“ thailand ” redirects here. For early uses, see Siam ( disambiguation ) Coordinates :
You may need rendering support to display the Thai text in this article correctly.
Thailand ( Thai : ประเทศไทย ), [ a ] historically known as Siam, [ bacillus ] officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia. It is located at the center of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning 513,120 square kilometres ( 198,120 sq myocardial infarction ), with a population of about 70 million people. [ 5 ] Thailand is bordered to the union by Myanmar and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the confederacy by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the west by the Andaman Sea and Myanmar. It besides shares maritime borders with Vietnam in the Gulf of Thailand to the southeast, and Indonesia and India ( Andaman and Nicobar Islands ) on the Andaman Sea to the southwest. Bangkok is the nation ‘s capital and largest city. nominally, Thailand is a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy ; however, in holocene history, its government has experienced multiple coups and periods of military dictatorships.
Reading: Wikipedia
Tai peoples migrated from southwestern China to mainland Southeast Asia from the eleventh hundred ; the oldest know mention of their presence in the region by the exonym Siamese dates to the twelfth hundred. Various Indianised kingdoms such as the Mon kingdoms, Khmer Empire and Malay states ruled the region, competing with Thai states such as the Kingdoms of Ngoenyang, Sukhothai, Lan Na and Ayutthaya, which rivalled each early. Documented european touch began in 1511 with a portuguese diplomatic mission to Ayutthaya, which became a regional power by the end of the fifteenth century. Ayutthaya reached its bill during cosmopolitan Narai ‘s predominate, gradually declining thereafter until being ultimately destroyed in the 1767 Burmese–Siamese War. Taksin cursorily reunified the disconnected territory and established the ephemeral Thonburi Kingdom. He was succeeded in 1782 by Buddha Yodfa Chulaloke, the first sovereign of the stream Chakri dynasty. Throughout the era of western imperialism in Asia, Siam remained the only nation in the region to avoid being colonized by extraneous powers, although it was much forced to cede both territory and trade concessions in unequal treaties. The thai system of politics was centralized and transformed into a advanced one absolute monarchy in the reign of Chulalongkorn. In World War I, Siam sided with the allies, a political decisiveness to amend the inadequate treaties. Following a bloodless revolution in 1932, it became a constitutional monarchy and changed its official list to Thailand, which was an ally of Japan in World War II. In the belated 1950s, a military coup under Field Marshal Sarit Thanarat revived the monarchy ‘s historically influential role in politics. Thailand became a major ally of the United States, and played an anti-communist function in the region as a extremity of the fail SEATO, but since 1975, had sought to improve relations with Communist China and Thailand ‘s neighbors. apart from a abbreviated menstruation of parliamentary majority rule in the mid-1970s, Thailand has sporadically alternated between majority rule and military rule. Since the 2000s, it has been caught in a series of bitter political conflict between supporters and opponents of Thaksin Shinawatra, which culminated in two coups, most recently in 2014 and the institution of its current and twentieth united states constitution and faces the ongoing pro-democracy protests. Thailand is a middle exponent in global affairs, and a establish penis of ASEAN ; ranking high in the Human Development Index. It has the second-largest economy in Southeast Asia, and the 20th-largest in the global by PPP. Thailand is classified as a newly industrialized economy ; fabricate, department of agriculture, and tourism are leading sectors of the economy. [ 12 ] [ 13 ]
etymology
Thailand ( TY-land or TY-lənd ; [ 14 ] thai : ประเทศไทย, RTGS : Prathet Thai, pronounced [ pratʰêːt tʰaj ] ( ) ), officially the Kingdom of Thailand ( Thai : ราชอาณาจักรไทย, RTGS : Ratcha-anachak Thai [ râːtt͡ɕʰaʔaːnaːt͡ɕàk tʰaj ] ( ) ), once known as Siam ( Thai : สยาม, RTGS : Sayam [ sajǎːm ] ), is a country at the center of the Indochinese peninsula in Southeast Asia .
etymology of Siam
The state has always been called Mueang Thai by its citizens. [ citation needed ] By outsiders, anterior to 1949, it was normally known by the exonym Siam ( Thai : สยาม RTGS : sayam, pronounced [ sajǎːm ], besides spelled Siem, Syâm, or Syâma ). The give voice Siam may have originated from Pali ( suvaṇṇabhūmi, ‘land of aureate ‘ ) or Sanskrit श्याम ( śyāma, ‘dark ‘ ) or Mon ရာမည ( rhmañña, ‘stranger ‘ ). The names Shan and A-hom appear to be variants of the like word. The word Śyâma is possibly not its origin, but a determine and artificial distorted shape. [ clarification needed ] [ 15 ] Another hypothesis is the list derives from taiwanese : “ Ayutthaya emerged as a dominant center in the belated fourteenth century. The Chinese called this area xian, which the Portuguese converted into Siam. ” [ 16 ] : 8 A promote hypothesis is that Mon -speaking peoples migrating confederacy called themselves syem as do the autochthonal Mon-Khmer -speaking inhabitants of the Malay Peninsula. [ citation needed ]
The signature of King Mongkut ( r. 1851–1868 ) reads SPPM ( Somdet Phra Poramenthra Maha ) Mongkut Rex Siamensium ( Mongkut, King of the Siamese ), and the custom of the list in the first external Bowring Treaty giving the name Siam official status until 24 June 1939 when it was changed to “ Thailand ”. [ 17 ] Thailand was renamed Siam from 1946 to 1948, after which it again reverted to “ Thailand ” .
etymology of “ Thailand ”
According to George Cœdès, the bible Thai ( ไทย ) means ‘free man ‘ in the Thai language, “ differentiating the thai from the natives encompassed in Thai company as serf ”. [ 18 ] : 197 A celebrated Thai scholar argued that Thai ( ไท ) just means ‘people ‘ or ‘human being ‘, since his investigation shows that in some rural areas the give voice “ Thai ” was used alternatively of the common Thai bible khon ( คน ) for people. [ 19 ] According to Michel Ferlus, the ethnonyms Thai-Tai ( or Thay-Tay ) would have evolved from the etymon *k(ə)ri: ‘human being ‘ through the be chain : *kəri: > *kəli: > *kədi:/*kədaj > *di:/*daj > *dajA ( Proto-Southwestern Tai ) > tʰajA2 ( in Siamese and Lao ) or > tajA2 ( in the early Southwestern and Central Tai languages classified by Li Fangkuei ). [ 20 ] Michel Ferlus ‘s work is based on some simple rules of phonetic change discernible in the Sinosphere and studied for the most separate by William H. Baxter ( 1992 ). [ 21 ] While Thai people will frequently refer to their country using the civilized class prathet Thai ( Thai : ประเทศไทย ), they most normally use the more colloquial term mueang Thai ( Thai : เมืองไทย ) or merely Thai; the word mueang, archaically referring to a city state, is normally used to refer to a city or town as the center of a region. Ratcha Anachak Thai ( Thai : ราชอาณาจักรไทย ) means ‘kingdom of Thailand ‘ or ‘kingdom of Thai ‘. Etymologically, its components are : ratcha ( Sanskrit : राजन्, rājan, ‘king, royal, region ‘ ) ; -ana- ( Pali āṇā ‘authority, command, office ‘, itself from the Sanskrit आज्ञा, ājñā, of the same mean ) -chak ( from Sanskrit चक्र cakra- ‘wheel ‘, a symbol of baron and predominate ). The Thai National Anthem ( Thai : เพลงชาติ ), written by Luang Saranupraphan during the patriotic 1930s, refers to the Thai nation as prathet Thai ( Thai : ประเทศไทย ). The first argumentation of the national hymn is : prathet thai ruam lueat nuea chat chuea thai ( Thai : ประเทศไทยรวมเลือดเนื้อชาติเชื้อไทย ), ‘Thailand is the one of Thai flesh and blood ‘ .
history
prehistory
There is testify of continuous homo dwelling in contemporary Thailand from 20,000 years ago to the present day. [ 23 ] : 4 The earliest evidence of rice originate is dated at 2,000 BCE. [ 22 ] : 4 Bronze appeared circa 1,250–1,000 BCE. [ 22 ] : 4 The site of Ban Chiang in northeast Thailand presently ranks as the earliest known center of copper and bronze production in Southeast Asia. [ 24 ] Iron appeared around 500 BCE. [ 22 ] : 5 The Kingdom of Funan was the beginning and most brawny southeast asian kingdom at the time ( second century BCE ). [ 23 ] : 5 The Mon people established the principalities of Dvaravati and Kingdom of Hariphunchai in the sixth hundred. The Khmer people established the Khmer empire, centred in Angkor, in the ninth century. [ 23 ] : 7 Tambralinga, a Malay state controlling barter through the Malacca Strait, rose in the tenth hundred. [ 23 ] : 5 The Indochina peninsula was heavy influenced by the acculturation and religions of India from the time of the Kingdom of Funan to that of the Khmer Empire. [ 25 ] The Thai people are of the Tai cultural group, characterised by coarse linguistic roots. [ 26 ] : 2 chinese chronicles first mention the Tai peoples in the sixth century BCE. While there are many assumptions regarding the origin of Tai peoples, David K. Wyatt, a historian of Thailand, argued that their ancestors which at the introduce dwell Laos, Thailand, Myanmar, India, and China came from the Điện Biên Phủ sphere between the 5th and the eighth century. [ 26 ] : 6 Thai people began migrating into contemporary Thailand around the eleventh century, which Mon and Khmer people occupied at the fourth dimension. [ 27 ] Thus Thai culture was influenced by indian, Mon, and Khmer cultures. [ 28 ] According to french historian George Cœdès, “ The Thai first enter history of Farther India in the eleventh century with the note of Syam slaves or prisoners of war in Champa epigraphy ”, and “ in the twelfth hundred, the bas-reliefs of Angkor Wat “ where “ a group of warriors ” are described as Syam. [ 18 ] : 190–191, 194–195
early on states and Sukhothai Kingdom
After the worsen of the Khmer Empire and Kingdom of Pagan in the early-13th hundred, diverse states thrived in their stead. The domains of Tai people existed from the northeasterly of contemporary India to the north of contemporary Laos and to the Malay peninsula. [ 26 ] : 38–9 During the thirteenth hundred, Tai people had already settled in the core land of Dvaravati and Lavo Kingdom to Nakhon Si Thammarat in the south. There are, however, no records detailing the arrival of the Tais. [ 26 ] : 50–1 Around 1240, Pho Khun Bang Klang Hao, a local Tai rule, rallied the people to rebel against the Khmer. He late crowned himself the first king of Sukhothai Kingdom in 1238. [ 26 ] : 52–3 Mainstream Thai historians count Sukhothai as the first kingdom of Thai people. Sukhothai expanded furthest during the reign of Ram Khamhaeng ( r. 1279–1298 ). however, it was largely a network of local lords who swore allegiance to Sukhothai, not immediately controlled by it. [ 26 ] : 55–6 He is believed have invented Thai script and Thai ceramics were an important export in his era. Sukhothai embraced Theravada Buddhism in the predominate of Maha Thammaracha I ( 1347–1368 ). To the north, Mangrai, who descended from a local rule linage of Ngoenyang, founded the kingdom of Lan Na in 1292, centered in Chiang Mai. He unified the surrounding sphere and his dynasty would rule the kingdom continuously for the future two centuries. He besides created a network of states through political alliances to the east and north of the Mekong. [ 16 ] : 8 While in the port in Lower Chao Phraya Basin, a federation around Phetchaburi, Suphan Buri, Lopburi, and the Ayutthaya area was created in the eleventh hundred. [ 16 ] : 8
Ayutthaya Kingdom
According to the most wide accept version of its lineage, the Ayutthaya Kingdom rose from the earlier, nearby Lavo Kingdom and Suvarnabhumi with Uthong as its first king. Ayutthaya was a patchwork of autonomous principalities and tributary provinces owing commitment to the King of Ayutthaya under the mandala system. [ 29 ] : 355 Its initial expansion was through seduction and political marriage. Before the end of the fifteenth century, Ayutthaya invaded the Khmer Empire three times and sacked its capital Angkor. [ 30 ] : 26 Ayutthaya then became a regional baron in place of the Khmer. changeless noise of Sukhothai efficaciously made it a vassal state of Ayutthaya and it was last incorporated into the kingdom. Borommatrailokkanat brought about bureaucratic reforms which lasted into the twentieth hundred and created a organization of social hierarchy called sakdina, where male commoners were conscripted as corvée labourers for six months a year. [ 31 ] : 107 Ayutthaya was concerned in the Malay peninsula, but failed to conquer the Malacca Sultanate which was supported by the taiwanese Ming Dynasty. [ 23 ] : 11, 13 european contact and trade started in the early-16th hundred, with the envoy of Portuguese duke Afonso de Albuquerque in 1511, Portugal became an allied and ceded some soldiers to King Rama Thibodi II. [ 32 ] The Portuguese were followed in the seventeenth hundred by the french, Dutch, and English. Rivalry for domination over Chiang Mai and the Mon people pitted Ayutthaya against the burmese Kingdom. several wars with its govern dynasty Taungoo Dynasty starting in the 1540s in the predominate of Tabinshwehti and Bayinnaung were ultimately ended with the capture of the capital in 1570. [ 31 ] : 146–7 then was a brief period of serfdom to Burma until Naresuan proclaimed independence in 1584. [ 16 ] : 11 Ayutthaya then sought to improve relations with european powers for many consecutive reigns. The kingdom specially prospered during cosmopolitan Narai ‘s reign ( 1656–1688 ) when some european travelers regarded Ayutthaya as an asian great exponent, alongside China and India. [ 22 ] : nine however, growing french influence later in his predominate was met with patriot sentiment and led finally to the thai revolution of 1688. [ 31 ] : 185–6 however, overall relations remained stable, with french missionaries still active in preaching Christianity. [ 31 ] : 186 After a bally period of dynastic conflict, Ayutthaya entered into what has been called the Siamese “ golden age “, a relatively peaceful episode in the second quarter of the eighteenth hundred when art, literature, and learning flourished. There were rarely foreign wars, apart from conflict with the Nguyễn Lords for operate of Cambodia starting around 1715. The last fifty years of the kingdom witnessed bally succession crises, where there were purges of motor hotel officials and able generals for many consecutive reigns. In 1765, a combined 40,000-strong wedge of burmese armies invaded it from the north and west. [ 33 ] : 250 The Burmese under the fresh Alaungpaya dynasty cursorily rose to become a modern local power by 1759. After a 14-month siege, the capital city ‘s walls fell and the city was burned in April 1767. [ 34 ] : 218
Thonburi Kingdom
The das kapital and much territories lied in chaos after the war. The former capital was occupied by the Burmese garrison united states army and five local leaders declared themselves overlords, including the lords of Sakwangburi, Pimai, Chanthaburi, and Nakhon Si Thammarat. Chao Tak, a capable military drawing card, proceeded to make himself a lord by properly of seduction, beginning with the fabled sack of Chanthaburi. Based at Chanthaburi, Chao Tak raised troops and resources, and sent a fleet up the Chao Phraya to take the fortress of Thonburi. In the same year, Chao Tak was able to retake Ayutthaya from the Burmese merely seven months after the fall of the city. [ 35 ] Chao Tak then crowned himself as Taksin and proclaimed Thonburi as impermanent capital in the like year. He besides quickly subdued the other warlords. His forces engaged in wars with Burma, Laos, and Cambodia, which successfully drove the Burmese out of Lan Na in 1775, [ 31 ] : 225 captured Vientiane in 1778 [ 31 ] : 227–8 and tried to install a pro-Thai king in Cambodia in the 1770s. In his concluding years there was a coup d’etat, caused purportedly by his “ insanity ”, and finally Taksin and his sons were executed by his longtime companion General Chao Phraya Chakri ( the future Rama I ). He was the first baron of the opinion Chakri Dynasty and fall through of the Rattanakosin Kingdom on 6 April 1782 .
modernization and centralization
Under Rama I ( 1782–1809 ), Rattanakosin successfully defended against burmese attacks and put an end to burmese incursions. He besides created suzerainty over big portions of Laos and Cambodia. [ 36 ] In 1821, Briton John Crawfurd was sent to negotiate a new trade wind agreement with Siam – the foremost sign of the zodiac of an issue which was to dominate nineteenth century thai politics. [ 37 ] Bangkok signed the Burney Treaty in 1826, after the british victory in the first Anglo-Burmese War. [ 31 ] : 281 Anouvong of Vientiane, who mistakenly held the belief that Britain was about to launch an invasion of Bangkok, started the Lao rebellion in 1826 which was suppressed. [ 31 ] : 283–5 Vientiane was destroyed and a large number of Lao people were relocated to Khorat Plateau as a consequence. [ 31 ] : 285–6 Bangkok besides waged several wars with Vietnam, where Siam successfully regained hegemony over Cambodia. [ 31 ] : 290–2 From the late-19th hundred, Siam tried to rule the ethnic groups in the region as colonies. [ 31 ] : 308 In the reign of Mongkut ( 1851–1868 ), who recognised the potential terror western powers posed to Siam, his court contacted the british government immediately to defuse tensions. [ 31 ] : 311 A british mission led by Sir John Bowring, Governor of Hong Kong, led to the sign of the Bowring Treaty, the first of many unequal treaties with western countries. This, however, brought deal and economic development to Siam. [ 38 ] The unexpected death of Mongkut from malaria led to the reign of underage Prince Chulalongkorn, with Somdet Chaophraya Sri Suriwongse ( Chuang Bunnag ) acting as regent. [ 31 ] : 327 Chulalongkorn ( r. 1868–1910 ) initiated centralization, set up a outhouse council, and abolished bondage and the corvée arrangement. The Front Palace crisis of 1874 stalled attempts at promote reforms. [ 31 ] : 331–3 In the 1870s and 1880s, he incorporated the protectorates up union into the kingdom proper, which late expanded to the protectorates in the northeast and the confederacy. [ 31 ] : 334–5 He established twelve krom in 1888, which were equivalent to contemporary ministries. [ 31 ] : 347 The crisis of 1893 erupted, caused by french demands for laotian territory east of Mekong. [ 31 ] : 350–3 Thailand is the only Southeast asian nation never to have been colonised by a western power, [ 39 ] in separate because Britain and France agreed in 1896 to make the Chao Phraya valley a buffer express. [ 40 ] not until the twentieth hundred could Siam renegotiate every inadequate treaty dating from the Bowring Treaty, including extraterritoriality. The advent of the monthon system marked the creation of the modern Thai nation-state. [ 31 ] : 362–3 In 1905, there were abortive rebellions in the ancient Patani area, Ubon Ratchathani, and Phrae in opposition to an attempt to blunt the office of local lords. [ 31 ] : 371–3 The Palace Revolt of 1912 was a fail attack by Western-educated military officers to overthrow the thai monarchy. [ 31 ] : 397 Vajiravudh ( r. 1910–1925 ) responded by propaganda for the entirety of his predominate. [ 31 ] : 402 He promoted the theme of the Thai nation. [ 31 ] : 404 In 1917, Siam joined the First World War on the slope of the Allies. [ 31 ] : 407 In the consequence Siam had a seat at the Paris Peace Conference, and gained freedom of taxation and the revocation of extraterritoriality. [ 31 ] : 408
Constitutional monarchy, World War II and Cold War
 Field Marshal Plaek Phibunsongkhram, the longest serve Prime Minister of Thailand A bloodless revolution took topographic point in 1932, in which Prajadhipok was forced to grant the nation ‘s first base constitution, thereby ending centuries of feudal and absolute monarchy. The unite results of economic hardships brought on by the Great Depression, aggressively falling rice prices, and a significant reduction in public spending caused discontentment among aristocrats. [ 23 ] : 25 In 1933, a counter-revolutionary rebellion occurred which aimed to reinstate absolute monarchy, but failed. [ 31 ] : 446–8 Prajadhipok ‘s conflict with the government finally led to abdication. The government selected Ananda Mahidol, who was studying in Switzerland, to be the new king. [ 31 ] : 448–9 later that ten, the army wing of Khana Ratsadon came to dominate thai politics. Plaek Phibunsongkhram who became premier in 1938, started political oppression and took an openly anti-royalist position. [ 31 ] : 457 His politics adopted nationalism and Westernisation, anti-Chinese and anti-French policies. [ 23 ] : 28 In 1939, there was a decree changing the name of the area from “ Siam ” to “ Thailand ”. In 1941, Thailand was in a brief conflict with Vichy France resulting in Thailand gaining some Lao and cambodian territories. [ 31 ] : 462 On 8 December 1941, the Empire of Japan launched an invasion of Thailand, and fighting broke out curtly before Phibun ordered an armistice. Japan was granted exempt passage, and on 21 December Thailand and Japan signed a military alliance with a secret protocol, wherein the japanese government agreed to help Thailand regain miss territories. [ 41 ] The Thai government declared war on the United States and the United Kingdom. [ 31 ] : 465 The Free Thai Movement was launched both in Thailand and abroad to oppose the government and japanese occupation. [ 31 ] : 465–6 After the war ended in 1945, Thailand signed ball agreements to end the express of war with the Allies. The main Allied powers had ignored Thailand ‘s announcement of war .
Field Marshal Plaek Phibunsongkhram, the longest serve Prime Minister of Thailand A bloodless revolution took topographic point in 1932, in which Prajadhipok was forced to grant the nation ‘s first base constitution, thereby ending centuries of feudal and absolute monarchy. The unite results of economic hardships brought on by the Great Depression, aggressively falling rice prices, and a significant reduction in public spending caused discontentment among aristocrats. [ 23 ] : 25 In 1933, a counter-revolutionary rebellion occurred which aimed to reinstate absolute monarchy, but failed. [ 31 ] : 446–8 Prajadhipok ‘s conflict with the government finally led to abdication. The government selected Ananda Mahidol, who was studying in Switzerland, to be the new king. [ 31 ] : 448–9 later that ten, the army wing of Khana Ratsadon came to dominate thai politics. Plaek Phibunsongkhram who became premier in 1938, started political oppression and took an openly anti-royalist position. [ 31 ] : 457 His politics adopted nationalism and Westernisation, anti-Chinese and anti-French policies. [ 23 ] : 28 In 1939, there was a decree changing the name of the area from “ Siam ” to “ Thailand ”. In 1941, Thailand was in a brief conflict with Vichy France resulting in Thailand gaining some Lao and cambodian territories. [ 31 ] : 462 On 8 December 1941, the Empire of Japan launched an invasion of Thailand, and fighting broke out curtly before Phibun ordered an armistice. Japan was granted exempt passage, and on 21 December Thailand and Japan signed a military alliance with a secret protocol, wherein the japanese government agreed to help Thailand regain miss territories. [ 41 ] The Thai government declared war on the United States and the United Kingdom. [ 31 ] : 465 The Free Thai Movement was launched both in Thailand and abroad to oppose the government and japanese occupation. [ 31 ] : 465–6 After the war ended in 1945, Thailand signed ball agreements to end the express of war with the Allies. The main Allied powers had ignored Thailand ‘s announcement of war .
In June 1946, young King Ananda was found dead under cryptic circumstances. His younger brother Bhumibol Adulyadej ascended to the throne. Thailand joined the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization ( SEATO ) to become an active ally of the United States in 1954. [ 31 ] : 493 Field Marshal Sarit Thanarat launched a coup in 1957, which removed Khana Ratsadon from politics. His dominion ( premiership 1959–1963 ) was autocratic ; he built his legitimacy around the god-like status of the sovereign and by channelling the government ‘s loyalty to the king. [ 31 ] : 511 His politics improved the country ‘s infrastructure and education. [ 31 ] : 514 After the United States joined the Vietnam War in 1961, there was a secret agreement wherein the U.S. promised to protect Thailand. [ 31 ] : 523 The period brought about increasing modernization and Westernisation of Thai society. rapid urbanization occurred when the rural populace sought exploit in growing cities. rural farmers gained class awareness and were charitable to the Communist Party of Thailand. [ 31 ] : 528 Economic development and education enabled the advance of a middle class in Bangkok and other cities. [ 31 ] : 534 In October 1971, there was a large demonstration against the dictatorship of Thanom Kittikachorn ( premiership 1963–1973 ), which led to civilian casualties. [ 31 ] : 541–3 Bhumibol installed Sanya Dharmasakti ( premiership 1973–1975 ) to replace him, making it the first time that the king intervened in Thai politics immediately since 1932. [ 42 ] The aftermath of the consequence marked a ephemeral parliamentary democracy, [ 42 ] often called the “ era when democracy blossomed ” ( ยุคประชาธิปไตยเบ่งบาน ) .
contemporary history
constant agitation and instability, arsenic well as fear of a communist coup d’etat after the fall of Saigon, made some ultra-right groups sword leftist students as communists. [ 31 ] : 548 This culminated in the Thammasat University massacre in October 1976. [ 31 ] : 548–9 A coup d’état on that day brought Thailand a fresh ultra-right government, which cracked down on media outlets, officials, and intellectuals, and fuelled the communist insurgency. Another coup d’etat the follow year installed a more mince politics, which offered amnesty to communist fighters in 1978. Fueled by Indochina refugee crisis, vietnamese bound raids and economic hardships, Prem Tinsulanonda launched a successful coup d’etat and became the Prime Minister from 1980 to 1988. The communists abandoned the insurgency by 1983. Prem ‘s premiership was dubbed “ semi-democracy ” because the Parliament was composed of all elected House and all appointed Senate. The 1980s besides saw increasing interposition in politics by the monarch, who rendered two coup attempts against Prem failed. Thailand had its first elected flower minister in 1988. [ 43 ] Suchinda Kraprayoon, who was the coup d’etat leader in 1991 and said he would not seek to become prime minister, was nominated as one by the majority coalition government after the 1992 general election. This caused a popular presentation in Bangkok, which ended with a military crackdown. Bhumibol intervened in the event and Suchinda then resigned .
The 1997 asian fiscal crisis originated in Thailand and ended the area ‘s 40 years of continuous economic growth. [ 44 ] : 3 Chuan Leekpai ‘s politics took an IMF lend with unpopular provisions. [ 31 ] : 576 The democrat Thai Rak Thai party, led by prime minister Thaksin Shinawatra, governed from 2001 until 2006. His policies were successful in reducing rural poverty [ 45 ] and initiated universal healthcare in the country. [ 46 ] A South Thailand insurgency escalated starting from 2004. The 2004 indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami hit the area, by and large in the south. massive protests against Thaksin led by the People ‘s Alliance for Democracy ( PAD ) started in his second base term as flower minister and his tenure ended with a coup d’etat d’état in 2006. The military junta installed a military government which lasted a year. In 2007, a civilian government led by the Thaksin-allied People ‘s Power Party ( PPP ) was elected. Another protest led by PAD ended with the adjournment of PPP, and the Democrat Party led a coalescence politics in its place. The pro-Thaksin United Front for Democracy Against Dictatorship ( UDD ) protested both in 2009 and in 2010, the latter of which ended with a fierce military crackdown causing more than 70 civilian deaths. [ 47 ] After the general election of 2011, the democrat Pheu Thai Party won a majority and Yingluck Shinawatra, Thaksin ‘s younger baby, became prime minister. The People ‘s democratic Reform Committee organised another anti-Shinawatra protest [ c ] after the ruling party proposed an amnesty bill which would benefit Thaksin. [ 48 ] Yingluck dissolved parliament and a general election was scheduled, but was invalidated by the Constitution Court. The crisis ended with another coup d’état in 2014, the moment coup in a ten. [ five hundred ] Since then, the state has been led by the National Council for Peace and Order, a military military junta led by General Prayut Chan-o-cha. Civil and political rights were restricted, and the nation saw a scend in lèse-majesté cases. political opponents and dissenters were sent to “ attitude adjustment ” camps, [ 49 ] academics mentioned as the upgrade of fascism. [ 50 ] Bhumibol, the longest-reigning Thai king, died in 2016, and his son Vajiralongkorn ascended to the throne. The referendum and borrowing of Thailand ‘s stream constitution happened under the military junta ‘s rule. [ e ] The military junta besides bound future governments to a 20-year national scheme ‘road map ‘ it laid down, effectively locking the nation into military-guided democracy. [ 52 ] In 2019, the military junta agreed to schedule a cosmopolitan election in March. [ 49 ] Prayut continued his premiership with the confirm of Palang Pracharath Party -coalition in the House and junta-appointed Senate, amid allegations of election fraud. [ 53 ] The ongoing pro-democracy protests were triggered by increasing royal prerogative, democratic and economic arrested development from the Military supported by the Monarchy denounce 2014 Thai coup d’état, dissolution of the pro-democracy Future Forward Party, misgiving in the 2019 general election and the current political organization, forced disappearance and deaths of political activists including Wanchalearm Satsaksit, political corruption scandals, [ 54 ] [ 55 ] which brought forward unprecedented demands to reform the monarchy [ 56 ] and the highest sense of republicanism in the country. [ 57 ]
Politics and government
anterior to 1932, Thai kings were feudal or absolute sovereign. During Sukhothai Kingdom, the baron was seen as a Dharmaraja or ‘king who rules in accordance with Dharma ‘. The arrangement of government was a net of tributaries ruled by local lords. Modern absolute monarchy and statehood was established by Chulalongkorn when he transformed the decentralized protectorate organization into a one state of matter. On 24 June 1932, Khana Ratsadon ( People ‘s Party ) carried out a bloodless rotation which marked the beginning of constituent monarchy. Thailand has had 20 constitutions and charters since 1932, including the latest and current 2017 constitution. Throughout this time, the phase of government has ranged from military dictatorship to electoral majority rule. [ 58 ] [ 59 ] Thailand has had the fourth-most coups in the world. [ 60 ] “ Uniformed or ex-military men have led Thailand for 55 of the 83 years ” between 1932 and 2009. [ 61 ] Most recently, the National Council for Peace and Order ruled the nation between 2014 and 2019. The politics of Thailand is conducted within the model of a constitutional monarchy, whereby a familial monarch serves as read/write head of state. The current King of Thailand is Vajiralongkorn ( or Rama X ), who has reigned since October 2016. The powers of the king are limited by the constitution and he is primarily a symbolic figurehead. The sovereign is question of the armed forces and is required to be Buddhist a well as the Defender of the Faith. He has the office to appoint his heir, the exponent to grant pardons, and the royal assent. The king is aided in his duties by the Privy Council of Thailand. however, the sovereign hush occasionally intervenes in Thai politics, as all constitutions pave the way for accustomed royal rulings. Some academics outside Thailand, including Duncan McCargo and Federico Ferrara, noted extraconstitutional character of the sovereign through a “ network monarchy “ behind the political scenes. [ 62 ] The monarchy is protected by the dangerous lèse majesté law, even though the people ‘s attitude towards the institution varies from one reign to another. [ 63 ] [ 64 ]
 Sappaya-Sapasathan, the current Parliament House of Thailand government is separated into three branches :
Sappaya-Sapasathan, the current Parliament House of Thailand government is separated into three branches :
military and bureaucratic aristocrats fully controlled political parties between 1946 and 1980s. [ 66 ] : 16 Most parties in Thailand are ephemeral. [ 67 ] : 246 Between 1992 and 2006, Thailand had a bipartisan system. [ 67 ] : 245 Since 2000, two political parties dominated Thai general elections : one was the Pheu Thai Party ( which was a successor of People ‘s Power Party and the Thai Rak Thai Party ), and the other was the Democrat Party. The political parties which support Thaksin Shinawatra won the most representatives every general election since 2001. Later constitutions created a multi-party system where a single party can not gain a majority in the house .
Lèse majesté
The 2007 constitution was partially abrogated by the military dictatorship that came to ability in May 2014. [ 68 ] Thailand ‘s kings are protected by lèse-majesté laws which allow critics to be jailed for three to fifteen years. [ 69 ] After the 2014 Thai coup d’état, Thailand had the highest number of lèse-majesté prisoners in the nation ‘s history. [ 70 ] [ 71 ] In 2017, the military woo in Thailand sentenced a world to 35 years in prison for violating the state ‘s lèse-majesté law. [ 71 ] Thailand has been rated not free on the Freedom House Index since 2014. [ 72 ] Thai militant and magazine editor Somyot Prueksakasemsuk, who was sentenced to eleven years ‘ imprisonment for lèse-majesté in 2013, [ 73 ] is a destine prisoner of conscience by Amnesty International. [ 74 ]
geography
 A satellite picture of Thailand. Totalling 513,120 square kilometres ( 198,120 sq mi ), Thailand is the 50th-largest area by total area. It is slightly smaller than Yemen and slightly larger than Spain. [ 1 ] Thailand comprises several discrete geographic regions, partially corresponding to the provincial groups. The north of the country is the mountainous area of the Thai highlands, with the highest point being Doi Inthanon in the Thanon Thong Chai Range at 2,565 metres ( 8,415 foot ) above sea level. The northeast, Isan, consists of the Khorat Plateau, bordered to the east by the Mekong River. The center of the nation is dominated by the predominantly flat Chao Phraya river valley, which runs into the Gulf of Thailand. southerly Thailand consists of the specialize Kra Isthmus that widens into the Malay Peninsula. politically, there are six geographic regions which differ from the others in population, basic resources, natural features, and level of sociable and economic development. The diverseness of the regions is the most marked assign of Thailand ‘s physical arrange. The Chao Phraya and the Mekong River are the essential water courses of rural Thailand. Industrial scale production of crops use both rivers and their tributaries. The Gulf of Thailand covers 320,000 feather kilometres ( 124,000 sq secret intelligence service ) and is fed by the Chao Phraya, Mae Klong, Bang Pakong, and Tapi Rivers. It contributes to the tourism sector owing to its unclutter shallow waters along the coasts in the southerly region and the Kra Isthmus. The easterly shore of the Gulf of Thailand is an industrial center of Thailand with the kingdom ‘s premier deepwater port in Sattahip and its busiest commercial port, Laem Chabang. The Andaman Sea is a precious natural resource as it hosts popular and deluxe resorts. Phuket, Krabi, Ranong, Phang Nga and Trang, and their islands, all lay along the coasts of the Andaman Sea and, despite the 2004 tsunami, they remain a tourist attraction .
A satellite picture of Thailand. Totalling 513,120 square kilometres ( 198,120 sq mi ), Thailand is the 50th-largest area by total area. It is slightly smaller than Yemen and slightly larger than Spain. [ 1 ] Thailand comprises several discrete geographic regions, partially corresponding to the provincial groups. The north of the country is the mountainous area of the Thai highlands, with the highest point being Doi Inthanon in the Thanon Thong Chai Range at 2,565 metres ( 8,415 foot ) above sea level. The northeast, Isan, consists of the Khorat Plateau, bordered to the east by the Mekong River. The center of the nation is dominated by the predominantly flat Chao Phraya river valley, which runs into the Gulf of Thailand. southerly Thailand consists of the specialize Kra Isthmus that widens into the Malay Peninsula. politically, there are six geographic regions which differ from the others in population, basic resources, natural features, and level of sociable and economic development. The diverseness of the regions is the most marked assign of Thailand ‘s physical arrange. The Chao Phraya and the Mekong River are the essential water courses of rural Thailand. Industrial scale production of crops use both rivers and their tributaries. The Gulf of Thailand covers 320,000 feather kilometres ( 124,000 sq secret intelligence service ) and is fed by the Chao Phraya, Mae Klong, Bang Pakong, and Tapi Rivers. It contributes to the tourism sector owing to its unclutter shallow waters along the coasts in the southerly region and the Kra Isthmus. The easterly shore of the Gulf of Thailand is an industrial center of Thailand with the kingdom ‘s premier deepwater port in Sattahip and its busiest commercial port, Laem Chabang. The Andaman Sea is a precious natural resource as it hosts popular and deluxe resorts. Phuket, Krabi, Ranong, Phang Nga and Trang, and their islands, all lay along the coasts of the Andaman Sea and, despite the 2004 tsunami, they remain a tourist attraction .
climate
 Thailand map of Köppen climate classification. Thailand ‘s climate is influenced by monsoon winds that have a seasonal quality ( the southwest and northeasterly monsoon ). [ 75 ] : 2 Most of the area is classified as Köppen ‘s tropical savanna climate. [ 76 ] The majority of the south arsenic well as the easterly gratuity of the east have a tropical monsoon climate. Parts of the south besides have a tropical rain forest climate. Thailand is divided into three seasons. [ 75 ] : 2 The first is the showery or southwest monsoon season ( mid–May to mid–October ), which is caused by southwestern scent from indian Ocean. [ 75 ] : 2 Rainfall is besides contributed by Intertropical Convergence Zone ( ITCZ ) and tropical cyclones. [ 75 ] : 2 August and September being the wettest period of the year. [ 75 ] : 2 The country receives a beggarly annual rain of 1,200 to 1,600 millimeter ( 47 to 63 in ). [ 75 ] : 4 winter or the northeast monsoon occurs from mid–October until mid–February. [ 75 ] : 2 Most of Thailand experiences dry weather with meek temperatures. [ 75 ] : 2, 4 summer or the pre–monsoon temper runs from mid–February until mid–May. [ 75 ] : 3 Due to its inland nature and latitude, the north, northeastern, cardinal and eastern parts of Thailand experience a retentive period of ardent weather, where temperatures can reach up to 40 °C ( 104 °F ) during March to May, [ 75 ] : 3 in contrast to close to or below 0 °C ( 32 °F ) in some areas in winter. [ 75 ] : 3 Southern Thailand is characterised by balmy weather year-round with less diurnal and seasonal variations in temperatures ascribable to nautical influences. [ 75 ] : 3 It receives abundant rain, particularly during October to November. [ 75 ] : 2 Thailand is among the earth ‘s ten countries that are most expose to climate change. In particular, it is highly vulnerable to rising sea levels and extreme weather events. [ 77 ] [ 78 ]
Thailand map of Köppen climate classification. Thailand ‘s climate is influenced by monsoon winds that have a seasonal quality ( the southwest and northeasterly monsoon ). [ 75 ] : 2 Most of the area is classified as Köppen ‘s tropical savanna climate. [ 76 ] The majority of the south arsenic well as the easterly gratuity of the east have a tropical monsoon climate. Parts of the south besides have a tropical rain forest climate. Thailand is divided into three seasons. [ 75 ] : 2 The first is the showery or southwest monsoon season ( mid–May to mid–October ), which is caused by southwestern scent from indian Ocean. [ 75 ] : 2 Rainfall is besides contributed by Intertropical Convergence Zone ( ITCZ ) and tropical cyclones. [ 75 ] : 2 August and September being the wettest period of the year. [ 75 ] : 2 The country receives a beggarly annual rain of 1,200 to 1,600 millimeter ( 47 to 63 in ). [ 75 ] : 4 winter or the northeast monsoon occurs from mid–October until mid–February. [ 75 ] : 2 Most of Thailand experiences dry weather with meek temperatures. [ 75 ] : 2, 4 summer or the pre–monsoon temper runs from mid–February until mid–May. [ 75 ] : 3 Due to its inland nature and latitude, the north, northeastern, cardinal and eastern parts of Thailand experience a retentive period of ardent weather, where temperatures can reach up to 40 °C ( 104 °F ) during March to May, [ 75 ] : 3 in contrast to close to or below 0 °C ( 32 °F ) in some areas in winter. [ 75 ] : 3 Southern Thailand is characterised by balmy weather year-round with less diurnal and seasonal variations in temperatures ascribable to nautical influences. [ 75 ] : 3 It receives abundant rain, particularly during October to November. [ 75 ] : 2 Thailand is among the earth ‘s ten countries that are most expose to climate change. In particular, it is highly vulnerable to rising sea levels and extreme weather events. [ 77 ] [ 78 ]
environment and wildlife
 [79] The population of asian elephants in Thailand ‘s rampantly has dropped to an estimated 2,000–3,000. Thailand has a mediocre but improving performance in the global Environmental Performance Index ( EPI ) with an overall ranking of 91 out of 180 countries in 2016. The environmental areas where Thailand performs worst ( i.e., highest ranking ) are air timbre ( 167 ), environmental effects of the agricultural diligence ( 106 ), and the climate and energy sector ( 93 ), the late chiefly because of a high CO2 emission per KWh produced. Thailand performs best ( i.e., lowest ranking ) in water resource management ( 66 ), with some major improvements expected for the future, and sanitation ( 68 ). [ 80 ] [ 81 ] The nation had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean sexual conquest of 6.00/10, ranking it 88th globally out of 172 countries. [ 82 ] The population of elephants, the state ‘s national symbol, has fallen from 100,000 in 1850 to an estimated 2,000. [ 79 ] Poachers have retentive hunted elephants for bone and hides, and now increasingly for kernel. [ 83 ] Young elephants are often captured for consumption in tourist attractions or as exercise animals, where there have been claims of mistreatment. [ 84 ] however, their use has declined since the government banned logging in 1989. Poaching of protected species remains a major problem. Tigers, leopards, and other big cats are hunted for their pelts. many are farmed or hunted for their kernel, which purportedly has medicative properties. Although such deal is illegal, the well-known Bangkok marketplace Chatuchak is still known for the sale of endanger species. [ 85 ] The practice of keeping crazy animals as pets affects species such as asian black bear, Malayan sunlight wear, white-handed lar, pileated gibbon, and binturong. [ 86 ]
[79] The population of asian elephants in Thailand ‘s rampantly has dropped to an estimated 2,000–3,000. Thailand has a mediocre but improving performance in the global Environmental Performance Index ( EPI ) with an overall ranking of 91 out of 180 countries in 2016. The environmental areas where Thailand performs worst ( i.e., highest ranking ) are air timbre ( 167 ), environmental effects of the agricultural diligence ( 106 ), and the climate and energy sector ( 93 ), the late chiefly because of a high CO2 emission per KWh produced. Thailand performs best ( i.e., lowest ranking ) in water resource management ( 66 ), with some major improvements expected for the future, and sanitation ( 68 ). [ 80 ] [ 81 ] The nation had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean sexual conquest of 6.00/10, ranking it 88th globally out of 172 countries. [ 82 ] The population of elephants, the state ‘s national symbol, has fallen from 100,000 in 1850 to an estimated 2,000. [ 79 ] Poachers have retentive hunted elephants for bone and hides, and now increasingly for kernel. [ 83 ] Young elephants are often captured for consumption in tourist attractions or as exercise animals, where there have been claims of mistreatment. [ 84 ] however, their use has declined since the government banned logging in 1989. Poaching of protected species remains a major problem. Tigers, leopards, and other big cats are hunted for their pelts. many are farmed or hunted for their kernel, which purportedly has medicative properties. Although such deal is illegal, the well-known Bangkok marketplace Chatuchak is still known for the sale of endanger species. [ 85 ] The practice of keeping crazy animals as pets affects species such as asian black bear, Malayan sunlight wear, white-handed lar, pileated gibbon, and binturong. [ 86 ]
administrative divisions
Thailand is a one state ; the administrative services of the executive branch are divided into three levels by National Government Organisation Act, BE 2534 ( 1991 ) : central, peasant and local. Thailand is composed of 76 provinces ( จังหวัด, changwat ), [ 87 ] which are first-level administrative divisions. There are besides two specially govern districts : the capital Bangkok and Pattaya. Bangkok is at provincial grade and therefore much counted as a province. Each state is divided into districts ( อำเภอ, amphoe ) and the districts are far divided into sub-districts ( ตำบล, tambons ). The name of each province ‘s capital city ( เมือง, mueang ) is the like as that of the province. For example, the capital of Chiang Mai Province ( Changwat Chiang Mai ) is Mueang Chiang Mai or Chiang Mai. All provincial governors and district chiefs, which are administrators of provinces and districts respectively, are appointed by the cardinal government. [ 88 ] Thailand ‘s provinces are sometimes grouped into four to six regions, depending on the generator .
A clickable map of Thailand exhibiting its provinces
foreign relations
The foreign relations of Thailand are handled by the Minister of Foreign Affairs. Thailand participates fully in external and regional organisations. It is a major non-NATO ally and Priority Watch List Special 301 Report of the United States. The area remains an active member of ASEAN Association of Southeast asian Nations. Thailand has developed increasingly close ties with other association of southeast asian nations members : Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Brunei, Laos, Cambodia, Myanmar, and Vietnam, whose extraneous and economic ministers hold annual meetings. regional co-operation is progressing in economic, barter, bank, political, and cultural matters. In 2003, Thailand served as APEC ( Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation ) host. Dr. Supachai Panitchpakdi, the former Deputy Prime Minister of Thailand, presently serves as Secretary-General of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development ( UNCTAD ). In 2005 Thailand attended the inaugural East Asia Summit. In late years, Thailand has taken an increasingly active agent function on the international stage. When East Timor gained independence from Indonesia, Thailand, for the first clock time in its history, contributed troops to the external peacekeeping feat. Its troops remain there nowadays as part of a UN peacekeeping force. As separate of its feat to increase international ties, Thailand has reached out to such regional organisations as the Organization of American States ( OAS ) and the Organisation for Security and Cooperation in Europe ( OSCE ). Thailand has contributed troops to reconstruction efforts in Afghanistan and Iraq. Thaksin initiated negotiations for respective rid craft agreements with China, Australia, Bahrain, India, and the US. The latter particularly was criticised, with claims that uncompetitive Thai industries could be wiped out. [ 89 ] Thaksin besides announced that Thailand would forsake foreign help, and exercise with donor countries to assist in the exploitation of neighbours in the Greater Mekong Sub-region. [ 90 ] Thaksin sought to position Thailand as a regional leader, initiating respective development projects in poor neighbor countries like Laos. More controversially, he established close, friendly ties with the burmese dictatorship. [ 91 ] thailand joined the US-led invasion of Iraq, sending a 423-strong humanitarian contingent. [ 92 ] It withdrew its troops on 10 September 2004. Two Thai soldiers died in Iraq in an guerrilla attack. Abhisit appointed Peoples Alliance for Democracy drawing card Kasit Piromya as foreign minister. In April 2009, fighting broke out between Thai and cambodian troops on district immediately adjacent to the 900-year-old ruins of Cambodia ‘s Preah Vihear Hindu temple near the margin. The cambodian government claimed its united states army had killed at least four Thais and captured 10 more, although the Thai government denied that any Thai soldiers were killed or injured. Two cambodian and three Thai soldiers were killed. Both armies blamed the other for firing beginning and denied entering the early ‘s territory. [ 93 ] [ 94 ]
Armed forces
The Royal Thai Armed Forces ( กองทัพไทย ; RTGS : Kong Thap Thai ) constitute the military of the Kingdom of Thailand. It consists of the Royal Thai Army ( กองทัพบกไทย ), the Royal Thai Navy ( กองทัพเรือไทย ), and the Royal Thai Air Force ( กองทัพอากาศไทย ). It besides incorporates assorted paramilitary forces. The Thai Armed Forces have a combined work force of 306,000 active duty personnel and another 245,000 active reserve personnel. [ 95 ] The head of the Thai Armed Forces ( จอมทัพไทย, Chom Thap Thai ) is the king, [ 96 ] although this status is alone nominal. The arm forces are managed by the Ministry of Defence of Thailand, which is headed by the Minister of Defence ( a penis of the cabinet of Thailand ) and commanded by the Royal Thai Armed Forces Headquarters, which in change state is headed by the Chief of Defence Forces of Thailand. [ 97 ] Thai annual defense budget about tripled from 78 billion baht in 2005 to 207 billion baht in 2016, accounting for approximately 1.5 % of 2019 Thai GDP. [ 98 ] Thailand ranked 16th cosmopolitan in the Military Strength Index based on the Credit Suisse reputation in September 2015 .
The military is besides tasked with humanitarian missions, such as escorting Rohingya to Malaysia or Indonesia, [ 99 ] ensuring security and benefit for refugees during Indochina refugee crisis. [ 100 ] According to the constitution, serving in the armed forces is a duty of all Thai citizens. [ 101 ] Thailand still use active draft system for males over the age of 21. They are subjected to varying lengths of active agent service depending on the duration of reserve prepare as territorial Defence Student and their level of education. Those who have completed three years or more of reserve train will be exempted wholly. The practice has long been criticized, as some media question its efficacy and value. [ 102 ] [ 103 ] It is alleged that conscripts end up as servants to senior officers [ 104 ] or clerks in military concerted shops. [ 105 ] [ 106 ] In a report issued in March 2020, Amnesty International charged that Thai military conscripts face institutionalised abuse systematically hushed up by military authorities. [ 107 ] Critics observed that Thai military ‘s main aim is to deal with inner quite than external threats. [ 108 ] Internal Security Operations Command is called the political weapon of the Thai military, which has overlapping social and political functions with civilian bureaucracy. It besides has anti-democracy mission. [ 108 ] The military is besides ill-famed for numerous corruption incidents, such as accusation of homo traffic, [ 109 ] and nepotism in promotion of high-level officers. [ 110 ] The military is deeply entrenched in politics. Most recently, the appointed senators include more than 100 active and put out military. [ 111 ] In 2017, Thailand signed and ratified the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons. [ 112 ]
education
Thailand ‘s young literacy rate was 98.1 % in 2015. [ 113 ] education is provided by a well-organised school system of kindergartens, basal, lower secondary coil and upper berth junior-grade schools, numerous vocational colleges, and universities. The individual sector of education is well develop and significantly contributes to the overall provision of education. Thailand has the second base highest number of English-medium private international schools in Southeast asian Nations. [ 114 ] department of education is compulsory up to and including senesce 14, with the government providing free education through to historic period 17. Teaching relies heavily on rote learning preferably than on student-centred methodology. The constitution of reliable and coherent course of study for its primary and secondary schools is submit to rapid changes. Issues concerning university capture has been in changeless turbulence for a phone number of years. Most of the younger generation Thais are calculator literate. As of 2020, Thailand was ranked 89th out of 100 countries globally for English proficiency. [ 115 ] The state is besides one of the few that even mandates consistent up to the university years, which is still a subject of ongoing debate. The timbre of providing education in the state is frequently questioned and cram schools are particularly popular for university entrance examination. The count of higher education institutions in Thailand has grown powerfully over the past decades to 156 officially. The two top-ranking universities in Thailand are Chulalongkorn University and Mahidol University. [ 116 ] Thai universities research output signal however relatively low, even though the country ‘s diary publications increased by 20 % between 2011 and 2016. [ 117 ] Recent initiatives, such as the National Research University [ 118 ] and Graduate research intensive university: VISTEC, designed to strengthen Thailand ‘s home inquiry universities, however, appear to be gaining traction .
Students in cultural minority areas score systematically lower in standardized national and international tests. [ 119 ] [ 120 ] [ 121 ] This is probably due to unequal allocation of educational resources, weak teacher training, poverty, and low Thai terminology skill, the terminology of the tests. [ 119 ] [ 122 ] [ 123 ] extensive nationally IQ tests were administered to 72,780 Thai students from December 2010 to January 2011. The average IQ was found to be 98.59, which is higher than previous studies have found. intelligence quotient levels were found to be discrepant throughout the nation, with the lowest average of 88.07 detect in the southern region of Narathiwat Province and the highest average of 108.91 reported in Nonthaburi Province. The Ministry of Public Health blames the discrepancies on tincture of iodine insufficiency, and as of 2011 steps were being taken to require that tincture of iodine be added to table salt, a practice common in many western countries. [ 124 ] In 2013, the Ministry of Information and Communication Technology announced that 27,231 schools would receive classroom-level access to high-speed internet. [ 125 ] however, the country ‘s educational infrastructure was even underprepared for on-line teach, as smaller and more outback schools were particularly hindered by COVID-19 restrictions. [ 126 ] Thailand is the third gear most popular study address in ASEAN. The number of external degree students in Thailand increased by 9.7 times between 1999 and 2012, from 1,882 to 20,309 students. Most of international students come from neighbor countries [ 114 ] from China, Myanmar, Cambodia and Vietnam. [ 127 ]
science and engineering
 Scientists are working in the lab In modern times, Thai scientists have made many significant contributions in assorted fields of study. For model, In chemistry, Krisana Kraisintu a known as the “ Gypsy pharmacist “. [ 128 ] She developed one of the inaugural generic ARV fixed-dose combinations and dedicated her life to making medicines more low-cost and accessible. Her efforts have saved countless lives in Africa, GPO-VIR has nowadays been chosen by World Health Organization as the beginning regimen treatment for HIV/AIDS patients in poor countries. [ 129 ] In Thailand, this drug ( GPO-VIR ) is used in the national HIV/AIDS treatment plan, making it release of charge for 100,000 patients. [ 130 ] while Pongrama Ramasoota, He discoveries production of therapeutic human monoclonal antibodies against dengue virus and the world ‘s beginning Dengue fever medication, include DNA vaccine exploitation for dengue and Canine parvovirus. [ 131 ] Thailand has besides made significant advances technology in the development of Medical Robotics. aesculapian robots have been used and promoted in Thailand in many areas, including operation, diagnosis, rehabilitation and services. [ 132 ] and their use has been increasing. such as, an aged wish automaton made by Thai manufacturer that japanese nursing homes are widely using. [ 133 ] In operation, in 2021, Mahidol University ‘s “ BART LAB ” team successfully researched the invention of the robot-assisted operating room ( Minimal Invasive Surgery ). [ 134 ] back in 2019, The Medical Services Department has unveiled Thailand ‘s automaton created to help surgeons in brain operating room on patients afflicted with epilepsy. [ 135 ] binding in 2017, Ramathibodi Hospital, a moderate government hospital in Bangkok and a reputable aesculapian school, successfully performed the first robot-assisted brain operation in Asia. [ 136 ] For reclamation and therapy robots, were developed to help patients with weapon and leg injuries perform drill movements aided by the robots is the first prize winner of the i-MEDBOT Innovation Contest 2018 hold by Thailand Center of Excellence for Life Sciences ( TCELS ). [ 137 ] According to the UNESCO Institute for Statistics, Thailand devoted 1 % of its GDP to science research and growth in 2017. [ 138 ] Between 2014 and 2016, Research and development work force in Thailand increased from 84,216 people to 112,386 people. [ 139 ] Thailand was ranked 44th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, down from 43rd in 2019. [ 140 ] [ 141 ] [ 142 ] [ 143 ] The Thai government is developing new growth hub by starting with the easterly Economic Corridor of Innovation ( EECi ) to accelerating human resource and research development. [ 144 ] The National Science and Technology Development Agency is an means of the politics of Thailand which supports research in science and technology and its application in the Thai economy. [ 145 ] By December 2020 with 308.35 Mbit/s Thailand had become populace leader in terms of Internet fixed broadband internet accelerate, with Switzerland and France in Europe in positions 5 and 8 respectively, with the US at place 10 with 173.67 Mbit/s. [ 146 ]
Scientists are working in the lab In modern times, Thai scientists have made many significant contributions in assorted fields of study. For model, In chemistry, Krisana Kraisintu a known as the “ Gypsy pharmacist “. [ 128 ] She developed one of the inaugural generic ARV fixed-dose combinations and dedicated her life to making medicines more low-cost and accessible. Her efforts have saved countless lives in Africa, GPO-VIR has nowadays been chosen by World Health Organization as the beginning regimen treatment for HIV/AIDS patients in poor countries. [ 129 ] In Thailand, this drug ( GPO-VIR ) is used in the national HIV/AIDS treatment plan, making it release of charge for 100,000 patients. [ 130 ] while Pongrama Ramasoota, He discoveries production of therapeutic human monoclonal antibodies against dengue virus and the world ‘s beginning Dengue fever medication, include DNA vaccine exploitation for dengue and Canine parvovirus. [ 131 ] Thailand has besides made significant advances technology in the development of Medical Robotics. aesculapian robots have been used and promoted in Thailand in many areas, including operation, diagnosis, rehabilitation and services. [ 132 ] and their use has been increasing. such as, an aged wish automaton made by Thai manufacturer that japanese nursing homes are widely using. [ 133 ] In operation, in 2021, Mahidol University ‘s “ BART LAB ” team successfully researched the invention of the robot-assisted operating room ( Minimal Invasive Surgery ). [ 134 ] back in 2019, The Medical Services Department has unveiled Thailand ‘s automaton created to help surgeons in brain operating room on patients afflicted with epilepsy. [ 135 ] binding in 2017, Ramathibodi Hospital, a moderate government hospital in Bangkok and a reputable aesculapian school, successfully performed the first robot-assisted brain operation in Asia. [ 136 ] For reclamation and therapy robots, were developed to help patients with weapon and leg injuries perform drill movements aided by the robots is the first prize winner of the i-MEDBOT Innovation Contest 2018 hold by Thailand Center of Excellence for Life Sciences ( TCELS ). [ 137 ] According to the UNESCO Institute for Statistics, Thailand devoted 1 % of its GDP to science research and growth in 2017. [ 138 ] Between 2014 and 2016, Research and development work force in Thailand increased from 84,216 people to 112,386 people. [ 139 ] Thailand was ranked 44th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, down from 43rd in 2019. [ 140 ] [ 141 ] [ 142 ] [ 143 ] The Thai government is developing new growth hub by starting with the easterly Economic Corridor of Innovation ( EECi ) to accelerating human resource and research development. [ 144 ] The National Science and Technology Development Agency is an means of the politics of Thailand which supports research in science and technology and its application in the Thai economy. [ 145 ] By December 2020 with 308.35 Mbit/s Thailand had become populace leader in terms of Internet fixed broadband internet accelerate, with Switzerland and France in Europe in positions 5 and 8 respectively, with the US at place 10 with 173.67 Mbit/s. [ 146 ]
economy
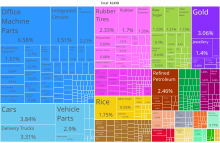 A proportional representation of Thailand exports, 2019 The economy of Thailand is heavily export-dependent, with exports accounting for more than two-thirds of gross domestic merchandise ( GDP ). Thailand exports over US $ 105 billion worth of goods and services per annum. [ 1 ] major exports include cars, computers, electric appliances, rice, textiles and footwear, fishery products, rubberize, and jewelry. [ 1 ] Thailand is an emerging economy and is considered a newly industrialised country. Thailand had a 2017 GDP of US $ 1.236 trillion ( on a purchasing power parity bit footing ). [ 147 ] Thailand is the 2nd largest economy in Southeast Asia after Indonesia. Thailand ranks center in the wealth banquet in Southeast Asia as it is the fourth rich nation according to GDP per head, after Singapore, Brunei, and Malaysia. Thailand functions as an anchor economy for the neighbor developing economies of Laos, Myanmar, and Cambodia. In the third base one-fourth of 2014, the unemployment rate in Thailand stood at 0.84 % according to Thailand ‘s National Economic and Social Development Board ( NESDB ). [ 148 ]
A proportional representation of Thailand exports, 2019 The economy of Thailand is heavily export-dependent, with exports accounting for more than two-thirds of gross domestic merchandise ( GDP ). Thailand exports over US $ 105 billion worth of goods and services per annum. [ 1 ] major exports include cars, computers, electric appliances, rice, textiles and footwear, fishery products, rubberize, and jewelry. [ 1 ] Thailand is an emerging economy and is considered a newly industrialised country. Thailand had a 2017 GDP of US $ 1.236 trillion ( on a purchasing power parity bit footing ). [ 147 ] Thailand is the 2nd largest economy in Southeast Asia after Indonesia. Thailand ranks center in the wealth banquet in Southeast Asia as it is the fourth rich nation according to GDP per head, after Singapore, Brunei, and Malaysia. Thailand functions as an anchor economy for the neighbor developing economies of Laos, Myanmar, and Cambodia. In the third base one-fourth of 2014, the unemployment rate in Thailand stood at 0.84 % according to Thailand ‘s National Economic and Social Development Board ( NESDB ). [ 148 ]
economic indicators for Thailand
Economic indicators
Nominal GDP
฿14.53 trillion ( 2016 )
[149]
GDP growth
3.9% ( 2017 )
[150]
Inflation
• Headline
• core
0.7% ( 2017 )
0.6% ( 2017 )
[150]
Employment-to-population ratio
68.0% ( 2017 )
[151] : 29
Unemployment
1.2% ( 2017 )
[150]
Total public debt
฿6.37 trillion (
Dec.
2017 )
[152]
Poverty
8.61% ( 2016 )
[151] : 36
Net household worth
฿20.34 trillion ( 2010 )
Read more: Willem Dafoe
[153] : 2
recent economic history
 Sathorn in Bangkok is a skyscraper-studded business district that is home to major hotels and embassies. Thailand experienced the world ‘s highest economic growth rate from 1985 to 1996 – averaging 12.4 % annually. In 1997 increased blackmail on the baht, a class in which the economy contracted by 1.9 %, led to a crisis that uncovered fiscal sector weaknesses and forced the Chavalit Yongchaiyudh administration to float the currency. Prime Minister Chavalit Yongchaiyudh was forced to resign after his cabinet came under fire for its boring response to the economic crisis. The baht was pegged at 25 to the US dollar from 1978 to 1997. The baht reached its lowest point of 56 to the US dollar in January 1998 and the economy contracted by 10.8 % that year, triggering the asian fiscal crisis. Thailand ‘s economy started to recover in 1999, expanding 4.2–4.4 % in 2000, thanks largely to potent exports. Growth ( 2.2 % ) was dampened by the soften of the global economy in 2001, but picked up in the subsequent years owing to solid growth in Asia, a relatively weak baht encouraging exports, and increased domestic outgo as a solution of several mega projects and incentives of Prime Minister Thaksin Shinawatra, known as Thaksinomics. Growth in 2002, 2003, and 2004 was 5–7 % annually. growth in 2005, 2006, and 2007 hovered around 4–5 %. Due both to the weaken of the US dollar and an increasingly hard Thai currentness, by March 2008 the dollar was hovering around the 33 baht mark. While Thaksinomics has received criticism, official economic data reveals that between 2001 and 2011, Isan ‘s GDP per head more than doubled to US $ 1,475, while, over the same period, GDP in the Bangkok area increased from US $ 7,900 to about US $ 13,000. [ 154 ] With the instability surrounding major 2010 protests, the GDP emergence of Thailand settled at around 4–5 %, from highs of 5–7 % under the former civilian administration. political doubt was identified as the primary induce of a decline in investor and consumer assurance. The IMF predicted that the Thai economy would rebound strongly from the abject 0.1 % GDP increase in 2011, to 5.5 % in 2012 and then 7.5 % in 2013, due to the monetary policy of the Bank of Thailand, a well as a software of fiscal stimulation measures introduced by the erstwhile Yingluck Shinawatra government. [ 155 ] Following the Thai military coup d’etat of 22 May 2014. In 2017, Concluded with information on the Thai economy ‘s grew an inflation-adjusted 3.9 %, up from 3.3 % in 2016, marking its fastest expansion since 2012. [ 156 ]
Sathorn in Bangkok is a skyscraper-studded business district that is home to major hotels and embassies. Thailand experienced the world ‘s highest economic growth rate from 1985 to 1996 – averaging 12.4 % annually. In 1997 increased blackmail on the baht, a class in which the economy contracted by 1.9 %, led to a crisis that uncovered fiscal sector weaknesses and forced the Chavalit Yongchaiyudh administration to float the currency. Prime Minister Chavalit Yongchaiyudh was forced to resign after his cabinet came under fire for its boring response to the economic crisis. The baht was pegged at 25 to the US dollar from 1978 to 1997. The baht reached its lowest point of 56 to the US dollar in January 1998 and the economy contracted by 10.8 % that year, triggering the asian fiscal crisis. Thailand ‘s economy started to recover in 1999, expanding 4.2–4.4 % in 2000, thanks largely to potent exports. Growth ( 2.2 % ) was dampened by the soften of the global economy in 2001, but picked up in the subsequent years owing to solid growth in Asia, a relatively weak baht encouraging exports, and increased domestic outgo as a solution of several mega projects and incentives of Prime Minister Thaksin Shinawatra, known as Thaksinomics. Growth in 2002, 2003, and 2004 was 5–7 % annually. growth in 2005, 2006, and 2007 hovered around 4–5 %. Due both to the weaken of the US dollar and an increasingly hard Thai currentness, by March 2008 the dollar was hovering around the 33 baht mark. While Thaksinomics has received criticism, official economic data reveals that between 2001 and 2011, Isan ‘s GDP per head more than doubled to US $ 1,475, while, over the same period, GDP in the Bangkok area increased from US $ 7,900 to about US $ 13,000. [ 154 ] With the instability surrounding major 2010 protests, the GDP emergence of Thailand settled at around 4–5 %, from highs of 5–7 % under the former civilian administration. political doubt was identified as the primary induce of a decline in investor and consumer assurance. The IMF predicted that the Thai economy would rebound strongly from the abject 0.1 % GDP increase in 2011, to 5.5 % in 2012 and then 7.5 % in 2013, due to the monetary policy of the Bank of Thailand, a well as a software of fiscal stimulation measures introduced by the erstwhile Yingluck Shinawatra government. [ 155 ] Following the Thai military coup d’etat of 22 May 2014. In 2017, Concluded with information on the Thai economy ‘s grew an inflation-adjusted 3.9 %, up from 3.3 % in 2016, marking its fastest expansion since 2012. [ 156 ]
Income, poverty and wealth
Thais have medial wealth per one pornographic person of $ 1,469 in 2016, [ 157 ] : 98 increasing from $ 605 in 2010. [ 157 ] : 34 In 2016, Thailand was ranked 87th in Human Development Index, and 70th in the inequality-adjusted HDI. [ 158 ] In 2017, Thailand ‘s median family income was ฿26,946 per month. [ 159 ] : 1 Top quintile households had a 45.0 % share of all income, while bed quintile households had 7.1 %. [ 159 ] : 4 There were 26.9 million persons who had the bottom 40 % of income earning less than ฿5,344 per person per month. [ 160 ] : 5 During 2013–2014 Thai political crisis, a survey found that anti-government PDRC largely ( 32 % ) had a monthly income of more than ฿50,000, while pro-government UDD largely ( 27 % ) had between ฿10,000 and ฿20,000. [ 161 ] : 7 In 2014, Credit Suisse reported that Thailand was the world ‘s third gear most unequal country, behind Russia and India. [ 162 ] The top 10 % deep held 79 % of the state ‘s assets. [ 162 ] The top 1 % rich held 58 % of the assets. [ 162 ] Thai 50 richest families had a total net worth account to 30 % of GDP. [ 162 ] In 2016, 5.81 million people lived in poverty, or 11.6 million people ( 17.2 % of population ) if “ near poor ” is included. [ 160 ] : 1 symmetry of the poor relative to total population in each region was 12.96 % in the Northeast, 12.35 % in the South, and 9.83 % in the North. [ 160 ] : 2 In 2017, there were 14 million people who applied for social wellbeing ( annual income of less than ฿100,000 was required ). [ 162 ] At the end of 2017, Thailand ‘s sum family debt was ฿11.76 trillion. [ 151 ] : 5 In 2010, 3 % of all family were bankrupt. [ 153 ] : 5 In 2016, there were estimated 30,000 homeless persons in the country. [ 163 ]
Exports and manufacture
 A proportional representation of Thailand ‘s exports The economy of Thailand is heavily export-dependent, with exports accounting for more than two-thirds of gross domestic product ( GDP ). Thailand exports over US $ 105 billion worth of goods and services annually. [ 1 ] major exports include cars, computers, electrical appliances, rice, textiles and footwear, fishery products, rubberize, and jewelry. [ 1 ] solid industries include electric appliances, components, computer components, and vehicles. Thailand ‘s convalescence from the 1997–1998 asian fiscal crisis depended chiefly on exports, among diverse early factors. As of 2012, the Thai automotive industry was the largest in Southeast Asia and the 9th largest in the global. [ 164 ] [ 165 ] [ 166 ] The Thailand diligence has an annual output signal of near 1.5 million vehicles, largely commercial vehicles. [ 166 ] Most of the vehicles built in Thailand are developed and licensed by foreign producers, chiefly japanese and american. The Thai car industry takes advantage of the ASEAN Free Trade Area ( AFTA ) to find a marketplace for many of its products. Eight manufacturers, five japanese, two US, and Tata of India, produce pick-up trucks in Thailand. [ 167 ] As of 2012, Due to its favorable taxation for 2-door pick-ups at entirely 3-12 % against 17-50 % for passenger cars, Thailand was the second largest consumer of pick-up trucks in the world, after the US. [ 168 ] In 2014, pick-ups accounted for 42 % of all modern vehicle sales in Thailand. [ 167 ]
A proportional representation of Thailand ‘s exports The economy of Thailand is heavily export-dependent, with exports accounting for more than two-thirds of gross domestic product ( GDP ). Thailand exports over US $ 105 billion worth of goods and services annually. [ 1 ] major exports include cars, computers, electrical appliances, rice, textiles and footwear, fishery products, rubberize, and jewelry. [ 1 ] solid industries include electric appliances, components, computer components, and vehicles. Thailand ‘s convalescence from the 1997–1998 asian fiscal crisis depended chiefly on exports, among diverse early factors. As of 2012, the Thai automotive industry was the largest in Southeast Asia and the 9th largest in the global. [ 164 ] [ 165 ] [ 166 ] The Thailand diligence has an annual output signal of near 1.5 million vehicles, largely commercial vehicles. [ 166 ] Most of the vehicles built in Thailand are developed and licensed by foreign producers, chiefly japanese and american. The Thai car industry takes advantage of the ASEAN Free Trade Area ( AFTA ) to find a marketplace for many of its products. Eight manufacturers, five japanese, two US, and Tata of India, produce pick-up trucks in Thailand. [ 167 ] As of 2012, Due to its favorable taxation for 2-door pick-ups at entirely 3-12 % against 17-50 % for passenger cars, Thailand was the second largest consumer of pick-up trucks in the world, after the US. [ 168 ] In 2014, pick-ups accounted for 42 % of all modern vehicle sales in Thailand. [ 167 ]
tourism
tourism makes up about 6 % of the state ‘s economy. Thailand was the most visit country in Southeast Asia in 2013, according to the World Tourism Organisation. Estimates of tourism receipts directly contributing to the Thai GDP of 12 trillion baht range from 9 percentage ( 1 trillion baht ) ( 2013 ) to 16 percentage. [ 169 ] When including the indirect effects of tourism, it is said to account for 20.2 percentage ( 2.4 trillion baht ) of Thailand ‘s GDP. [ 170 ] : 1 asian tourists primarily visit Thailand for Bangkok and the historical, natural, and cultural sights in its vicinity. western tourists not only visit Bangkok and surroundings, but in addition many travel to the southerly beaches and islands. The north is the headman finish for trekking and venture travel with its divers cultural minority groups and forested mountains. The region hosting the fewest tourists is Isan. To accommodate foreign visitors, a separate tourism patrol with offices were set up in the major tourist areas and an emergency telephone number. [ 171 ] Thailand ranks 5th biggest checkup tourism address of inbound aesculapian tourism spend, according to World Travel and Tourism Council, attracting over 2.5 million visitors in 2018. [ 172 ] The area is besides Asia ‘s count one. [ 173 ] The area is popular for the growing rehearse of sex reassignment surgery ( SRS ) and cosmetic surgery. In 2010–2012, more than 90 % of checkup tourists travelled to Thailand for SRS. [ 174 ] prostitution in Thailand and sex tourism besides form a de facto part of the economy. Campaigns promote Thailand as exotic to attract tourists. [ 175 ] One calculate published in 2003 placed the trade wind at US $ 4.3 billion per year or about 3 % of the Thai economy. [ 176 ] It is believed that at least 10 % of tourist dollars are spent on the sex barter. [ 177 ]
farming and natural resources
forty-nine per penny of Thailand ‘s labor force is employed in department of agriculture. [ 178 ] This is polish from 70 % in 1980. [ 178 ] Rice is the most significant snip in the country and Thailand had long been the world ‘s lead exporter of rice, until recently falling behind both India and Vietnam. [ 179 ] Thailand has the highest share of arable land, 27.25 %, of any nation in the Greater Mekong Subregion. [ 180 ] About 55 % of the arable land area is used for rice production. [ 181 ] agriculture has been experiencing a transition from labor-intensive and transitional methods to a more industrialized and competitive sector. [ 178 ] Between 1962 and 1983, the agrarian sector grew by 4.1 % per year on average and continued to grow at 2.2 % between 1983 and 2007. [ 178 ] The relative contribution of agriculture to GDP has declined while exports of goods and services have increased. furthermore, access to biocapacity in Thailand is lower than populace average. In 2016, Thailand had 1.2 global hectares [ 182 ] of biocapacity per person within its territory, a fiddling less than world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. [ 183 ] In contrast, in 2016, they used 2.5 ball-shaped hectares of biocapacity – their ecological footprint of pulmonary tuberculosis. This means they use about twice american samoa much biocapacity as Thailand contains. As a result, Thailand is running a biocapacity deficit. [ 182 ]
Energy
75 % of Thailand ‘s electrical generation is powered by natural flatulence in 2014. [ 184 ] coal-fired baron plants produce an extra 20 % of electricity, with the remainder coming from biomass, hydro, and biogas. [ 184 ] Thailand produces roughly one-third of the petroleum it consumes. It is the second largest importer of vegetable oil in SE Asia. Thailand is a large manufacturer of natural natural gas, with reserves of at least 10 trillion cubic feet. After Indonesia, it is the largest char producer in SE Asia, but must import extra coal to meet domestic demand .
informal economy
Thailand has a divers and robust informal labor sector—in 2012, it was estimated that informal workers comprised 62.6 % of the Thai work force. The Ministry of Labour defines informal workers to be individuals who work in informal economies and do not have employee condition under a given country ‘s Labour Protection Act ( LPA ). The informal sector in Thailand has grown importantly over the past 60 years over the course of Thailand ‘s gradual transition from an agriculture-based economy to becoming more industrialize and service-oriented. [ 185 ] Between 1993 and 1995, ten percentage of the Thai labor push moved from the agrarian sector to urban and industrial jobs, specially in the fabrication sector. It is estimated that between 1988 and 1995, the phone number of factory workers in the country doubled from two to four million, as Thailand ‘s GDP tripled. [ 186 ] While the asian Financial Crisis that followed in 1997 hit the Thai economy hard, the industrial sector continued to expand under far-flung deregulation, as Thailand was mandated to adopt a crop of geomorphologic adaptation reforms upon receiving fund from the IMF and World Bank. These reforms implemented an agenda of increase denationalization and trade liberalization in the state, and decreased federal subsidization of public goods and utilities, agricultural price supports, and regulations on fairly wages and labor conditions. [ 187 ] These changes put far blackmail on the agrarian sector, and prompted continued migration from the rural countryside to the growing cities. many migrant farmers found work in Thailand ‘s growing fabrication diligence, and took jobs in sweatshops and factories with few british labour party regulations and often exploitative conditions. [ 188 ] Those that could not find formal factory work, including illegal migrants and the families of rural Thai migrants that followed their relatives to the urban centres, turned to the informal sector to provide the extra support needed for survival—under the far-flung regulation imposed by the morphologic allowance programs, one family member working in a factory or sweatshop made very little. Scholars argue that the economic consequences and social costs of Thailand ‘s tug reforms in the awaken of the 1997 asian Financial Crisis fell on individuals and families rather than the country. This can be described as the “ externalization of commercialize risk ”, meaning that as the country ‘s labor market became increasingly deregulated, the charge and duty of providing an adequate support shifted from employers and the country to the workers themselves, whose families had to find jobs in the informal sector to make up for the losses and subsidise the wages being made by their relatives in the formal sector. The slant of these economic changes hit migrants and the urban hapless specially hard, and the informal sector expanded quickly as a result. [ 187 ] today, cozy tug in Thailand is typically break down into three main groups : subcontracted/self employed/home-based workers, service workers ( including those that are employed in restaurants, as street vendors, masseuses, taxi drivers, and as domestic workers ), and agricultural workers. not included in these categories are those that work in entertainment, nightlife, and the arouse diligence. Individuals employed in these facets of the informal tug sector face extra vulnerabilities, including recruitment into circles of sexual exploitation and human traffic. [ 185 ] In general, department of education levels are first gear in the informal sector. A 2012 discipline found that 64 % of cozy workers had not completed education beyond primary school. many informal workers are besides migrants, only some of which have legal status in the area. education and citizenship are two main barriers to entry for those looking to work in formal industries, and enjoy the labor protections and social security benefits that come along with dinner dress employment. Because the cozy parturiency sector is not recognised under the Labour Protection Act ( LPA ), cozy workers are much more vulnerable labor to exploitation and dangerous working conditions than those employed in more dinner dress and federally greet industries. While some Thai labour laws provide minimal protections to domestic and agricultural workers, they are frequently decrepit and unmanageable to enforce. Furthermore, Thai social security policies fail to protect against the risks many cozy workers face, including workplace accidents and compensation equally well as unemployment and retirement indemnity. many informal workers are not legally contracted for their use, and many do not make a living engage. [ 185 ] As a leave, british labour party traffic is common in the region, affecting children and adults, men and women, and migrants and Thai citizens alike .
transportation system
 The BTS Skytrain is an lift rapid transit system in Bangkok The State Railway of Thailand ( SRT ) operates all of Thailand ‘s national vilify lines. Bangkok Railway Station ( Hua Lamphong Station ) is the independent end point of all routes. Phahonyothin and ICD Lat Krabang are the main cargo terminals. As of 2017 SRT had 4,507 km ( 2,801 mile ) of track, all of it meter gauge except the Airport Link. closely all is single-track ( 4,097 kilometer ), although some important sections around Bangkok are double ( 303 kilometer or 188 michigan ) or triple-tracked ( 107 kilometer or 66 security service ) and there are plans to extend this. [ 189 ] Rail enchant in Bangkok includes long-distance services, and some day by day commuter trains running from and to the outskirts of the city during the rush hour, but passenger numbers have remained low. There are besides three rapid transit rail systems in the capital. Thailand has 390,000 kilometres ( 240,000 miles ) of highways. [ 190 ] According to the BBC Thailand has 462,133 roads and many multi-lane highways. As of 2017 Thailand has 37 million register vehicles, 20 million of them motorbikes. A count of undivided two-lane highways have been converted into divided four-lane highways. A Bangkok – Chon Buri expressway ( Route 7 ) now links to the new airport and Eastern Seaboard. There are 4,125 public vans operating on 114 routes from Bangkok alone. [ 191 ] other forms of road transport includes tuk-tuks, taxis—as of November 2018, Thailand has 80,647 registered cab nationally [ 192 ] —vans ( minibus ), minibike taxis and songthaews. As of 2012, Thailand had 103 airports with 63 paved runways, in addition to 6 heliports. The busiest airport in the county is Bangkok ‘s Suvarnabhumi Airport .
The BTS Skytrain is an lift rapid transit system in Bangkok The State Railway of Thailand ( SRT ) operates all of Thailand ‘s national vilify lines. Bangkok Railway Station ( Hua Lamphong Station ) is the independent end point of all routes. Phahonyothin and ICD Lat Krabang are the main cargo terminals. As of 2017 SRT had 4,507 km ( 2,801 mile ) of track, all of it meter gauge except the Airport Link. closely all is single-track ( 4,097 kilometer ), although some important sections around Bangkok are double ( 303 kilometer or 188 michigan ) or triple-tracked ( 107 kilometer or 66 security service ) and there are plans to extend this. [ 189 ] Rail enchant in Bangkok includes long-distance services, and some day by day commuter trains running from and to the outskirts of the city during the rush hour, but passenger numbers have remained low. There are besides three rapid transit rail systems in the capital. Thailand has 390,000 kilometres ( 240,000 miles ) of highways. [ 190 ] According to the BBC Thailand has 462,133 roads and many multi-lane highways. As of 2017 Thailand has 37 million register vehicles, 20 million of them motorbikes. A count of undivided two-lane highways have been converted into divided four-lane highways. A Bangkok – Chon Buri expressway ( Route 7 ) now links to the new airport and Eastern Seaboard. There are 4,125 public vans operating on 114 routes from Bangkok alone. [ 191 ] other forms of road transport includes tuk-tuks, taxis—as of November 2018, Thailand has 80,647 registered cab nationally [ 192 ] —vans ( minibus ), minibike taxis and songthaews. As of 2012, Thailand had 103 airports with 63 paved runways, in addition to 6 heliports. The busiest airport in the county is Bangkok ‘s Suvarnabhumi Airport .
Demographics
 population pyramid 2016 Thailand had a population of 69,799,978 as of 2020. [ citation needed ] Thailand ‘s population is largely rural, concentrated in the rice-growing areas of the central, northeastern and northern regions. About 45.7 % of Thailand ‘s population lived in urban areas as of 2010, concentrated by and large in and around the Bangkok Metropolitan Area. Thailand ‘s government-sponsored family planning program resulted in a dramatic decline in population growth from 3.1 % in 1960 to around 0.4 % today. In 1970, an average of 5.7 people lived in a Thai family. At the time of the 2010 census, the average Thai family size was 3.2 people .
population pyramid 2016 Thailand had a population of 69,799,978 as of 2020. [ citation needed ] Thailand ‘s population is largely rural, concentrated in the rice-growing areas of the central, northeastern and northern regions. About 45.7 % of Thailand ‘s population lived in urban areas as of 2010, concentrated by and large in and around the Bangkok Metropolitan Area. Thailand ‘s government-sponsored family planning program resulted in a dramatic decline in population growth from 3.1 % in 1960 to around 0.4 % today. In 1970, an average of 5.7 people lived in a Thai family. At the time of the 2010 census, the average Thai family size was 3.2 people .
ethnic groups
 Hill tribes girls in the Northeast of Thailand thai nationals make up the majority of Thailand ‘s population, 95.9 % in 2010. The remaining 4.1 % of the population are Burmese ( 2.0 % ), others 1.3 %, and unspecified 0.9 %. [ 1 ] According to the Royal Thai Government ‘s 2011 Country Report to the UN Committee responsible for the International Convention for the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination, available from the Department of Rights and Liberties Promotion of the Thai Ministry of Justice, : 3 62 heathen communities are officially recognised in Thailand. Twenty million Central Thai ( together with approximately 650,000 Khorat Thai ) make up approximately 20,650,000 ( 34.1 percentage ) of the nation ‘s population of 60,544,937 [ 193 ] at the time of completion of the Mahidol University Ethnolinguistic Maps of Thailand data ( 1997 ). [ 194 ] The 2011 Thailand Country Report provides population numbers for batch peoples ( ‘hill tribes ‘ ) and cultural communities in the Northeast and is explicit about its main reliance on the Mahidol University Ethnolinguistic Maps of Thailand data. [ 194 ] Thus, though over 3.288 million people in the Northeast alone could not be categorised, the population and percentages of other heathen communities circa 1997 are known for all of Thailand and constitute minimum populations. In descending rate, the largest ( adequate to or greater than 400,000 ) are a ) 15,080,000 Lao ( 24.9 percentage ) consist of the Thai Lao ( 14 million ) and other smaller Lao groups, namely the Thai Loei ( 400–500,000 ), Lao Lom ( 350,000 ), Lao Wiang/Klang ( 200,000 ), Lao Khrang ( 90,000 ), Lao Ngaew ( 30,000 ), and Lao Ti ( 10,000 ; bacillus ) six million Khon Muang ( 9.9 percentage, besides called Northern Thais ) ; c ) 4.5 million Pak Tai ( 7.5 percentage, besides called Southern Thais ) ; five hundred ) 1.4 million Khmer Leu ( 2.3 percentage, besides called Northern Khmer ) ; e ) 900,000 Malay ( 1.5 % ) ; f ) 500,000 Nyaw ( 0.8 percentage ) ; gigabyte ) 470,000 Phu Thai ( 0.8 percentage ) ; h ) 400,000 Kuy/Kuay ( besides known as Suay ) ( 0.7 percentage ), and i ) 350,000 Karen ( 0.6 percentage ). : 7–13 Thai Chinese, those of meaning chinese inheritance, are 14 % of the population, while Thais with overtone chinese lineage comprise up to 40 % of the population. [ 195 ] Thai Malays represent 3 % of the population, with the end consist of Mons, Khmers and respective “ mound tribes “. The country ‘s official lyric is Thai and the primary religion is Theravada Buddhism, which is practised by around 95 % of the population. Increasing numbers of migrants from neighbouring Myanmar, Laos, and Cambodia, equally well as from Nepal and India, have pushed the total number of non-national residents to around 3.5 million as of 2009, up from an estimated 2 million in 2008, and about 1.3 million in 2000. [ 196 ] Some 41,000 Britons and 20,000 Australians live in Thailand. [ 197 ] [ 198 ]
Hill tribes girls in the Northeast of Thailand thai nationals make up the majority of Thailand ‘s population, 95.9 % in 2010. The remaining 4.1 % of the population are Burmese ( 2.0 % ), others 1.3 %, and unspecified 0.9 %. [ 1 ] According to the Royal Thai Government ‘s 2011 Country Report to the UN Committee responsible for the International Convention for the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination, available from the Department of Rights and Liberties Promotion of the Thai Ministry of Justice, : 3 62 heathen communities are officially recognised in Thailand. Twenty million Central Thai ( together with approximately 650,000 Khorat Thai ) make up approximately 20,650,000 ( 34.1 percentage ) of the nation ‘s population of 60,544,937 [ 193 ] at the time of completion of the Mahidol University Ethnolinguistic Maps of Thailand data ( 1997 ). [ 194 ] The 2011 Thailand Country Report provides population numbers for batch peoples ( ‘hill tribes ‘ ) and cultural communities in the Northeast and is explicit about its main reliance on the Mahidol University Ethnolinguistic Maps of Thailand data. [ 194 ] Thus, though over 3.288 million people in the Northeast alone could not be categorised, the population and percentages of other heathen communities circa 1997 are known for all of Thailand and constitute minimum populations. In descending rate, the largest ( adequate to or greater than 400,000 ) are a ) 15,080,000 Lao ( 24.9 percentage ) consist of the Thai Lao ( 14 million ) and other smaller Lao groups, namely the Thai Loei ( 400–500,000 ), Lao Lom ( 350,000 ), Lao Wiang/Klang ( 200,000 ), Lao Khrang ( 90,000 ), Lao Ngaew ( 30,000 ), and Lao Ti ( 10,000 ; bacillus ) six million Khon Muang ( 9.9 percentage, besides called Northern Thais ) ; c ) 4.5 million Pak Tai ( 7.5 percentage, besides called Southern Thais ) ; five hundred ) 1.4 million Khmer Leu ( 2.3 percentage, besides called Northern Khmer ) ; e ) 900,000 Malay ( 1.5 % ) ; f ) 500,000 Nyaw ( 0.8 percentage ) ; gigabyte ) 470,000 Phu Thai ( 0.8 percentage ) ; h ) 400,000 Kuy/Kuay ( besides known as Suay ) ( 0.7 percentage ), and i ) 350,000 Karen ( 0.6 percentage ). : 7–13 Thai Chinese, those of meaning chinese inheritance, are 14 % of the population, while Thais with overtone chinese lineage comprise up to 40 % of the population. [ 195 ] Thai Malays represent 3 % of the population, with the end consist of Mons, Khmers and respective “ mound tribes “. The country ‘s official lyric is Thai and the primary religion is Theravada Buddhism, which is practised by around 95 % of the population. Increasing numbers of migrants from neighbouring Myanmar, Laos, and Cambodia, equally well as from Nepal and India, have pushed the total number of non-national residents to around 3.5 million as of 2009, up from an estimated 2 million in 2008, and about 1.3 million in 2000. [ 196 ] Some 41,000 Britons and 20,000 Australians live in Thailand. [ 197 ] [ 198 ]
population centres
language
 An ethnolinguistic map of Thailand .
An ethnolinguistic map of Thailand . The Silajaruek of Sukhothai Kingdom are hundreds of stone inscriptions that form a historic read of the period. The official language of Thailand is Thai, a Kra–Dai language closely related to Lao, Shan in Myanmar, and numerous smaller languages spoken in an bow from Hainan and Yunnan south to the chinese bound. It is the principal linguistic process of education and government and spoken throughout the nation. The criterion is based on the dialect of the cardinal Thai people, and it is written in the Thai alphabet, an abugida script that evolved from the Khmer rudiment. sixty-two languages were recognised by the Royal Thai Government. For the purposes of the national census, four dialects of Thai exist ; these partially coincide with regional designations, such as Southern Thai and Northern Thai. The largest of Thailand ‘s minority languages is the Lao dialect of Isan speak in the northeastern provinces. Although sometimes considered a Thai dialect, it is a Lao dialect, and the region where it is traditionally spoken was historically separate of the Lao kingdom of Lan Xang. [ citation needed ] In the far confederacy, Kelantan-Pattani Malay is the chief language of Malay Muslims. Varieties of Chinese are besides spoken by the boastfully Thai Chinese population, with the Teochew dialect best-represented. numerous tribal languages are besides spoken, including many Austroasiatic languages such as Mon, Khmer, Viet, Mlabri and Orang Asli ; austronesian languages such as Cham and Moken ; sino-tibetan languages like Lawa, Akha, and Karen ; and other Tai languages such as Tai Yo, Phu Thai, and Saek. Hmong is a member of the Hmong–Mien languages, which is now regarded as a linguistic process kin of its own .
The Silajaruek of Sukhothai Kingdom are hundreds of stone inscriptions that form a historic read of the period. The official language of Thailand is Thai, a Kra–Dai language closely related to Lao, Shan in Myanmar, and numerous smaller languages spoken in an bow from Hainan and Yunnan south to the chinese bound. It is the principal linguistic process of education and government and spoken throughout the nation. The criterion is based on the dialect of the cardinal Thai people, and it is written in the Thai alphabet, an abugida script that evolved from the Khmer rudiment. sixty-two languages were recognised by the Royal Thai Government. For the purposes of the national census, four dialects of Thai exist ; these partially coincide with regional designations, such as Southern Thai and Northern Thai. The largest of Thailand ‘s minority languages is the Lao dialect of Isan speak in the northeastern provinces. Although sometimes considered a Thai dialect, it is a Lao dialect, and the region where it is traditionally spoken was historically separate of the Lao kingdom of Lan Xang. [ citation needed ] In the far confederacy, Kelantan-Pattani Malay is the chief language of Malay Muslims. Varieties of Chinese are besides spoken by the boastfully Thai Chinese population, with the Teochew dialect best-represented. numerous tribal languages are besides spoken, including many Austroasiatic languages such as Mon, Khmer, Viet, Mlabri and Orang Asli ; austronesian languages such as Cham and Moken ; sino-tibetan languages like Lawa, Akha, and Karen ; and other Tai languages such as Tai Yo, Phu Thai, and Saek. Hmong is a member of the Hmong–Mien languages, which is now regarded as a linguistic process kin of its own .
religion
Religion in Thailand (2018)[199]
Religion
Percent
Buddhism
93.46%
Islam
5.37%
Christianity
1.13%
Hinduism
0.018%
Unaffiliated/others
0.003%
The country ‘s most prevailing religion is Theravada Buddhism, which is an integral separate of Thai identity and culture. active participation in Buddhism is among the highest in the world. Thailand has the second-largest number of Buddhists in the populace after China. [ 200 ] According to the 2000 census, 94.6 % and 93.58 % in 2010 of the nation ‘s population self-identified as Buddhists of the Theravada custom .
Muslims constitute the moment largest religious group in Thailand, comprising 5.4 % of the population in 2018. [ 201 ] Islam is concentrated largely in the nation ‘s southernmost provinces : Pattani, Yala, Satun, Narathiwat, and part of Songkhla Chumphon, which are predominantly Malay, most of whom are Sunni Muslims. Christians represented 1.13 % ( 2018 ) of the population in 2018, with the remaining population consisting of Hindus and Sikhs, who live by and large in the country ‘s cities. There is besides a little but historically significant Jewish community in Thailand dating rear to the seventeenth century. The constitution does not name official country religion, and provides for exemption of religion. evening the authority formally does not register new religious groups that have not been accepted and limit the count of missionaries, unregistered religious organisations american samoa well as missionaries who are allowed to operate freely. There have been no widespread reports of social abuses or discrimination based on religious belief or practice. [ 202 ] Thai law officially recognizes five religious groups : Buddhists, Muslims, Brahmin-Hindus, Sikhs, and Christians. [ 203 ] however, some laws are inspired from Buddhist practices, such as banning alcohol sales on religious holidays. [ 204 ]
Health
Thailand ranks world ‘s 6th, and Asia ‘s 1st in the 2019 Global Health Security Index of ball-shaped health security capabilities in 195 countries, [ 205 ] making it the entirely developing state on the earth ‘s peak ten. Thailand had 62 hospitals accredited by Joint Commission International. [ 206 ] In 2002, Bumrungrad became the first base hospital in Asia to meet the standard. Health and medical care is overseen by the Ministry of Public Health ( MOPH ), along with several other non-ministerial government agencies, with entire national expenditures on health amounting to 4.3 percentage of GDP in 2009. Non-communicable diseases form the major burden of unwholesomeness and mortality, while infectious diseases including malaria and tuberculosis, vitamin a well as traffic accidents, are besides important public health issues. The stream Minister for Public Health is Anutin Charnvirakul. In December 2018 the interim parliament voted to legalise the use of cannabis for medical reasons. Recreational use remained improper. The National Legislative Assembly had 166 votes in favor of the amendment to the Narcotics Bill, while there were no nay votes and 13 abstentions. The vote makes Thailand the first Southeast asian state to allow the use of medical cannabis. [ 207 ]
culture
thai culture and traditions incorporate a great deal of influence from India, China, Cambodia, and the rest of Southeast Asia. Thailand ‘s national religion, Theravada Buddhism, is cardinal to modern Thai identity. Thai Buddhism has evolved over time to include many regional beliefs originating from Hinduism, animism, ampere well as ancestor worship. The official calendar in Thailand is based on the eastern version of the Buddhist Era ( BE ). Thai identity nowadays is a social construct of Phibun regimen in 1940s. several cultural groups mediated change between their traditional local culture, national Thai, and global cultural influences. Overseas Chinese besides form a significant contribution of Thai society, particularly in and around Bangkok. Their successful integration into Thai society has allowed them to hold positions of economic and political ability. Thai chinese businesses prosper as character of the larger bamboo net. [ 208 ]
 People floating krathong rafts during the Loi Krathong festival in Chiang Mai, Thailand Respects for aged and superiors ( by historic period, position, monks, or certain professions ) is thai mores. As with other asian cultures, deference towards ancestors is an essential function of Thai spiritual exercise. Thais have strong sense of social hierarchy, reflecting in many classes of honorifics. Elders have by custom ruled in family decisions or ceremonies. Wai is a traditional Thai greeting, and is generally offered first by person who is younger or lower in social status and stead. Older siblings have duties to younger ones. Thais have a hard smell of cordial reception and generosity. [ citation needed ] Taboos in Thai acculturation include touching person ‘s promontory or pointing with the feet, as the head is considered the most sacred and the foot the lowest partially of the body .
People floating krathong rafts during the Loi Krathong festival in Chiang Mai, Thailand Respects for aged and superiors ( by historic period, position, monks, or certain professions ) is thai mores. As with other asian cultures, deference towards ancestors is an essential function of Thai spiritual exercise. Thais have strong sense of social hierarchy, reflecting in many classes of honorifics. Elders have by custom ruled in family decisions or ceremonies. Wai is a traditional Thai greeting, and is generally offered first by person who is younger or lower in social status and stead. Older siblings have duties to younger ones. Thais have a hard smell of cordial reception and generosity. [ citation needed ] Taboos in Thai acculturation include touching person ‘s promontory or pointing with the feet, as the head is considered the most sacred and the foot the lowest partially of the body .
art
The origins of Thai art were very much influenced by Buddhist artwork and by scenes from the amerind epics. traditional Thai sculpt about entirely depicts images of the Buddha, being very similar with the other styles from Southeast Asia. Traditional Thai paintings normally consist of book illustrations, and painted ornamentation of buildings such as palaces and temples. Thai artwork was influenced by autochthonal civilisations of the Mon and other civilisations. By the Sukothai and Ayutthaya period, thai had developed into its own alone style and was subsequently far influenced by the other asian styles, largely by Sri Lankan and Chinese. Thai sculpt and paint, and the royal courts provided patronize, erecting temples and other religious shrines as acts of deserve or to commemorate crucial events. [ 209 ] traditional Thai paintings showed subjects in two dimensions without perspective. The size of each component in the picture reflected its degree of importance. The primary technique of composition is that of apportioning areas : the main elements are isolated from each other by space transformers. This eliminated the average anchor, which would otherwise imply position. perspective was introduced only as a result of western influence in the mid-19th century. Monk artist Khrua In Khong is well known as the first artist to introduce linear perspective to Thai traditional art. [ 210 ] The most frequent narrative subjects for paintings were or are : the Jataka stories, episodes from the animation of the Buddha, the Buddhist heavens and hells, themes derived from the Thai versions of the Ramayana and Mahabharata, not to mention scenes of casual life. Some of the scenes are influenced by Thai folklore alternatively of following rigorous Buddhist iconography. [ 209 ]
architecture
 Two sculptures guarding the easterly gate to the main chapel of Wat Arun architecture is the leading medium of the area ‘s cultural bequest and reflects both the challenges of animation in Thailand ‘s sometimes extreme climate vitamin a well as, historically, the importance of architecture to the Thai people ‘s common sense of community and religious beliefs. Influenced by the architectural traditions of many of Thailand ‘s neighbours, it has besides developed significant regional mutant within its common and religious buildings. The Ayutthaya Kingdom movement, which went from approximately 1350 to 1767, was one of the most fruitful and creative periods in Thai architecture The identity of architecture in Ayutthaya period is designed to display might and riches so it has big size and appearance. The temples in Ayutthaya rarely built eaves stretching from the masterhead. The dominant feature of this dash is sunlight shining into buildings. During the latter depart of the Ayutthaya period, architecture was regarded as a vertex accomplishment that responded to the requirements of people and expressed the gracefulness of Thainess. [ 211 ] buddhist temples in Thailand are known as “ wats “, from the Pāḷi vāṭa, meaning an enclosure. A temple has an enclosing wall that divides it from the laic worldly concern. Wat architecture has seen many changes in Thailand in the run of history. Although there are many differences in layout and style, they all adhere to the like principles. [ 212 ]
Two sculptures guarding the easterly gate to the main chapel of Wat Arun architecture is the leading medium of the area ‘s cultural bequest and reflects both the challenges of animation in Thailand ‘s sometimes extreme climate vitamin a well as, historically, the importance of architecture to the Thai people ‘s common sense of community and religious beliefs. Influenced by the architectural traditions of many of Thailand ‘s neighbours, it has besides developed significant regional mutant within its common and religious buildings. The Ayutthaya Kingdom movement, which went from approximately 1350 to 1767, was one of the most fruitful and creative periods in Thai architecture The identity of architecture in Ayutthaya period is designed to display might and riches so it has big size and appearance. The temples in Ayutthaya rarely built eaves stretching from the masterhead. The dominant feature of this dash is sunlight shining into buildings. During the latter depart of the Ayutthaya period, architecture was regarded as a vertex accomplishment that responded to the requirements of people and expressed the gracefulness of Thainess. [ 211 ] buddhist temples in Thailand are known as “ wats “, from the Pāḷi vāṭa, meaning an enclosure. A temple has an enclosing wall that divides it from the laic worldly concern. Wat architecture has seen many changes in Thailand in the run of history. Although there are many differences in layout and style, they all adhere to the like principles. [ 212 ]
literature
Thai literature has had a long history. tied before the constitution of the Sukhothai Kingdom there existed oral and written works. During the Sukhothai Kingdom, Most literary works were written in simple prose with certain alliteration schemes. major works include King Ram Khamhaeng Inscription describing biography at the time, which is considered the first literary oeuvre in Thai script, but some historians questioned its authenticity. [ 213 ] Trai Phum Phra Ruang, written in 1345 by King Maha Thammaracha I, expounds Buddhist philosophy based on a fundamental and extensive sketch with reference to over 30 hallowed texts and could be considered the state ‘s first while of research dissertation. [ 214 ]
During the Ayutthaya Kingdom, new poetic forms were created, with unlike rhyme schemes and metres. It is park to find a combination of different poetic forms in one poetic work. Lilit Yuan Phai is a narrative poem describing the war between King Borommatrailokkanat of Ayutthaya and Prince Tilokkarat of Lan Na. One of the most beautiful literary work is Kap He Ruea composed by Prince Thammathibet in the nirat tradition. traditionally, the poetry is sung during the colorful royal barge procession and has been the model for subsequent poets to emulate. The same prince besides composed the greatly admired Kap Ho Khlong on the Visit to Than Thongdaeng and Kap Ho Khlong Nirat Phrabat. [ 215 ] Despite its abruptly menstruation of 15 years, Thon Buri Period produced Ramakian, a poetry drama contributed by King Taksin the Great. The era marked the revival of literature after the fall of Ayutthaya. During the eighteenth century Rattanakosin period, which calm fought with the Burmese, many of the early Rattanakosin works conduct with war and military strategy. Some examples are Nirat Rop Phama Thi Tha Din Daeng, Phleng Yao Rop Phama Thi Nakhon Si Thammarat. In the perform arts, possibly the most significant dramatic accomplishment is the complete study of Ramakian by King Rama I. In summation, There were besides verse recitals with musical complement, such as Mahori telling the report of Kaki, Sepha relating the history of Khun Chang Khun Phaen. early recitals include Sri Thanonchai. The most authoritative Thai poet in this period was Sunthorn Phu ( สุนทรภู่ ) ( 1786–1855 ), wide known as “ the bard of Rattanakosin ” ( Thai : กวีเอกแห่งกรุงรัตนโกสินทร์ ). Sunthorn Phu is best known for his epic poem Phra Aphai Mani ( Thai : พระอภัยมณี ), written during 1822 and 1844. Phra Aphai Mani is a verse fantasy-adventure fresh, a music genre of thai literature known as nithan kham klon ( Thai : นิทานคำกลอน ). [ 215 ] Some of the most well-known modern Thai writers include Kukrit Pramoj, Kulap Saipradit, ( penname Siburapha ), Suweeriya Sirisingh ( penname Botan ), Chart Korbjitti, Prabda Yoon and Duanwad Pimwana. [ 216 ] The works tended to be light fabrication .
Music and dance
 Khon show is the most stylised form of Thai performance. apart from folk music and regional dances ( southern Thailand ‘s Menora ( dance ) and Ramwong, for example ), the two major forms of Thai classical dance play are Khon and Lakhon nai. In the begin, both were entirely court entertainments and it was not until much later that a democratic stylus of dancing theater, likay, evolved as a diversion for common folk music who had no access to royal performances. [ 217 ] Folk dance forms include dance field forms like likay, numerous regional dances ( ram ), the ritual dance crash muay, and court to the teacher, wai khru. Both crash muay and wai khru take topographic point before all traditional muay Thai matches. The wai is besides an annual ceremony performed by Thai classical dance groups to honor their artistic ancestors. Thai classical music music is synonymous with those stylized court ensembles and repertoires that emerged in their confront kind within the imperial centers of Central Thailand some 800 years ago. These ensembles, while being influenced by older practices are today uniquely Thai expressions. While the three primary classical ensembles, the Piphat, Khrueang sai and Mahori differ in significant ways, they all partake a basic instrumentation and theoretical approach. Each employs small ching hand cymbals and krap wooden sticks to mark the primary beat reference. Thai authoritative music has had a wide influence on the musical traditions of neighboring countries. The traditional music of Myanmar was strongly influenced by the Thai music repertoire, called Yodaya ( ယိုးဒယား ), which was brought over from the Ayutthaya Kingdom. As Siam expanded its political and cultural influence to Laos and Cambodia during the early Rattanakosin period, its music was quickly absorbed by the Cambodia and Lao courts .
Khon show is the most stylised form of Thai performance. apart from folk music and regional dances ( southern Thailand ‘s Menora ( dance ) and Ramwong, for example ), the two major forms of Thai classical dance play are Khon and Lakhon nai. In the begin, both were entirely court entertainments and it was not until much later that a democratic stylus of dancing theater, likay, evolved as a diversion for common folk music who had no access to royal performances. [ 217 ] Folk dance forms include dance field forms like likay, numerous regional dances ( ram ), the ritual dance crash muay, and court to the teacher, wai khru. Both crash muay and wai khru take topographic point before all traditional muay Thai matches. The wai is besides an annual ceremony performed by Thai classical dance groups to honor their artistic ancestors. Thai classical music music is synonymous with those stylized court ensembles and repertoires that emerged in their confront kind within the imperial centers of Central Thailand some 800 years ago. These ensembles, while being influenced by older practices are today uniquely Thai expressions. While the three primary classical ensembles, the Piphat, Khrueang sai and Mahori differ in significant ways, they all partake a basic instrumentation and theoretical approach. Each employs small ching hand cymbals and krap wooden sticks to mark the primary beat reference. Thai authoritative music has had a wide influence on the musical traditions of neighboring countries. The traditional music of Myanmar was strongly influenced by the Thai music repertoire, called Yodaya ( ယိုးဒယား ), which was brought over from the Ayutthaya Kingdom. As Siam expanded its political and cultural influence to Laos and Cambodia during the early Rattanakosin period, its music was quickly absorbed by the Cambodia and Lao courts .
entertainment
Thai films are exported and exhibited in Southeast Asia. [ 218 ] Thai film has developed its own singular identity and nowadays being internationally recognized for their culture-driven. [ 219 ] Films such as Ong-Bak: Muay Thai Warrior ( 2003 ) and Tom-Yum-Goong ( 2005 ), starred Tony Jaa, feature distinctive aspects of Thai martial arts “ Muay Thai “. Thai horror has always had a significant cult following, alone take on tales from beyond the grave. More recently, horror films such as Shutter ( 2004 ), was one of the best-known Thai repugnance movies and recognized worldwide. [ 220 ] other examples include The Unseeable ( 2006 ), Alone ( 2007 ), Body ( 2007 ), Coming Soon ( 2008 ), 4bia ( 2008 ), Phobia 2 ( 2009 ), Ladda Land ( 2011 ), Pee Mak ( 2013 ), The Promise ( 2017 ), and The Medium ( 2021 ). Thai burglarize thriller film Bad Genius ( 2017 ), was one of the most internationally successful Thai film, It broke Thai film earning records in several asian countries, [ 221 ] Bad Genius won in 12 categories at the 27th Suphannahong National Film Awards, and besides won the Jury Award at the 16th New York Asian Film Festival with a global collection of more than $ 42 million. [ 222 ] Thailand television drama, known as Lakorn, Lakorn have become democratic in Thailand and its neighbors. [ 223 ] Many dramas tend to have a amatory focus, such as Khluen Chiwit, U-Prince, Ugly Duckling, The Crown Princess and adolescent drama television series, such as 2gether: The Series, The Gifted, Girl From Nowhere, Hormones: The Series. The Entertainment industries ( film and television ) are estimated to have directly contributed $ 2.1 billion in crude domestic product ( GDP ) to the Thai economy in 2011. They besides directly supported 86,600 jobs. [ 224 ] Amongst respective Dance-pop artists who have made internationally successful can be mentioned “ Lisa ” Lalisa Manoban [ 225 ] and Tata Young .
cuisine
Thai cuisine is one of the most popular in the populace. [ 226 ] [ 227 ] Thai food blends five cardinal tastes : odoriferous, blue, false, bitter, and salty. The herb and spices most used in Thai cooking themselves have medicative qualities such as garlic, lemongrass, kaffir calcium hydroxide, galingale, turmeric, coriander, coconut milk. [ 228 ] Each area of Thailand has its specialities : kaeng khiao wan ( park curry ) in the cardinal region, som tam ( park papaya salad ) in the northeast, khao soi in the north, and massaman dress in the south. In 2017, seven Thai dishes appeared on a list of the “ World ‘s 50 Best Foods ” — an on-line cosmopolitan poll by CNN Travel. Thailand had more dishes on the list than any other state. They were : tom yam goong ( 4th ), pad Thai ( 5th ), som tam ( 6th ), massaman dress ( 10th ), green curry ( 19th ), Thai fried rice ( 24th ) and mu nam tok ( 36th ). [ 229 ] The staple food in Thailand is rice, particularly jasmine rice ( besides known as hom Mali ) which forms partially of about every meal. Thailand is a leading exporter of rice, and Thais consume over 100 kg of mill rice per person per class. [ 230 ]
Units of measurement
Thailand broadly uses the metric function system, but traditional units of measurement for land area are used, and imperial units of measurement are occasionally used for build up materials, such as wood and plumbing fixtures. Years are numbered as B.E. ( Buddhist Era ) in educational settings, civil serve, government, contracts, and newspaper datelines. however, in bank, and increasingly in diligence and department of commerce, standard western year ( christian or Common Era ) count is the criterion practice. [ 231 ]
Sports
Muay Thai ( Thai : มวยไทย, RTGS : Muai Thai, [ muaj tʰaj ], unhorse. “ Thai boxing ” ) is a fight mutant of Thailand that uses stand-up striking along with diverse clinching techniques. Muay Thai became widespread internationally in the late-20th to twenty-first century, when Westernized practitioners from Thailand began competing in kickboxing and interracial rules matches angstrom well as matches under muay Thai rules around the worldly concern, celebrated practitioners such as Buakaw Banchamek, Samart Payakaroon, Dieselnoi Chor Thanasukarn and Apidej Sit-Hirun. Buakaw Banchamek has credibly brought more external interest in Muay Thai than any other Muay Thai fighters ever had. [ 232 ] Association football has overtaken muay Thai as the most widely followed fun in contemporary Thai company. Thailand national football team has played the AFC asian Cup six times and reached the semifinals in 1972. The nation has hosted the asian Cup doubly, in 1972 and in 2007. The 2007 edition was co-hosted in concert with Indonesia, Malaysia and Vietnam. It is not rare to see Thais cheering their favorite english Premier League teams on television and walking round in replica kit out. Another widely enjoyed pastime, and once a competitive sport, is kite flying. Volleyball is quickly growing as one of the most popular sports. The women ‘s team has much participated in the World Championship, World Cup, and World Grand Prix Asian Championship. They have won the asian Championship twice and asian Cup once. By the success of the women ‘s team, the men team has been growing ampere well. Takraw ( Thai : ตะกร้อ ) is a mutant native to Thailand, in which the players hit a rattan ball and are only allowed to use their feet, knees, thorax, and lead to touch the musket ball. Sepak takraw is a form of this mutant which is like to volleyball. The players must volley a musket ball over a net and force it to hit the background on the adversary ‘s side. It is besides a popular sport in early countries in Southeast Asia. A quite similar game but played only with the feet is buka ball. Snooker has enjoyed increasing popularity in Thailand in recent years, with sake in the game being stimulated by the achiever of Thai snooker actor James Wattana in the 1990s. [ 233 ] other celebrated players produced by the area include Ratchayothin Yotharuck, Noppon Saengkham and Dechawat Poomjaeng. [ 234 ] Rugby is besides a growing sport in Thailand with the Thailand home rugby union team rising to be ranked 61st in the world. [ 235 ] Thailand became the first state in the world to host an external 80 welterweight rugby tournament in 2005. [ 236 ] The national domestic Thailand Rugby Union ( TRU ) competition includes several universities and services teams such as Chulalongkorn University, Mahasarakham University, Kasetsart University, Prince of Songkla University, Thammasat University, Rangsit University, the Thai Police, the Thai Army, the Thai Navy and the Royal Thai Air Force. local sports clubs which besides compete in the TRU include the british Club of Bangkok, the Southerners Sports Club ( Bangkok ) and the Royal Bangkok Sports Club. Thailand has been called the golf capital of Asia [ 237 ] as it is a popular destination for golf. The country attracts a large number of golfers from Japan, Korea, Singapore, South Africa, and western countries who come to play golf in Thailand every year. [ 238 ] The growing popularity of golf, particularly among the center classes and immigrants, is apparent as there are more than 200 first golf courses countrywide, [ 239 ] and some of them are chosen to host PGA and LPGA tournaments, such as Amata Spring Country Club, Alpine Golf and Sports Club, Thai Country Club, and Black Mountain Golf Club. basketball is a growing sport in Thailand, specially on the master sports club level. The Chang Thailand Slammers won the 2011 ASEAN Basketball League Championship. [ 240 ] The Thailand national basketball team had its most successful year at the 1966 asian Games where it won the silver medal decoration. [ 241 ] other sports in Thailand are slowly growing as the country develops its dissipated infrastructure. The success in sports like weightlifting and tae kwon do at the last two summer Olympic Games has demonstrated that box is no long the only decoration option for Thailand .
Sporting venues
The well-known Lumpinee Boxing Stadium primitively sited at Rama IV Road near Lumphini Park hosted its final Muay Thai boxing matches on 8 February 2014 after the venue first opened in December 1956. Managed by the Royal Thai Army, the stadium was formally selected for the purpose of muay Thai bouts following a competition that was staged on 15 March 1956. From 11 February 2014, the stadium will relocate to Ram Intra Road, due to the new venue ‘s capacity to accommodate audiences of up to 3,500. Foreigners typically pay between 1,000 and 2,000 baht to view a meet, with prices depending on the location of the seat. [ 242 ] Thammasat Stadium is a multi-purpose stadium in Bangkok. It is presently used by and large for football matches. The stadium holds 25,000. It is on Thammasat University ‘s Rangsit campus. It was built for the 1998 asian Games by construction firm Christiani and Nielsen, the same company that constructed the Democracy Monument in Bangkok. Rajamangala National Stadium is the biggest sporting arena in Thailand. It presently has a capability of 65,000. It is in Bang Kapi, Bangkok. The stadium was built in 1998 for the 1998 asian Games and is the home stadium of the Thailand national football team .
See besides
Notes
References
far reading
- Chachavalpongpun, Pavin, ed. Routledge Handbook Of Contemporary Thailand (2020)
- Cooper, Robert. Culture Shock! Thailand: A Survival Guide to Customs and Etiquette (2008)
- London, Ellen. Thailand Condensed: 2000 Years of History & Culture (2008)
- Lonely Planet’s Best of Thailand (2020)
- Mishra, Patit Paban. The History of Thailand (Greenwood, 2010)
- Moore, Frank J. ed. Thailand: Its People, Its Society, Its Culture (HRAF Press, 1974).
- Wyatt, David K. Thailand: A Short History (Yale University Press, 2003)
- Zawacki, Benjamin. Thailand: Shifting ground between the US and a rising China (2nd ed.. Bloomsbury, 2021).
- Government
- General information
- Travel
- Tourism Authority of Thailand – official tourism website
- Other
Read more: Wikipedia
