manoeuver on the River Thames, [ 126 ] [ 127 ] which is under the jurisdiction of the Port of London Authority from Teddington Lock to the ocean. [ 128 ]
National politics
London is the seat of the Government of the United Kingdom. many government departments, angstrom well as the prime minister ‘s residence at 10 Downing Street, are based stopping point to the Palace of Westminster, peculiarly along Whitehall. [ 129 ] There are 73 members of Parliament ( MPs ) from London, elected from local parliamentary constituencies in the national Parliament. As of December 2019, 49 are from the Labour Party, 21 are Conservatives, and three are liberal Democrat. [ 130 ] The ministerial post of minister for London was created in 1994. The current Minister for London is Paul Scully MP. [ 131 ]
Policing and crime
Policing in Greater London, with the exception of the City of London, is provided by the Metropolitan Police, oversee by the mayor through the Mayor ‘s agency for Policing and Crime ( MOPAC ). [ 132 ] [ 133 ] The City of London has its own police force – the City of London Police. [ 134 ] The british Transport Police are responsible for patrol services on National Rail, London Underground, Docklands Light Railway and Tramlink services. [ 135 ] The Ministry of Defence Police is a particular police impel in London, which does not generally become involved with policing the general public. [ 136 ] crime rates vary widely across different areas of London. Crime figures are made available nationally at Local Authority and Ward charge. [ 137 ] In 2015, there were 118 homicides, a 25.5 % increase over 2014. [ 138 ] The Metropolitan Police have made detail crime figures, broken down by class at borough and cellblock level, available on their web site since 2000. [ 139 ] [ 140 ] Recorded crime has been rising in London, notably crimson crime and mangle by stabbing and other means have risen. There were 50 murders from the start of 2018 to mid April 2018. Funding cuts to police in London are likely to have contributed to this, though other factors are besides involved. [ 141 ]
geography
oscilloscope
 Satellite view of London in June 2018 London, besides known as Greater London, is one of nine regions of England and the top subsection covering most of the city ‘s city. [ note 4 ] The small City of London at its kernel once comprised the whole settlement, but as its urban sphere grew, the Corporation of London resisted attempts to amalgamate the City with its suburbs, causing “ London ” to be defined several ways. [ 142 ] Forty per cent of Greater London is covered by the London post town, in which ‘LONDON ‘ forms part of postal addresses. [ 143 ] [ 144 ] The London telephone area code ( 020 ) covers a larger area, similar in size to Greater London, although some out districts are excluded and some equitable outside included. The Greater London limit has been aligned to the M25 expressway in places. [ 145 ] further urban expansion is immediately prevented by the Metropolitan Green Belt, [ 146 ] although the built-up area extends beyond the limit in places, producing a individually defined Greater London Urban Area. beyond this is the huge London commuter belt. [ 147 ] Greater London is split for some purposes into Inner London and Outer London, [ 148 ] and by the River Thames into North and South, with an informal central London area. The coordinates of the nominal kernel of London, traditionally the master Eleanor Cross at Charing Cross near the junction of Trafalgar Square and Whitehall, are about. [ 149 ] however, the geographic center of London on one definition is in the London Borough of Lambeth, 0.1 miles to the northeast of Lambeth North metro place. [ 150 ]
Satellite view of London in June 2018 London, besides known as Greater London, is one of nine regions of England and the top subsection covering most of the city ‘s city. [ note 4 ] The small City of London at its kernel once comprised the whole settlement, but as its urban sphere grew, the Corporation of London resisted attempts to amalgamate the City with its suburbs, causing “ London ” to be defined several ways. [ 142 ] Forty per cent of Greater London is covered by the London post town, in which ‘LONDON ‘ forms part of postal addresses. [ 143 ] [ 144 ] The London telephone area code ( 020 ) covers a larger area, similar in size to Greater London, although some out districts are excluded and some equitable outside included. The Greater London limit has been aligned to the M25 expressway in places. [ 145 ] further urban expansion is immediately prevented by the Metropolitan Green Belt, [ 146 ] although the built-up area extends beyond the limit in places, producing a individually defined Greater London Urban Area. beyond this is the huge London commuter belt. [ 147 ] Greater London is split for some purposes into Inner London and Outer London, [ 148 ] and by the River Thames into North and South, with an informal central London area. The coordinates of the nominal kernel of London, traditionally the master Eleanor Cross at Charing Cross near the junction of Trafalgar Square and Whitehall, are about. [ 149 ] however, the geographic center of London on one definition is in the London Borough of Lambeth, 0.1 miles to the northeast of Lambeth North metro place. [ 150 ]
condition
Within London, both the City of London and the City of Westminster have city status and both the City of London and the remainder of Greater London are counties for the purposes of lieutenancies. [ 151 ] The area of Greater London includes areas that are separate of the historic counties of Middlesex, Kent, Surrey, Essex and Hertfordshire. [ 152 ] London ‘s status as the capital of England, and later the United Kingdom, has never been granted or confirmed officially—by codified or in written form. [ note 5 ] Its position was formed through constitutional convention, making its condition as de facto capital a separate of the UK ‘s uncodified united states constitution. The capital of England was moved to London from Winchester as the Palace of Westminster developed in the 12th and 13th centuries to become the permanent placement of the royal court, and frankincense the political capital of the nation. [ 156 ] More recently, Greater London has been defined as a region of England and in this context is known as London. [ 157 ]
topography
Greater London encompasses a total area of 1,583 square kilometres ( 611 sq nautical mile ), an area which had a population of 7,172,036 in 2001 and a population concentration of 4,542 inhabitants per squarely kilometer ( 11,760/sq mile ). The extend area known as the London Metropolitan Region or the London Metropolitan Agglomeration, comprises a full area of 8,382 square kilometres ( 3,236 sq myocardial infarction ) has a population of 13,709,000 and a population density of 1,510 inhabitants per square kilometer ( 3,900/sq mile ). [ 158 ] Modern London stands on the Thames, its primary geographic feature of speech, a navigable river which crosses the city from the southwest to the east. The Thames Valley is a flood plain surrounded by gently rolling hills including Parliament Hill, Addington Hills, and Primrose Hill. Historically London grew up at the lowest bridge degree on the Thames. The Thames was once a much broader, shallower river with across-the-board marshlands ; at high tide, its shores reached five times their give width. [ 159 ] Since the Victorian earned run average the Thames has been extensively embanked, and many of its London tributaries nowadays flow underground. The Thames is a tidal river, and London is vulnerable to flooding. [ 160 ] The menace has increased over clock time because of a dense but continuous rise in high water level by the behind ’tilting ‘ of the british Isles ( up in Scotland and Northern Ireland and down in southern parts of England, Wales and Ireland ) caused by post-glacial rebound. [ 161 ] [ 162 ] In 1974 a ten of oeuvre began on the construction of the Thames Barrier across the Thames at Woolwich to deal with this threat. While the barrier is expected to function as designed until roughly 2070, concepts for its future enlargement or redesign are already being discussed. [ 163 ]
climate
| London, United Kingdom | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
London has a moderate oceanic climate ( Köppen : Cfb ). rain records have been kept in the city since at least 1697, when records began at Kew. At Kew, the most rain in one calendar month is 7.4 inches ( 189 millimeter ) in November 1755 and the least is 0 inches ( 0 millimeter ) in both December 1788 and July 1800. Mile End besides had 0 inches ( 0 millimeter ) in April 1893. [ 164 ] The wettest year on record is 1903, with a total fall of 38.1 inches ( 969 millimeter ) and the dry is 1921, with a entire fall of 12.1 inches ( 308 millimeter ). [ 165 ] The average annual precipitation amounts to about 600 mm, lower than cities such as Rome, Lisbon, New York City and Sydney. [ 166 ] [ 167 ] [ 168 ] Nevertheless, despite its relatively low annual precipitation, London calm receives 109.6 showery days on the 1.0 millimeter threshold annually – higher than or at least very like to the cities mentioned. temperature extremes in London stove from 38.1 °C ( 100.6 °F ) at Kew on 10 August 2003 [ 169 ] down to −16.1 °C ( 3.0 °F ) at Northolt on 1 January 1962. [ 170 ] [ 171 ] Records for atmospheric atmospheric pressure have been kept at London since 1692. The highest press always reported is 1,049.8 millibars ( 31.00 inHg ) on 20 January 2020. [ 172 ] Summers are generally warm, sometimes hot. London ‘s average July high is 23.5 °C ( 74.3 °F ). On average each class, London experiences 31 days above 25 °C ( 77.0 °F ) and 4.2 days above 30.0 °C ( 86.0 °F ). During the 2003 european heat wave prolonged heat led to hundreds of heat-related deaths. [ 173 ] There was besides a former spell of 15 consecutive days above 32.2 °C ( 90.0 °F ) in England in 1976 which besides caused many heat refer deaths. [ 174 ] A former temperature of 37.8 °C ( 100.0 °F ) in August 1911 at the Greenwich station, though this was late disregarded as non-standard. [ 175 ] Droughts can besides, occasionally, be a problem, particularly in summer. Most recently in Summer 2018 [ 176 ] and with much drier than modal conditions prevailing from May to December. [ 177 ] however, the most straight days without rain was 73 days in the form of 1893. [ 178 ] Winters are broadly cool with little temperature mutant. Heavy snow is rare but snow normally falls at least once each winter. bounce and fall can be pleasant. As a large city, London has a considerable urban heat island effect, [ 179 ] making the center of London at times 5 °C ( 9 °F ) warmer than the suburb and outskirts. This can be seen below when comparing London Heathrow, 15 miles ( 24 kilometer ) west of London, with the London Weather Centre. [ 180 ]
- ^ Averages are taken from Heathrow, and extremes are taken from stations across London .
| Climate data for Greenwich Park, elevation: 47 m (154 ft), 1981–2010 normals | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.4 (57.9) |
19.7 (67.5) |
21.7 (71.1) |
25.6 (78.1) |
30.0 (86.0) |
32.8 (91.0) |
35.3 (95.5) |
37.5 (99.5) |
30.0 (86.0) |
25.6 (78.1) |
18.9 (66.0) |
15.0 (59.0) |
37.5 (99.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.1 (46.6) |
8.6 (47.5) |
11.6 (52.9) |
14.6 (58.3) |
18.1 (64.6) |
21.0 (69.8) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.1 (73.6) |
20.0 (68.0) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.3 (52.3) |
8.4 (47.1) |
15.3 (59.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.6 (42.1) |
5.7 (42.3) |
8.1 (46.6) |
10.3 (50.5) |
13.5 (56.3) |
16.4 (61.5) |
18.6 (65.5) |
18.5 (65.3) |
15.7 (60.3) |
12.2 (54.0) |
8.6 (47.5) |
5.9 (42.6) |
11.6 (52.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 3.1 (37.6) |
2.7 (36.9) |
4.6 (40.3) |
5.9 (42.6) |
8.9 (48.0) |
11.8 (53.2) |
13.7 (56.7) |
13.8 (56.8) |
11.4 (52.5) |
8.8 (47.8) |
5.8 (42.4) |
3.4 (38.1) |
7.8 (46.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.4 (15.1) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
−7.8 (18.0) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
5.0 (41.0) |
7.2 (45.0) |
6.1 (43.0) |
2.8 (37.0) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 41.6 (1.64) |
36.3 (1.43) |
40.3 (1.59) |
40.1 (1.58) |
44.9 (1.77) |
47.4 (1.87) |
34.6 (1.36) |
54.3 (2.14) |
51.0 (2.01) |
61.1 (2.41) |
57.5 (2.26) |
48.4 (1.91) |
557.4 (21.94) |
| Average precipitation days ( ≥ 1.0 millimeter ) | 11.4 | 8.5 | 9.8 | 9.0 | 9.2 | 7.4 | 6.3 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 9.5 | 109.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 44.7 | 65.4 | 101.7 | 148.3 | 170.9 | 171.4 | 176.7 | 186.1 | 133.9 | 105.4 | 59.6 | 45.8 | 1,410 |
| Source 1: Met Office[189][190][191] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: BBC Weather[192] | |||||||||||||
Districts
Places within London ‘s huge urban area are identified using zone names, such as Mayfair, Southwark, Wembley and Whitechapel. These are either informal designations, reflect the names of villages that have been absorbed by sprawl, or are superseded administrative units such as parishes or erstwhile boroughs. such names have remained in use through tradition, each referring to a local area with its own classifiable fictional character, but without official boundaries. Since 1965 Greater London has been divided into 32 London boroughs in addition to the ancient City of London. [ 193 ] [ 194 ] The City of London is the main fiscal zone, [ 195 ] and Canary Wharf has recently developed into a raw fiscal and commercial hub in the Docklands to the east. The West end is London ‘s main entertainment and patronize district, attracting tourists. [ 196 ] West London includes expensive residential areas where properties can sell for tens of millions of pounds. [ 197 ] The average price for properties in Kensington and Chelsea is over £2 million with a similarly high gear spending in most of central London. [ 198 ] [ 199 ] The East end is the sphere airless to the original Port of London, known for its high immigrant population, a well as for being one of the poorest areas in London. [ 200 ] The surrounding East London area saw much of London ‘s early industrial development ; now, brownfield sites throughout the sphere are being redeveloped as part of the Thames Gateway including the London Riverside and Lower Lea Valley, which was developed into the Olympic Park for the 2012 Olympics and Paralympics. [ 200 ]
architecture
 Trafalgar Square and its fountains, with Nelson ‘s Column on the mighty London ‘s buildings are besides diverse to be characterised by any finical architectural style, partially because of their varying ages. many expansive houses and public buildings, such as the National Gallery, are constructed from Portland stone. Some areas of the city, peculiarly those just west of the center, are characterised by white stucco or whitewashed buildings. few structures in central London pre-date the Great Fire of 1666, these being a few decipher Roman remains, the Tower of London and a few break up Tudor survivors in the city. Further out is, for example, the Tudor-period Hampton Court Palace, England ‘s oldest surviving Tudor palace, built by Cardinal Thomas Wolsey in about 1515. [ 201 ] part of the change architectural inheritance are the 17th-century churches by Wren, neoclassic fiscal institutions such as the Royal Exchange and the Bank of England, to the early twentieth century Old Bailey and the 1960s barbican Estate. The disused—but soon [ when? ] to be rejuvenated—1939 Battersea Power Station by the river in the southwest is a local anesthetic landmark, while some railroad track termini are excellent examples of priggish architecture, most notably St. Pancras and Paddington. [ 202 ] The concentration of London varies, with high use density in the cardinal area and Canary Wharf, high gear residential densities in inner London, and lower densities in Outer London .
Trafalgar Square and its fountains, with Nelson ‘s Column on the mighty London ‘s buildings are besides diverse to be characterised by any finical architectural style, partially because of their varying ages. many expansive houses and public buildings, such as the National Gallery, are constructed from Portland stone. Some areas of the city, peculiarly those just west of the center, are characterised by white stucco or whitewashed buildings. few structures in central London pre-date the Great Fire of 1666, these being a few decipher Roman remains, the Tower of London and a few break up Tudor survivors in the city. Further out is, for example, the Tudor-period Hampton Court Palace, England ‘s oldest surviving Tudor palace, built by Cardinal Thomas Wolsey in about 1515. [ 201 ] part of the change architectural inheritance are the 17th-century churches by Wren, neoclassic fiscal institutions such as the Royal Exchange and the Bank of England, to the early twentieth century Old Bailey and the 1960s barbican Estate. The disused—but soon [ when? ] to be rejuvenated—1939 Battersea Power Station by the river in the southwest is a local anesthetic landmark, while some railroad track termini are excellent examples of priggish architecture, most notably St. Pancras and Paddington. [ 202 ] The concentration of London varies, with high use density in the cardinal area and Canary Wharf, high gear residential densities in inner London, and lower densities in Outer London .
The Monument in the City of London provides views of the surrounding area while commemorating the Great Fire of London, which originated nearby. marble Arch and Wellington Arch, at the north and south ends of Park Lane, respectively, have royal connections, as do the Albert Memorial and Royal Albert Hall in Kensington. Nelson ‘s Column is a nationally recognized memorial in Trafalgar Square, one of the focal points of cardinal London. Older buildings are chiefly brick built, most normally the chicken London stock brick or a warm orange-red kind, often decorated with carvings and white plaster mouldings. [ 203 ] In the dense areas, most of the concentration is via medium- and high-rise buildings. London ‘s skyscrapers, such as 30 St Mary Axe, Tower 42, the Broadgate Tower and One Canada Square, are largely in the two fiscal districts, the City of London and Canary Wharf. High-rise development is restricted at certain sites if it would obstruct protected views of St Paul ‘s Cathedral and other historic buildings. however, there are a number of tall skyscrapers in central London ( see Tall buildings in London ), including the 95-storey Shard London Bridge, the tallest build in the United Kingdom. other celebrated mod buildings include City Hall in Southwark with its distinctive ellipse determine, [ 204 ] the Art Deco BBC Broadcasting House plus the Postmodernist British Library in Somers Town / Kings Cross and No 1 Poultry by James Stirling. What was once the Millennium Dome, by the Thames to the east of Canary Wharf, is now an entertainment venue called the O2 Arena .
cityscape
natural history
The London Natural History Society suggests that London is “ one of the World ‘s Greenest Cities ” with more than 40 per cent green space or overt water. They indicate that 2000 species of flowering plant have been found growing there and that the tidal Thames supports 120 species of pisces. [ 205 ] They besides state that over 60 species of bird nest in central London and that their members have recorded 47 species of butterfly, 1173 moths and more than 270 kinds of spider around London. London ‘s wetland areas support nationally important populations of many water birds. London has 38 Sites of particular Scientific Interest ( SSSIs ), two national nature reserves and 76 local anesthetic nature reserves. [ 206 ] Amphibians are common in the capital, including smooth newt living by the Tate Modern, and common frogs, common toads, palmate newts and bang-up crested newt. On the early hand, native reptiles such as slowworms, common lizards, barred eatage snakes and adders, are largely alone seen in Outer London. [ 207 ]
Among early inhabitants of London are 10,000 crimson foxes, so that there are now 16 foxes for every square nautical mile ( 6 per square kilometer ) of London. These urban foxes are perceptibly bolder than their country cousins, sharing the paving with pedestrians and raising cubs in people ‘s backyards. Foxes have even sneaked into the Houses of Parliament, where one was found asleep on a file cabinet. Another broke into the grounds of Buckingham Palace, reportedly killing some of Queen Elizabeth II ‘s pry tap flamingo. [ 208 ] Generally, however, foxes and city folk appear to get along. A view in 2001 by the London-based Mammal Society found that 80 per cent of 3,779 respondents who volunteered to keep a diary of garden mammal visits liked having them around. This sample can not be taken to represent Londoners as a whole. [ 209 ] [ 210 ] early mammals found in Greater London are hedgehog, brown fink, mouse, rabbit, shrew, vole, and grey squirrel. [ 211 ] In wild areas of Outer London, such as Epping Forest, a wide-eyed variety of mammals are found, including european hare, tease, field, depository financial institution and water vole, wood mouse, yellow-necked mouse, gram molecule, shrew, and weasel, in addition to red confuse, gray squirrel and porcupine. A dead otter was found at The Highway, in Wapping, about a mile from the Tower Bridge, which would suggest that they have begun to move back after being absent a hundred years from the city. [ 212 ] Ten of England ‘s eighteen species of bats have been recorded in Epping Forest : soprano, Nathusius ‘ and common pipistrelles, common noctule, serotine, barbastelle, Daubenton ‘s, brown long-eared, Natterer ‘s and Leisler ‘s. [ 213 ] Among the foreign sights in London have been a giant in the Thames, [ 214 ] while the BBC Two plan “ natural global : affected History of London ” shows feral pigeons using the London Underground to get around the city, a navy seal that takes pisces from fishmongers outside Billingsgate Fish Market, and foxes that will “ sit ” if given sausages. [ 215 ] Herds of loss and fallow deer besides roam freely within much of Richmond and Bushy Park. A cull takes position each November and February to ensure numbers can be sustained. [ 216 ] Epping Forest is besides known for its fallow deer, which can frequently be seen in herds to the north of the Forest. A rare population of melanistic, bootleg fallow deer is besides maintained at the Deer Sanctuary near Theydon Bois. Muntjac deer, which escaped from deer parks at the twist of the twentieth century, are besides found in the forest. While Londoners are accustomed to wildlife such as birds and foxes sharing the city, more recently urban deer have started becoming a even have, and wholly herds of fallow deer come into residential areas at night to take advantage of London ‘s green spaces. [ 217 ] [ 218 ]
demography
 Population concentration map The 2011 census recorded that 2,998,264 people or 36.7 % of London ‘s population were foreign-born making it the city with the second largest immigrant population after New York, in terms of absolute numbers. About 69 % of children born in London in 2015 had at least one parent who was born abroad. [ 220 ] The mesa to the proper shows the common countries of birth of London residents. note that some of the German-born population, in 18th situation, are british citizens from parturition born to parents serving in the british Armed Forces in Germany. [ 221 ] Increasing industrialization swelled London ‘s population throughout the 19th and early on twentieth centuries, and for some clock in the late 19th and early on twentieth centuries it was the most populous city in the world. It peaked at 8,615,245 in 1939, just before the outbreak of the Second World War, but had declined to 7,192,091 by the 2001 Census. however, the population then grew by fair over a million between the 2001 and 2011 Censuses, to reach 8,173,941 in the latter. [ 222 ] however, London ‘s continuous urban area extends beyond Greater London and numbered 9,787,426 people in 2011, [ 29 ] while its wide metropolitan area had a population of 12–14 million, depending on the definition used. [ 223 ] [ 224 ] According to Eurostat, London is the second gear most populous metropolitan area in Europe. A net income 726,000 immigrants arrived there in the period 1991–2001. [ 225 ] The region covers 1,579 square kilometres ( 610 sq michigan ), giving a population density of 5,177 inhabitants per squarely kilometer ( 13,410/sq mile ), [ 226 ] more than ten-spot times that of any other british region. [ 227 ] In population terms, London is the 19th largest city and the 18th largest metropolitan region. [ 228 ] [ 229 ]
Population concentration map The 2011 census recorded that 2,998,264 people or 36.7 % of London ‘s population were foreign-born making it the city with the second largest immigrant population after New York, in terms of absolute numbers. About 69 % of children born in London in 2015 had at least one parent who was born abroad. [ 220 ] The mesa to the proper shows the common countries of birth of London residents. note that some of the German-born population, in 18th situation, are british citizens from parturition born to parents serving in the british Armed Forces in Germany. [ 221 ] Increasing industrialization swelled London ‘s population throughout the 19th and early on twentieth centuries, and for some clock in the late 19th and early on twentieth centuries it was the most populous city in the world. It peaked at 8,615,245 in 1939, just before the outbreak of the Second World War, but had declined to 7,192,091 by the 2001 Census. however, the population then grew by fair over a million between the 2001 and 2011 Censuses, to reach 8,173,941 in the latter. [ 222 ] however, London ‘s continuous urban area extends beyond Greater London and numbered 9,787,426 people in 2011, [ 29 ] while its wide metropolitan area had a population of 12–14 million, depending on the definition used. [ 223 ] [ 224 ] According to Eurostat, London is the second gear most populous metropolitan area in Europe. A net income 726,000 immigrants arrived there in the period 1991–2001. [ 225 ] The region covers 1,579 square kilometres ( 610 sq michigan ), giving a population density of 5,177 inhabitants per squarely kilometer ( 13,410/sq mile ), [ 226 ] more than ten-spot times that of any other british region. [ 227 ] In population terms, London is the 19th largest city and the 18th largest metropolitan region. [ 228 ] [ 229 ]
Age social organization and medial old age
Children younger than 14 constituted 20.6 % of the population in Outer London in 2018, and 18 % in Inner London. The 15–24 senesce group was 11.1 % in Outer and 10.2 % in Inner London, those aged 25–44 years 30.6 % in Outer London and 39.7 % in Inner London, those aged 45–64 years 24 % and 20.7 % in Outer and Inner London respectively. Those aged 65 and complete are 13.6 % in Outer London, but only 9.3 % in Inner London. [ 230 ] The median age of London in 2018 was 36.5, which was younger than the UK medial of 40.3. [ 230 ]
heathen groups
Maps of Greater London showing percentage distribution of selected races according to the 2011 Census White
White asian
asian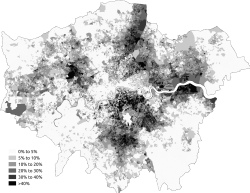 black According to the Office for National Statistics, based on 2011 Census estimates, 59.8 per penny of the 8,173,941 inhabitants of London were White, with 44.9 % White British, 2.2 % White Irish, 0.1 % itinerant / Irish traveler and 12.1 % classified as other White. [ 231 ] meanwhile 20.9 % of Londoners were of asian and mixed-Asian descent, 19.7 % being of broad asian descents and those of mixed-Asian heritage 1.2 % of the population. Indians accounted for 6.6 %, followed by Pakistanis and Bangladeshis at 2.7 % each. chinese peoples accounted for 1.5 % and Arabs for 1.3 %. A far 4.9 % were classified as “ other asian ”. [ 231 ] 15.6 % of London ‘s population were of Black and mixed-Black descent. 13.3 % of full Black descent, with mixed-Black heritage comprising 2.3 %. Black Africans accounted for 7.0 % of London ‘s population, with 4.2 % as Black Caribbean and 2.1 % as “ other Black ”. 5.0 % were of blend race. [ 231 ] As of 2007, Black and asian children outnumbered White british children by about three to two in express schools across London. [ 232 ] wholly at the 2011 census, of London ‘s 1,624,768 population aged 0 to 15, 46.4 % were White, 19.8 % asian, 19 % Black, 10.8 % Mixed and 4 % another cultural group. [ 233 ] In January 2005, a survey of London ‘s ethnic and religious diverseness claimed that more than 300 languages were spoken in London and more than 50 non-indigenous communities had populations of more than 10,000. [ 234 ] Figures from the Office for National Statistics show that in 2010, London ‘s foreign-born population was 2,650,000 ( 33 % ), improving from 1,630,000 in 1997. The 2011 census showed that 36.7 % of Greater London ‘s population were born outside the UK. [ 235 ] Some of the German-born population were probably to be british nationals born to parents serving in the british Armed Forces in Germany. [ 236 ] Estimates by the Office for National Statistics indicate that the five largest foreign-born groups living in London in the time period July 2009 to June 2010 were born in India, Poland, the Republic of Ireland, Bangladesh and Nigeria. [ 237 ]
black According to the Office for National Statistics, based on 2011 Census estimates, 59.8 per penny of the 8,173,941 inhabitants of London were White, with 44.9 % White British, 2.2 % White Irish, 0.1 % itinerant / Irish traveler and 12.1 % classified as other White. [ 231 ] meanwhile 20.9 % of Londoners were of asian and mixed-Asian descent, 19.7 % being of broad asian descents and those of mixed-Asian heritage 1.2 % of the population. Indians accounted for 6.6 %, followed by Pakistanis and Bangladeshis at 2.7 % each. chinese peoples accounted for 1.5 % and Arabs for 1.3 %. A far 4.9 % were classified as “ other asian ”. [ 231 ] 15.6 % of London ‘s population were of Black and mixed-Black descent. 13.3 % of full Black descent, with mixed-Black heritage comprising 2.3 %. Black Africans accounted for 7.0 % of London ‘s population, with 4.2 % as Black Caribbean and 2.1 % as “ other Black ”. 5.0 % were of blend race. [ 231 ] As of 2007, Black and asian children outnumbered White british children by about three to two in express schools across London. [ 232 ] wholly at the 2011 census, of London ‘s 1,624,768 population aged 0 to 15, 46.4 % were White, 19.8 % asian, 19 % Black, 10.8 % Mixed and 4 % another cultural group. [ 233 ] In January 2005, a survey of London ‘s ethnic and religious diverseness claimed that more than 300 languages were spoken in London and more than 50 non-indigenous communities had populations of more than 10,000. [ 234 ] Figures from the Office for National Statistics show that in 2010, London ‘s foreign-born population was 2,650,000 ( 33 % ), improving from 1,630,000 in 1997. The 2011 census showed that 36.7 % of Greater London ‘s population were born outside the UK. [ 235 ] Some of the German-born population were probably to be british nationals born to parents serving in the british Armed Forces in Germany. [ 236 ] Estimates by the Office for National Statistics indicate that the five largest foreign-born groups living in London in the time period July 2009 to June 2010 were born in India, Poland, the Republic of Ireland, Bangladesh and Nigeria. [ 237 ]
religion
According to the 2011 Census, the largest religious groupings were Christians ( 48.4 % ), followed by those of no religion ( 20.7 % ), Muslims ( 12.4 % ), no response ( 8.5 % ), Hindus ( 5.0 % ), Jews ( 1.8 % ), Sikhs ( 1.5 % ), Buddhists ( 1.0 % ) and other ( 0.6 % ). [ 238 ] London has traditionally been Christian, and has a big total of churches, peculiarly in the City of London. The long-familiar St Paul ‘s Cathedral in the City and Southwark Cathedral south of the river are anglican administrative centres, [ 239 ] while the Archbishop of Canterbury, star bishop of the Church of England and global Anglican Communion, has his independent mansion at Lambeth Palace in the London Borough of Lambeth. [ 240 ]
Important home and royal ceremonies are shared between St Paul ‘s and Westminster Abbey. [ 241 ] The Abbey is not to be confused with nearby Westminster Cathedral, which is the largest Roman Catholic cathedral in England and Wales. [ 242 ] Despite the prevalence of Anglican churches, observation is low within the denomination. Church attendance continues a long, steadily refuse, according to Church of England statistics. [ 243 ] London besides has ample Muslim, Hindu, Sikh, and jewish communities. noteworthy mosques include the East London Mosque in Tower Hamlets, which is allowed to give the Islamic address to prayer through loudspeakers, the London Central Mosque on the edge of Regent ‘s Park [ 244 ] and the Baitul Futuh of the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community. After the vegetable oil boom, increasing numbers of affluent Middle-Eastern Arab Muslims based themselves around Mayfair, Kensington and Knightsbridge in West London. [ 245 ] [ 246 ] [ 247 ] There are big Bengali Muslim communities in the eastern borough of Tower Hamlets and Newham. [ 248 ] large Hindu communities are found in the north-western boroughs of Harrow and Brent, the latter hosting what was until 2006, [ 249 ] Europe ‘s largest Hindu temple, Neasden Temple. [ 250 ] London is besides home to 44 Hindu temples, including the BAPS Shri Swaminarayan Mandir London. There are Sikh communities in East and West London, peculiarly in Southall, home plate to one of the largest sikh populations and the largest Sikh temple outside India. [ 251 ] The majority of british Jews survive in London, with celebrated jewish communities in Stamford Hill, Stanmore, Golders Green, Finchley, Hampstead, Hendon and Edgware in North London. Bevis Marks Synagogue in the City of London is affiliated to London ‘s historic Sephardic Jewish community. It is the lone synagogue in Europe to have held regular services continually for over 300 years. Stanmore and Canons Park Synagogue has the largest membership of any Orthodox synagogue in Europe, overtaking Ilford synagogue ( besides in London ) in 1998. [ 252 ] The London Jewish Forum was set up in 2006 in response to the growing meaning of devolve London Government. [ 253 ]
Accents
Cockney is an stress hear across London, chiefly spoken by propertyless and lower-middle class Londoners. It is chiefly attributed to the East End and wider East London, having originated there in the eighteenth hundred, although it has been suggested that the Cockney style of language is much older. [ 254 ] John Camden Hotten, in his Slang Dictionary of 1859, makes citation to “ their use of a peculiar slang language ” when describing the costermongers of the East End. Since the change by reversal of the century Cockney dialect is less coarse in parts of the East End itself, with modern strongholds including other parts of London and suburbs in the home counties. [ 255 ] [ 256 ] estuary English is an average dialect between Cockney and Received Pronunciation. [ 257 ] It is widely spoken by people of all classes in London and south-eastern England, associated with the River Thames and its estuary. [ 258 ] Multicultural London English ( MLE ) is a multiethnolect becoming increasingly park in multicultural areas amongst young, wage-earning people from divers backgrounds. It is a fusion of an array of heathen accents, in detail Afro-Caribbean and South Asian, with a significant Cockney influence. [ 259 ] Received Pronunciation ( RP ) is the accent traditionally regarded as the standard for british English. [ 260 ] It has no specific geographic correlate, [ 261 ] although it is besides traditionally defined as the standard actor’s line used in London and south-eastern England. [ 262 ] It is chiefly spoken by upper-class and upper-middle class Londoners. [ 263 ] [ 264 ]
economy
 [265] The City of London, one of the largest fiscal centres in the world London ‘s gross regional merchandise in 2019 was £503 billion, around a quarter of UK GDP. [ 266 ] London has five major clientele districts : the city, Westminster, Canary Wharf, Camden & Islington and Lambeth & Southwark. One way to get an theme of their relative importance is to look at proportional amounts of office quad : Greater London had 27 million m2 of function space in 2001, and the City contains the most space, with 8 million m2 of function space. London has some of the highest very estate of the realm prices in the populace. [ 267 ] [ 268 ] London is the world ‘s most expensive office marketplace according to world place journal ( 2015 ) reputation. [ 269 ] As of 2015 the residential property in London is deserving $ 2.2 trillion – the lapp value as that of Brazil ‘s annual GDP. [ 270 ] The city has the highest property prices of any european city according to the Office for National Statistics and the European Office of Statistics. [ 271 ] On average the price per square meter in cardinal London is €24,252 ( April 2014 ). This is higher than the property prices in other G8 European capital cities ; Berlin €3,306, Rome €6,188 and Paris €11,229. [ 272 ]
[265] The City of London, one of the largest fiscal centres in the world London ‘s gross regional merchandise in 2019 was £503 billion, around a quarter of UK GDP. [ 266 ] London has five major clientele districts : the city, Westminster, Canary Wharf, Camden & Islington and Lambeth & Southwark. One way to get an theme of their relative importance is to look at proportional amounts of office quad : Greater London had 27 million m2 of function space in 2001, and the City contains the most space, with 8 million m2 of function space. London has some of the highest very estate of the realm prices in the populace. [ 267 ] [ 268 ] London is the world ‘s most expensive office marketplace according to world place journal ( 2015 ) reputation. [ 269 ] As of 2015 the residential property in London is deserving $ 2.2 trillion – the lapp value as that of Brazil ‘s annual GDP. [ 270 ] The city has the highest property prices of any european city according to the Office for National Statistics and the European Office of Statistics. [ 271 ] On average the price per square meter in cardinal London is €24,252 ( April 2014 ). This is higher than the property prices in other G8 European capital cities ; Berlin €3,306, Rome €6,188 and Paris €11,229. [ 272 ]
The City of London
London ‘s finance diligence is based in the City of London and Canary Wharf, the two major business districts in London. London is one of the pre-eminent fiscal centres of the world as the most authoritative placement for international finance. [ 273 ] [ 274 ] London took over as a major fiscal center concisely after 1795 when the Dutch Republic collapsed before the Napoleonic armies. For many bankers established in Amsterdam ( e.g. Hope, Baring ), this was alone time to move to London. The London fiscal elect was strengthened by a potent Jewish community from all over Europe adequate to of mastering the most sophisticated fiscal tools of the time. [ 84 ] This singular concentration of talents accelerated the transition from the commercial Revolution to the Industrial Revolution. By the end of the nineteenth hundred, Britain was the wealthiest of all nations, and London a leading fiscal center. still, as of 2016 London tops the worldly concern rankings on the Global Financial Centres Index ( GFCI ), [ 275 ] and it ranked moment in A.T. Kearney ‘s 2018 Global Cities Index. [ 276 ]
London ‘s largest diligence is finance, and its fiscal exports make it a bombastic subscriber to the UK ‘s poise of payments. Around 325,000 people were employed in fiscal services in London until mid-2007. London has over 480 overseas banks, more than any other city in the worldly concern. It is besides the populace ‘s biggest currency trade center, accountancy for some 37 per penny of the $ 5.1 trillion average daily volume, according to the BIS. [ 277 ] Over 85 per penny ( 3.2 million ) of the use population of greater London works in the services industries. Because of its big ball-shaped role, London ‘s economy had been affected by the fiscal crisis of 2007–2008. however, by 2010 the city had recovered, put in place modern regulative powers, proceeded to regain lost ground and re-established London ‘s economic authority. [ 278 ] Along with professional services headquarters, the City of London is home to the Bank of England, London Stock Exchange, and Lloyd ‘s of London policy market. Over half the UK ‘s top 100 listed companies ( the FTSE 100 ) and over 100 of Europe ‘s 500 largest companies have their headquarters in central London. Over 70 per penny of the FTSE 100 are within London ‘s metropolitan area, and 75 per penny of Fortune 500 companies have offices in London. [ 279 ]
Media and engineering
Media companies are concentrated in London, and the media distribution industry is London ‘s second most competitive sector. [ 280 ] The BBC is a significant employer, while early broadcasters besides have headquarters around the city. many national newspapers are edited in London. London is a major retail center and in 2010 had the highest non-food retail sales of any city in the earth, with a total spend of around £64.2 billion. [ 281 ] The Port of London is the second largest in the United Kingdom, handling 45 million tonnes of cargo each year. [ 282 ] A growing number of technology companies are based in London, notably in East London Tech City, besides known as Silicon Roundabout. In April 2014 the city was among the beginning to receive a geoTLD. [ 283 ] [ 284 ] [ 285 ] In February 2014 London was ranked as the European City of the Future [ 286 ] in the 2014/15 list by FDi Magazine. [ 287 ] The gas and electricity distribution networks that do and operate the towers, cables and coerce systems that deliver energy to consumers across the city are managed by National Grid plc, SGN [ 288 ] and UK Power Networks. [ 289 ]
tourism
London is one of the leading tourist destinations in the global and in 2015 was ranked as the most visit city in the world with over 65 million visits. [ 290 ] [ 291 ] It is besides the top city in the world by visitor cross-border spending, estimated at US $ 20.23 billion in 2015. [ 292 ] Tourism is one of London ‘s prime industries, employing 700,000 full-time workers in 2016, and contributes £36 billion a year to the economy. [ 293 ] The city accounts for 54 % of all inbound visitor spending in the UK. [ 294 ] As of 2016 London was the worldly concern top city destination as ranked by TripAdvisor users. [ 295 ] In 2015 the crown most-visited attractions in the UK were all in London. The top 10 most visit attractions were : ( with visits per venue ) [ 296 ]
The number of hotel rooms in London in 2015 resist at 138,769, and is expected to grow over the years. [ 297 ]
transmit
 [298] Journeys in Greater London by mood from 1997 to 2018 transport is one of the four chief areas of policy administered by the Mayor of London, [ 299 ] but the mayor ‘s fiscal control condition does not extend to the longer-distance rail net that enters London. In 2007 the Mayor of London assumed province for some local anesthetic lines, which nowadays form the London Overground network, adding to the existing responsibility for the London Underground, trams and buses. The public conveyance network is administered by Transport for London ( TfL ). [ 300 ] The lines that formed the London Underground, ampere well as trams and buses, became separate of an integrated transport arrangement in 1933 when the London Passenger Transport Board or London Transport was created. Transport for London is now the statutory pot creditworthy for most aspects of the transport system in Greater London, and is run by a dining table and a commissioner appointed by the Mayor of London. [ 301 ]
[298] Journeys in Greater London by mood from 1997 to 2018 transport is one of the four chief areas of policy administered by the Mayor of London, [ 299 ] but the mayor ‘s fiscal control condition does not extend to the longer-distance rail net that enters London. In 2007 the Mayor of London assumed province for some local anesthetic lines, which nowadays form the London Overground network, adding to the existing responsibility for the London Underground, trams and buses. The public conveyance network is administered by Transport for London ( TfL ). [ 300 ] The lines that formed the London Underground, ampere well as trams and buses, became separate of an integrated transport arrangement in 1933 when the London Passenger Transport Board or London Transport was created. Transport for London is now the statutory pot creditworthy for most aspects of the transport system in Greater London, and is run by a dining table and a commissioner appointed by the Mayor of London. [ 301 ]
aviation
London is a major external breeze transport hub with the busiest city airspace in the world. Eight airports use the parole London in their name, but most traffic passes through six of these. additionally, assorted other airports besides serve London, catering primarily to general aviation flights .
rail
metro and DLR
The London Underground, normally referred to as the Tube, is the oldest [ 317 ] and third longest [ 318 ] metro system in the world. The organization serves 270 stations [ 319 ] and was formed from several private companies, including the earth ‘s first underground electric line, the City and South London Railway. [ 320 ] It dates from 1863. [ 321 ] Over four million journeys are made every day on the Underground network, over 1 billion each class. [ 322 ] An investment program is attempting to reduce congestion and improve dependability, including £6.5 billion ( €7.7 billion ) exhausted before the 2012 Summer Olympics. [ 323 ] The Docklands Light Railway ( DLR ), which opened in 1987, is a second, more local metro system using smaller and lighter tram-type vehicles that serve the Docklands, Greenwich and Lewisham .
suburban
There are more than 360 railway stations in the London Travelcard Zones on an extensive above-ground suburban railway network. South London, peculiarly, has a gamey concentration of railways as it has fewer Underground lines. Most rail lines terminate around the center of London, running into eighteen end stations, with the exception of the Thameslink trains connecting Bedford in the north and Brighton in the south via Luton and Gatwick airports. [ 324 ] London has Britain ‘s busiest station by number of passengers— Waterloo, with over 184 million people using the counterchange place complex ( which includes Waterloo East station ) each year. [ 325 ] [ 326 ] Clapham Junction is the busiest station in Europe by the number of trains passing. With the need for more vilify capacity in London, Crossrail is expected to open in 2021. [ 327 ] It will be a modern railroad track line running east to west through London and into the Home Counties with a outgrowth to Heathrow Airport. [ 328 ] It is Europe ‘s biggest construction visualize, with a £15 billion projected price. [ 329 ] [ 330 ]
Inter-city and international
London is the centre of the National Rail network, with 70 per penny of rail journeys starting or ending in London. [ 331 ] King ‘s Cross post and Euston station, which are both in London, are the starting points of the East Coast Main Line and the West Coast Main Line – the two main railroad track lines in Britain. Like suburban fulminate services, regional and inter-city trains depart from respective terminus around the city center, linking London with the pillow of Britain including Aberdeen, Birmingham, Blackpool, Bradford, Brighton, Bristol, Cambridge, Cardiff, Carlisle, Chester, Coventry, Crewe, Derby, Doncaster, Dover, Edinburgh, Exeter, Glasgow, Holyhead ( for Dublin ), Hull, Ipswich, Lancaster, Leeds, Liverpool, Nottingham, Manchester, Newcastle upon Tyne, Norwich, Oxford, Peterborough, Plymouth, Portsmouth, Preston, Reading, Sheffield, Southampton, Sunderland, Stevenage, Swansea, Weymouth, Wolverhampton and York. [ 332 ] London besides has convenient vilify connections with airports out of Greater London. These airports include Birmingham Airport ( via Birmingham International railroad track place ), East Midlands Airport ( via East Midlands Parkway railway station ), Inverness Airport ( via Inverness railway station ), Leeds Bradford Airport ( via Bradford Interchange or Leeds railway station ) and Liverpool John Lennon Airport ( via Liverpool South Parkway railway station ). [ 332 ] Some external railway services to Continental Europe were operated during the twentieth hundred as boat trains, such as the Admiraal de Ruijter to Amsterdam and the Night Ferry to Paris and Brussels. The open of the Channel Tunnel in 1994 connect London directly to the continental rail network, allowing Eurostar services to begin. Since 2007, high-speed trains link St. Pancras International with Lille, Calais, Paris, Disneyland Paris, Brussels, Amsterdam and other european tourist destinations via the High Speed 1 railing liaison and the Channel Tunnel. [ 333 ] The first gear high-speed domestic trains started in June 2009 linking Kent to London. [ 334 ] There are plans for a second high amphetamine course linking London to the Midlands, North West England, and Yorkshire .
freight
Although rail freight levels are far down compared to their height, significant quantities of cargo are besides carried into and out of London by vilify ; chiefly build materials and landfill pine away. As a major hub of the british railroad track network, London ‘s tracks besides carry large amounts of freight for the early regions, such as container freight from the Channel Tunnel and English Channel ports, and nuclear neutralize for reprocessing at Sellafield. [ 335 ]
Buses, coaches and trams
London ‘s busbar network runs 24 hours a day with about 9,300 vehicles, over 675 busbar routes and about 19,000 bus stops. [ 336 ] In 2019/1920 the network had over 2 billion commuter trips per year. [ 337 ] Since 2010 and median of £1.2 billion is taken in tax income each year. [ 338 ] London has one of the largest wheelchair-accessible networks in the universe [ 339 ] and from the one-third quarter of 2007, became more accessible to hearing and visually afflicted passengers as audio-visual announcements were introduced. [ 340 ] London ‘s bus hub is Victoria Coach Station, an Art Deco build opened in 1932. The passenger car station was initially run by a group of coach companies under the name of London Coastal Coaches ; however, in 1970 the service and post were included in the nationalization of the area ‘s coach services, becoming part of the National Bus Company. In 1988, the coach place was purchased by London Transport which then became Transport for London. Victoria Coach Station has weekly passenger numbers of over 200,000 and provides services across the UK and Europe. [ 341 ] [ failed verification ] London has a modern tram network, known as Tramlink, centred on Croydon in South London. The network has 39 stops and four routes, and carried 28 million people in 2013. [ 342 ] [ 343 ] Since June 2008, Transport for London has wholly owned and operated Tramlink. [ 344 ]
cable car
London ‘s beginning and to date lone cable car is the Emirates Air Line, which opened in June 2012. The cable car crosses the River Thames, and links Greenwich Peninsula and the Royal Docks in the east of the city. It is integrated with London ‘s Oyster Card ticketing system, although the Emirates Air Line fares are not included in the Oyster daily cap. [ 345 ] It cost £60 million to build and can carry up to 2,500 passengers per hour in each direction at peak times. exchangeable to the Santander Cycles bike hire outline, the cable car is sponsored in a 10-year softwood by the airline Emirates. [ 346 ]
cycle
 Santander Cycle Hire near Victoria in Central London In the Greater London Area, around 670,000 people use a bicycle every day, [ 347 ] meaning about 7 % of the full population of around 8.8 million use a bicycle on an average day. [ 348 ] [ 349 ] This relatively low percentage of bicycle users may be due to the inadequate investments for bicycle in London of about £110 million per year, [ 350 ] equating to around £12 per person, which can be compared to £22 in the Netherlands. [ 351 ] bicycle has become an increasingly popular means to get around London. The plunge of a bicycle hire system in July 2010 was successful and broadly well received. [ 352 ]
Santander Cycle Hire near Victoria in Central London In the Greater London Area, around 670,000 people use a bicycle every day, [ 347 ] meaning about 7 % of the full population of around 8.8 million use a bicycle on an average day. [ 348 ] [ 349 ] This relatively low percentage of bicycle users may be due to the inadequate investments for bicycle in London of about £110 million per year, [ 350 ] equating to around £12 per person, which can be compared to £22 in the Netherlands. [ 351 ] bicycle has become an increasingly popular means to get around London. The plunge of a bicycle hire system in July 2010 was successful and broadly well received. [ 352 ]
Port and river boats
The Port of London, once the largest in the earth, is nowadays only the second-largest in the United Kingdom, handling 45 million tonnes of cargo each class as of 2009. [ 282 ] Most of this cargo passes through the Port of Tilbury, outside the limit of Greater London. [ 282 ] London has river gravy boat services on the Thames known as Thames Clippers, which offer both commuter and tourist boat services. [ 353 ] At major piers including Canary Wharf, London Bridge City, Battersea Power Station and London Eye ( Waterloo ), services depart at least every 20 minutes during commuter times. [ 354 ] The Woolwich Ferry, with 2.5 million passengers every year, is a frequent service linking the North and South Circular Roads. [ 355 ]
Roads
Although the majority of journeys in cardinal London are made by public transport, cable car travel is common in the suburb. The inner band road ( around the city center ), the North and South Circular roads ( just within the suburb ), and the out orbital expressway ( the M25, barely outside the built-up area in most places ) encircle the city and are intersected by a act of busy radial routes—but very few motorways penetrate into inner London. A plan for a comprehensive examination network of motorways throughout the city ( the Ringways Plan ) was prepared in the 1960s but was largely cancelled in the early 1970s. [ 356 ] The M25 is the second-longest ring-road expressway in Europe at 117 secret intelligence service ( 188 km ) hanker. [ 357 ] The A1 and M1 connect London to Leeds, and Newcastle and Edinburgh. London is ill-famed for its traffic congestion ; in 2009, the average speed of a car in the rush hour was recorded at 10.6 miles per hour ( 17.1 kilometers per hour ). [ 358 ] In 2003, a congestion charge was introduced to reduce traffic volumes in the city center. With a few exceptions, motorists are required to pay to drive within a defined zone encompassing much of cardinal London. [ 359 ] Motorists who are residents of the specify partition can buy a greatly reduced temper exceed. [ 360 ] [ 361 ] The London government initially expected the Congestion Charge Zone to increase daily extremum time period Underground and bus users, reduce road dealings, increase traffic speeds, and reduce queues ; [ 362 ] however, the increase in private for hire vehicles has affected these expectations. Over the course of several years, the average phone number of cars entering the center of London on a weekday was reduced from 195,000 to 125,000 cars – a 35-per-cent decrease of vehicles driven per day. [ 363 ] [ 364 ]
education
tertiary education
London is a major ball-shaped center of higher education teaching and research and has the largest concentration of higher education institutes in Europe. [ 20 ] According to the QS World University Rankings 2015/16, London has the greatest concentration of top class universities in the earth [ 365 ] [ 366 ] and its international scholar population of around 110,000 is larger than any other city in the worldly concern. [ 367 ] A 2014 PricewaterhouseCoopers composition termed London the global capital of higher department of education. [ 368 ]
A number of world-leading education institutions are based in London. In the 2021 QS World University Rankings, Imperial College London is ranked # 8 in the earth, University College London ( UCL ) is rank tenth, and King ‘s College London ( KCL ) is rank thirty-first. [ 369 ] The London School of Economics has been described as the world ‘s leadership social science mental hospital for both teaching and inquiry. [ 370 ] The London Business School is considered one of the world ‘s lead business schools and in 2015 its MBA broadcast was ranked second-best in the world by the Financial Times. [ 371 ] The city is besides family to three of the world ‘s top ten-spot performing arts schools ( as ranked by the 2020 QS World University Rankings [ 372 ] ) : the Royal College of Music ( ranking 2nd in the global ), the Royal Academy of Music ( ranking 4th ) and the Guildhall School of Music and Drama ( ranking 6th ). With students in London [ 373 ] and around 48,000 in University of London Worldwide, [ 374 ] the federal University of London is the largest contact teaching university in the UK. [ 375 ] It includes five multi-faculty universities – City, King ‘s College London, Queen Mary, Royal Holloway and UCL – and a number of smaller and more specialize institutions including Birkbeck, the Courtauld Institute of Art, Goldsmiths, the London Business School, the London School of Economics, the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, the Royal Academy of Music, the Central School of Speech and Drama, the Royal Veterinary College and the School of Oriental and African Studies. [ 376 ] Members of the University of London have their own admissions procedures, and most award their own degrees. A numeral of universities in London are outside the University of London arrangement, including Brunel University, Imperial College London, [ note 6 ] Kingston University, London Metropolitan University, [ 377 ] University of East London, University of West London, University of Westminster, London South Bank University, Middlesex University, and University of the Arts London ( the largest university of art, design, fashion, communication and the perform arts in Europe ). [ 378 ] In summation there are three external universities in London – Regent ‘s University London, Richmond, The American International University in London and Schiller International University .
London is home to five major aesculapian schools – Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry ( region of Queen Mary ), King ‘s College London School of Medicine ( the largest medical educate in Europe ), Imperial College School of Medicine, UCL Medical School and St George ‘s, University of London – and has many affiliated teach hospitals. It is besides a major centre for biomedical research, and three of the UK ‘s eight academic health science centres are based in the city – Imperial College Healthcare, King ‘s Health Partners and UCL Partners ( the largest such center in Europe ). [ 379 ] Additionally, many biomedical and biotechnology spin out companies from these inquiry institutions are based around the city, most prominently in White City .There are a act of business schools in London, including the London School of Business and Finance, Cass Business School ( separate of City University London ), Hult International Business School, ESCP Europe, European Business School London, Imperial College Business School, the London Business School and the UCL School of Management. London is besides home to many specialist arts education institutions, including the Academy of Live and Recorded Arts, Central School of Ballet, LAMDA, London College of Contemporary Arts ( LCCA ), London Contemporary Dance School, National Centre for Circus Arts, RADA, Rambert School of Ballet and Contemporary Dance, the Royal College of Art and Trinity Laban .
Primary and secondary education
The majority of chief and secondary schools and further-education colleges in London are controlled by the London boroughs or otherwise state-funded ; leading examples include Ashbourne College, Bethnal Green Academy, Brampton Manor Academy, City and Islington College, City of Westminster College, David Game College, Ealing, Hammersmith and West London College, Leyton Sixth Form College, London Academy of Excellence, Tower Hamlets College, and Newham Collegiate Sixth Form Centre. There are besides a phone number of private schools and colleges in London, some erstwhile and celebrated, such as City of London School, Harrow, St Paul ‘s School, Haberdashers ‘ Aske ‘s Boys ‘ School, University College School, The John Lyon School, Highgate School and Westminster School .
culture
leisure and entertainment
leisure is a major part of the London economy. A 2003 report attributed a quarter of the entire UK leisure economy to London [ 380 ] at 25.6 events per 1000 people. [ 381 ] Globally the city is one of the big four fashion capitals of the universe, and according to official statistics, it is the universe ‘s third-busiest film production center, presents more populate drollery than any other city, [ 382 ] and has the biggest dramaturgy consultation of any city in the world. [ 383 ]
Within the City of Westminster in London, the entertainment zone of the West end has its focus around Leicester Square, where London and universe film premieres are held, and Piccadilly Circus, with its giant electronic advertisements. [ 384 ] London ‘s dramaturgy district is here, as are many cinemas, bars, clubs, and restaurants, including the city ‘s Chinatown zone ( in Soho ), and precisely to the east is Covent Garden, an area caparison forte shops. The city is the home of Andrew Lloyd Webber, whose musicals have dominated the West End dramaturgy since the late twentieth hundred. [ 385 ] The United Kingdom ‘s Royal Ballet, English National Ballet, Royal Opera, and English National Opera are based in London and perform at the Royal Opera House, the London Coliseum, Sadler ‘s Wells Theatre, and the Royal Albert Hall, equally well as touring the country. [ 386 ]
Islington ‘s 1 sea mile ( 1.6 km ) long Upper Street, extending northwards from Angel, has more bars and restaurants than any other street in the United Kingdom. [ 387 ] Europe ‘s busiest denounce area is Oxford Street, a shop street about 1 nautical mile ( 1.6 km ) long, making it the longest shopping street in the UK. Oxford Street is home to huge numbers of retailers and department stores, including the world-famous Selfridges flagship shop. [ 388 ] Knightsbridge, home to the equally celebrated Harrods department store, lies to the southwest. London is home to designers Vivienne Westwood, Galliano, Stella McCartney, Manolo Blahnik, and Jimmy Choo, among others ; its celebrated art and fashion schools make it an external center of fashion alongside Paris, Milan, and New York City. London offers a great variety show of cuisine as a resultant role of its ethnically divers population. Gastronomic centres include the Bangladeshi restaurants of Brick Lane and the chinese restaurants of Chinatown. [ 389 ]
There is a kind of annual events, beginning with the relatively new New Year ‘s Day Parade, a firework display at the London Eye ; the universe ‘s second largest street party, the Notting Hill Carnival, is held on the late August Bank Holiday each year. Traditional parades include November ‘s Lord Mayor ‘s Show, a centuries-old consequence celebrating the annual appointment of a newly Lord Mayor of the City of London with a progress along the streets of the city, and June ‘s Trooping the Colour, a formal military pageant performed by regiments of the Commonwealth and british armies to celebrate the Queen ‘s official Birthday. [ 390 ] The Boishakhi Mela is a Bengali New Year festival celebrated by the british Bangladeshi community. It is the largest alfresco asian festival in Europe. After the Notting Hill Carnival, it is the second-largest street festival in the United Kingdom attracting over 80,000 visitors from across the area. [ 391 ]
literature, film and television
London has been the setting for many works of literature. The pilgrims in Geoffrey Chaucer ‘s deep 14th-century Canterbury Tales set out for Canterbury from London—specifically, from the Tabard hostel, Southwark. William Shakespeare spent a big partially of his life surviving and working in London ; his contemporary Ben Jonson was besides based there, and some of his sour, most notably his act The Alchemist, was set in the city. [ 392 ] A Journal of the Plague Year ( 1722 ) by Daniel Defoe is a fictionalization of the events of the 1665 Great Plague. [ 392 ] The literary centres of London have traditionally been cragged Hampstead and ( since the early twentieth hundred ) Bloomsbury. Writers closely associated with the city are the diarist Samuel Pepys, noted for his eyewitness account of the Great Fire ; Charles Dickens, whose representation of a fogged, snow-white, begrimed London of street sweepers and pickpockets has been a major influence on people ‘s imagination of early victorian London ; and Virginia Woolf, regarded as one of the foremost modernist literary figures of the twentieth hundred. [ 392 ] Later important depictions of London from the 19th and early twentieth centuries are Dickens ‘ novels, and Arthur Conan Doyle ‘s Sherlock Holmes stories. [ 392 ] besides of meaning is Letitia Elizabeth Landon ‘s Calendar of the London Seasons ( 1834 ). modern writers pervasively influenced by the city include Peter Ackroyd, generator of a “ biography ” of London, and Iain Sinclair, who writes in the genre of psychogeography .
London has played a significant role in the film industry. major studios within or bordering London include Twickenham, Ealing, Shepperton, Pinewood, Elstree and Borehamwood, [ 393 ] and a particular effects and post-production community centred in Soho. Working Title Films has its headquarters in London. [ 394 ] London has been the set for films including Oliver Twist ( 1948 ), Scrooge ( 1951 ), Peter Pan ( 1953 ), The 101 Dalmatians ( 1961 ), My Fair Lady ( 1964 ), Mary Poppins ( 1964 ), Blowup ( 1966 ), The Long Good Friday ( 1980 ), The Great Mouse Detective ( 1986 ), Notting Hill ( 1999 ), Love Actually ( 2003 ), V For Vendetta ( 2005 ), Sweeney Todd: The Demon Barber of Fleet Street ( 2008 ) and The King’s Speech ( 2010 ). celebrated actors and filmmakers from London include ; Charlie Chaplin, Alfred Hitchcock, Michael Caine, Helen Mirren, Gary Oldman, Christopher Nolan, Jude Law, Benedict Cumberbatch, Tom Hardy, Keira Knightley and Daniel Day-Lewis. Since 2008, the british Academy Film Awards have taken rate at the Royal Opera House. London is a major center for television product, with studios including BBC Television Centre, The Fountain Studios and The London Studios. many television receiver programmes have been set in London, including the popular television soap opera EastEnders, broadcast by the BBC since 1985 .
Museums, artwork galleries and libraries
London is home to many museums, galleries, and other institutions, many of which are free of admission charges and are major tourist attractions american samoa well as playing a inquiry character. The foremost of these to be established was the british Museum in Bloomsbury, in 1753. [ 395 ] Originally containing antiquities, natural history specimens, and the national library, the museum immediately has 7 million artefacts from around the ball. In 1824, the National Gallery was founded to house the british national collection of western paintings ; this now occupies a big position in Trafalgar Square. The british Library is the second largest library in the world, and the national library of the United Kingdom. [ 396 ] [ 397 ] [ 398 ] There are many early inquiry libraries, including the Wellcome Library and Dana Centre, vitamin a well as university libraries, including the british Library of Political and Economic Science at LSE, the Central Library at Imperial, the Maughan Library at King ‘s, and the Senate House Libraries at the University of London. [ 399 ] [ 400 ] In the latter half of the nineteenth hundred the venue of South Kensington was developed as “ Albertopolis “, a cultural and scientific one-fourth. Three major national museums are there : the Victoria and Albert Museum ( for the put on arts ), the Natural History Museum, and the Science Museum. The National Portrait Gallery was founded in 1856 to family depictions of figures from british history ; its holdings now comprise the universe ‘s most extensive solicitation of portraits. [ 401 ] The national veranda of british art is at Tate Britain, originally established as an annex of the National Gallery in 1897. The Tate Gallery, as it was once known, besides became a major center for modern art. In 2000, this collection moved to Tate Modern, a fresh veranda housed in the early Bankside Power Station, which was built by the Basel -based computer architecture tauten of Herzog & de Meuron. [ 402 ]
music
London is one of the major classical music and democratic music capitals of the world and hosts major music corporations, such as Universal Music Group International and Warner Music Group, equally well as countless bands, musicians and industry professionals. The city is besides home to many orchestras and concert halls, such as the Barbican Arts Centre ( star base of the London Symphony Orchestra and the London Symphony Chorus ), the Southbank Centre ( London Philharmonic Orchestra and the Philharmonia Orchestra ), Cadogan Hall ( Royal Philharmonic Orchestra ) and the Royal Albert Hall ( The Proms ). [ 386 ] London ‘s two chief opera houses are the Royal Opera House and the London Coliseum ( home to the English National Opera ). [ 386 ] The UK ‘s largest shriek organ is at the Royal Albert Hall. other significant instruments are at the cathedrals and major churches. several conservatoires are within the city : Royal Academy of Music, Royal College of Music, Guildhall School of Music and Drama and Trinity Laban. London has numerous venues for rock and pop music concerts, including the universe ‘s busiest indoor venue, The O2 Arena [ 403 ] and Wembley Arena, vitamin a well as many mid-sized venues, such as Brixton Academy, the Hammersmith Apollo and the Shepherd ‘s Bush Empire. [ 386 ] several music festivals, including the Wireless Festival, South West Four, Lovebox, and Hyde Park ‘s british Summer Time are all held in London. [ 404 ] The city is home to the original Hard Rock Cafe and the Abbey Road Studios, where The Beatles recorded many of their hits. In the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s, musicians and groups like Elton John, Pink Floyd, Cliff Richard, David Bowie, Queen, The Kinks, The Rolling Stones, The Who, Eric Clapton, Led Zeppelin, The Small Faces, Iron Maiden, Fleetwood Mac, Elvis Costello, Cat Stevens, The Police, The Cure, Madness, The Jam, Ultravox, Spandau Ballet, Culture Club, Dusty Springfield, Phil Collins, Rod Stewart, Adam Ant, Status Quo and Sade, derived their sound from the streets and cycle of London. [ 405 ] London was implemental in the development of punk rocker music, with figures such as the Sex Pistols, The Clash, and Vivienne Westwood all based in the city. [ 406 ] [ 407 ] More holocene artists to emerge from the London music picture include George Michael ‘s Wham !, Kate Bush, Seal, the Pet Shop Boys, Bananarama, Siouxsie and the Banshees, Bush, the Spice Girls, Jamiroquai, Blur, McFly, The Prodigy, Gorillaz, Bloc Party, Mumford & Sons, Coldplay, Amy Winehouse, Adele, Sam Smith, Ed Sheeran, Paloma Faith, Ellie Goulding, One guidance and Florence and the Machine. [ 408 ] [ 409 ] [ 410 ] London is besides a centre for urban music. In particular the genres UK garage, drum and bass, dubstep and dirty evolved in the city from the extraneous genres of house, hip hop, and reggae, aboard local drum and bass. music station BBC Radio 1Xtra was set up to support the rise of local urban contemporaneous music both in London and in the rest of the United Kingdom .
refreshment
Parks and exposed spaces
A 2013 report by the City of London Corporation said that London is the “ greenest city ” in Europe with 35,000 acres of populace parks, woodlands and gardens. [ 411 ] The largest park in the cardinal sphere of London are three of the eight Royal Parks, namely Hyde Park and its neighbor Kensington Gardens in the west, and Regent ‘s Park to the north. [ 412 ] Hyde Park in particular is popular for sports and sometimes hosts alfresco concerts. Regent ‘s Park contains London Zoo, the universe ‘s oldest scientific menagerie, and is approximate Madame Tussauds Wax Museum. [ 413 ] [ 414 ] Primrose Hill, immediately to the north of Regent ‘s Park, at 256 feet ( 78 thousand ) [ 415 ] is a democratic spotlight from which to view the city horizon. close to Hyde Park are smaller Royal Parks, Green Park and St. James ‘s Park. [ 416 ] A count of boastfully parks lie outside the city center, including Hampstead Heath and the remaining Royal Parks of Greenwich Park to the southeast [ 417 ] and Bushy Park and Richmond Park ( the largest ) to the southwest, [ 418 ] [ 419 ] Hampton Court Park is besides a royal park, but, because it contains a palace, it is administered by the Historic Royal Palaces, unlike the eight Royal Parks. [ 420 ] close to Richmond Park is Kew Gardens, which has the world ‘s largest collection of animation plants. In 2003, the gardens were put on the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites. [ 421 ] There are besides parks administered by London ‘s borough Councils, including Victoria Park in the East End and Battersea Park in the center. Some more informal, semi-natural open spaces besides exist, including the 320-hectare ( 790-acre ) Hampstead Heath of North London, [ 422 ] and Epping Forest, which covers 2,476 hectares ( 6,118 acres ) [ 423 ] in the east. Both are controlled by the City of London Corporation. [ 424 ] [ 425 ] Hampstead Heath incorporates Kenwood House, a erstwhile baronial home and a popular location in the summer months when classical music musical concerts are held by the lake, attracting thousands of people every weekend to enjoy the music, scenery and fireworks. [ 426 ] Epping Forest is a popular venue for versatile outdoor activities, including batch bicycle, walk, sawhorse riding, golf, angling, and orienteering. [ 427 ]
Walking
Walking is a popular recreational bodily process in London. Areas that provide for walks include Wimbledon Common, Epping Forest, Hampton Court Park, Hampstead Heath, the eight Royal Parks, canals and disused railroad track tracks. [ 428 ] Access to canals and rivers has improved recently, including the universe of the Thames Path, some 28 miles ( 45 kilometer ) of which is within Greater London, and The Wandle Trail ; this runs 12 miles ( 19 kilometer ) through South London along the River Wandle, a conducive of the River Thames. [ 429 ] other long-distance paths, linking green spaces, have besides been created, including the das kapital Ring, the Green Chain Walk, London Outer Orbital Path ( “ Loop ” ), Jubilee Walkway, Lea Valley Walk, and the Diana, Princess of Wales Memorial Walk. [ 428 ]
sport
London has hosted the Summer Olympics three times : in 1908, 1948, and 2012, [ 430 ] [ 431 ] making it the first city to host the mod Games three times. [ 23 ] The city was besides the server of the british Empire Games in 1934. [ 432 ] In 2017, London hosted the World Championships in Athletics for the first time. [ 433 ] London ‘s most democratic sport is football and it has six clubs in the English Premier League as of the 2021–22 season : Arsenal, Brentford, Chelsea, Crystal Palace, Tottenham Hotspur, and West Ham United. [ 434 ] other professional teams in London are AFC Wimbledon, Barnet, Bromley, Charlton Athletic, Dagenham & Redbridge, Fulham, Leyton Orient, Millwall, Queens Park Rangers and Sutton United .
From 1924, the original Wembley Stadium was the home of the English national football team. It hosted the 1966 FIFA World Cup Final, with England defeating West Germany, and served as the venue for the FA Cup Final a well as rugby league ‘s Challenge Cup concluding. [ 436 ] The new Wembley Stadium serves precisely the same purposes and has a capability of 90,000. [ 437 ] Two Premiership Rugby union teams are based in London, Harlequins and London Irish. [ 438 ] Ealing Trailfinders, Richmond and Saracens play in the RFU Championship and other rugby union clubs in the city include London Scottish, Rosslyn Park F.C., Westcombe Park R.F.C. and Blackheath F.C. . Twickenham Stadium in southwest London hosts home matches for the England national rugby union team and has a capability of 82,000 now that the newly south resist has been completed. [ 439 ] While rugby league is more popular in the north of England, there are two professional rugby league clubs in London – the London Broncos in the second-tier RFL Championship, who play at the Trailfinders Sports Ground in West Ealing, and the third-tier League 1 team, the London Skolars from Wood Green, Haringey. One of London ‘s best-known annual sports competitions is the Wimbledon Tennis Championships, held at the All England Club in the south-western suburb of Wimbledon. [ 440 ] Played in deep June to early July, it is the oldest tennis tournament in the world and widely considered the most prestigious. [ 441 ] [ 442 ] [ 443 ] London has two Test cricket grounds, Lord ‘s ( home of Middlesex C.C.C. ) in St John ‘s Wood [ 444 ] and the Oval ( home of Surrey C.C.C. ) in Kennington. [ 445 ] Lord ‘s has hosted four finals of the Cricket World Cup and is known as the Home of Cricket. [ 446 ] other key events are the annual mass-participation London Marathon, in which some 35,000 runners attempt a 26.2-mile ( 42.2 kilometer ) class around the city, [ 447 ] and the University Boat Race on the River Thames from Putney to Mortlake. [ 448 ]
celebrated people
See besides
Notes
References
bibliography
London at Wikipedia’s at Wikipedia ‘s
sister projects
Read more: 2015–16 Liverpool F.C. season – Wikipedia
