discovery [edit ]
The condition binary was first used in this context by Sir William Herschel in 1802, [ 1 ] when he wrote : [ 2 ]
If, on the contrary, two stars should truly be situated very near each early, and at the lapp meter so far insulated as not to be materially affected by the attractions of neighbouring stars, they will then compose a break system, and remain unify by the bond of their own reciprocal gravity towards each other. This should be called a actual double leading ; and any two stars that are therefore mutually connected, form the binary sidereal system which we are now to consider.
Reading: Binary star
By the modern definition, the term binary star is by and large restricted to pairs of stars which revolve around a coarse center of mass. Binary stars which can be resolved with a telescope or interferometric methods are known as visual binaries. [ 3 ] [ 4 ] For most of the known ocular binary stars one whole revolution has not been observed so far ; quite, they are observed to have travelled along a swerve path or a fond arch. [ 5 ]
 Binary arrangement of two stars The more general term double star is used for pairs of stars which are seen to be close together in the sky. [ 1 ] This distinction is rarely made in languages other than English. [ 3 ] Double stars may be binary systems or may be merely two stars that appear to be near together in the flip but have vastly different genuine distances from the Sun. The latter are termed optical doubles or optical pairs. [ 6 ] Since the invention of the telescope, many pairs of double stars have been found. early examples include Mizar and Acrux. Mizar, in the Big Dipper ( Ursa Major ), was observed to be double by Giovanni Battista Riccioli in 1650 [ 7 ] [ 8 ] ( and probably earlier by Benedetto Castelli and Galileo ). [ 9 ] The bright southern headliner Acrux, in the Southern Cross, was discovered to be duplicate by Father Fontenay in 1685. [ 7 ] John Michell was the first to suggest that double stars might be physically attached to each other when he argued in 1767 that the probability that a double leading was due to a opportunity alignment was small. [ 10 ] [ 11 ] William Herschel began observing doubling stars in 1779 and soon thereafter published catalogs of about 700 double over stars. [ 12 ] By 1803, he had observed changes in the relative positions in a phone number of bivalent stars over the course of 25 years, and concluded that they must be binary systems ; [ 13 ] the first orbit of a binary star, however, was not computed until 1827, when Félix Savary computed the orb of Xi Ursae Majoris. [ 14 ] Since this time, many more double stars have been catalogued and measured. The Washington Double Star Catalog, a database of ocular double stars compiled by the United States Naval Observatory, contains over 100,000 pairs of double stars, [ 15 ] including ocular doubles vitamin a well as binary stars. Orbits are known for lone a few thousand of these double stars, [ 16 ] and most have not been ascertained to be either on-key binaries or ocular doubly stars. [ 17 ] This can be determined by observing the relative gesticulate of the pairs. If the apparent motion is part of an eye socket, or if the stars have similar radial velocities and the difference in their proper motions is modest compared to their coarse proper motion, the match is probably physical. [ 18 ] One of the tasks that remains for ocular observers of double stars is to obtain sufficient observations to prove or disprove gravitational connection .
Binary arrangement of two stars The more general term double star is used for pairs of stars which are seen to be close together in the sky. [ 1 ] This distinction is rarely made in languages other than English. [ 3 ] Double stars may be binary systems or may be merely two stars that appear to be near together in the flip but have vastly different genuine distances from the Sun. The latter are termed optical doubles or optical pairs. [ 6 ] Since the invention of the telescope, many pairs of double stars have been found. early examples include Mizar and Acrux. Mizar, in the Big Dipper ( Ursa Major ), was observed to be double by Giovanni Battista Riccioli in 1650 [ 7 ] [ 8 ] ( and probably earlier by Benedetto Castelli and Galileo ). [ 9 ] The bright southern headliner Acrux, in the Southern Cross, was discovered to be duplicate by Father Fontenay in 1685. [ 7 ] John Michell was the first to suggest that double stars might be physically attached to each other when he argued in 1767 that the probability that a double leading was due to a opportunity alignment was small. [ 10 ] [ 11 ] William Herschel began observing doubling stars in 1779 and soon thereafter published catalogs of about 700 double over stars. [ 12 ] By 1803, he had observed changes in the relative positions in a phone number of bivalent stars over the course of 25 years, and concluded that they must be binary systems ; [ 13 ] the first orbit of a binary star, however, was not computed until 1827, when Félix Savary computed the orb of Xi Ursae Majoris. [ 14 ] Since this time, many more double stars have been catalogued and measured. The Washington Double Star Catalog, a database of ocular double stars compiled by the United States Naval Observatory, contains over 100,000 pairs of double stars, [ 15 ] including ocular doubles vitamin a well as binary stars. Orbits are known for lone a few thousand of these double stars, [ 16 ] and most have not been ascertained to be either on-key binaries or ocular doubly stars. [ 17 ] This can be determined by observing the relative gesticulate of the pairs. If the apparent motion is part of an eye socket, or if the stars have similar radial velocities and the difference in their proper motions is modest compared to their coarse proper motion, the match is probably physical. [ 18 ] One of the tasks that remains for ocular observers of double stars is to obtain sufficient observations to prove or disprove gravitational connection .
Classifications [edit ]
 Edge-on magnetic disk of boast and dust show around the binary leading system HD 106906
Edge-on magnetic disk of boast and dust show around the binary leading system HD 106906
Methods of observation [edit ]
binary star stars are classified into four types according to the way in which they are observed : visually, by observation ; spectroscopically, by periodic changes in apparitional lines ; photometrically, by changes in brightness caused by an overshadow ; or astrometrically, by measuring a deviation in a star topology ‘s place caused by an unobserved company. [ 3 ] [ 19 ] Any binary asterisk can belong to respective of these classes ; for exercise, several spectroscopic binaries are besides eclipsing binaries .
ocular binaries [edit ]
A visual binary star is a binary star for which the angular separation between the two components is big enough to permit them to be observed as a duplicate star in a telescope, or even high-powered binoculars. The angular resolution of the telescope is an important factor in the detection of ocular binaries, and as better angular resolutions are applied to binary star star observations, an increasing number of ocular binaries will be detected. The relative luminosity of the two stars is besides an significant factor, as glare from a brilliantly star may make it unmanageable to detect the presence of a faint part. The bright star topology of a ocular binary is the primary star, and the black is considered the secondary. In some publications ( particularly older ones ), a faint secondary coil is called the comes ( plural comites ; companion ). If the stars are the like brightness, the inventor appointment for the primary is customarily accepted. [ 20 ] The position lean of the secondary with respect to the chief is measured, together with the angular distance between the two stars. The time of observation is besides recorded. After a sufficient issue of observations are recorded over a period of clock time, they are plotted in polar coordinates with the primary asterisk at the origin, and the most probable ellipse is drawn through these points such that the Keplerian police of areas is quenched. This ellipse is known as the apparent ellipse, and is the protrusion of the actual egg-shaped eye socket of the secondary coil with regard to the primary on the airplane of the sky. From this projected ellipse the accomplished elements of the scope may be computed, where the semi-major bloc can only be expressed in angular units unless the stellar parallax, and hence the distance, of the system is known. [ 4 ]
Spectroscopic binaries [edit ]
 Algol B orbits Algol A. This liveliness was assembled from 55 images of the CHARA interferometer in the near-infrared H-band, sorted according to orbital phase. sometimes, the merely tell of a binary star topology comes from the Doppler effect on its emit clean. In these cases, the binary consists of a pair of stars where the spectral lines in the light emitted from each star shifts first gear towards the blue, then towards the bolshevik, as each moves first towards us, and then away from us, during its apparent motion about their common center of mass, with the time period of their coarse sphere. In these systems, the separation between the stars is normally very small, and the orbital speed very eminent. Unless the plane of the orbit happens to be perpendicular to the note of spy, the orbital velocities will have components in the line of spy and the ascertained radial speed of the system will vary sporadically. Since radial speed can be measured with a mass spectrometer by observing the Doppler shift of the stars ‘ apparitional lines, the binaries detected in this manner are known as spectroscopic binaries. Most of these can not be resolved as a ocular binary star, even with telescopes of the highest existing resolving exponent. In some spectroscopic binaries, apparitional lines from both stars are visible and the lines are alternately double and individual. Such a system is known as a double-lined spectroscopic binary ( frequently denoted “ SB2 ” ). In other systems, the spectrum of merely one of the stars is seen and the lines in the spectrum shift sporadically towards the blue sky, then towards red and back again. such stars are known as single-lined spectroscopic binaries ( “ SB1 ” ). The sphere of a spectroscopic binary star is determined by making a long series of observations of the radial speed of one or both components of the system. The observations are plotted against time, and from the resulting crook a period is determined. If the scope is circular then the curve will be a sine arch. If the scope is elliptic, the shape of the arch will depend on the eccentricity of the ellipse and the orientation of the major axis with reference to the line of batch. It is impossible to determine individually the semi-major bloc a and the dip of the eye socket flat i. however, the product of the semi-major axis and the sine of the inclination ( i.e. a sin i ) may be determined directly in linear units ( e.g. kilometres ). If either a or i can be determined by other means, as in the case of eclipsing binaries, a complete solution for the orbit can be found. [ 21 ] binary stars that are both ocular and spectroscopic binaries are rare, and are a valuable source of information when find oneself. About 40 are known. ocular binary star stars frequently have large true separations, with periods measured in decades to centuries ; consequently, they normally have orbital speeds besides small to be measured spectroscopically. conversely, spectroscopic binary stars move firm in their orbits because they are close together, normally besides close to be detected as ocular binaries. Binaries that are found to be both ocular and spectroscopic thus must be relatively stopping point to Earth .
Algol B orbits Algol A. This liveliness was assembled from 55 images of the CHARA interferometer in the near-infrared H-band, sorted according to orbital phase. sometimes, the merely tell of a binary star topology comes from the Doppler effect on its emit clean. In these cases, the binary consists of a pair of stars where the spectral lines in the light emitted from each star shifts first gear towards the blue, then towards the bolshevik, as each moves first towards us, and then away from us, during its apparent motion about their common center of mass, with the time period of their coarse sphere. In these systems, the separation between the stars is normally very small, and the orbital speed very eminent. Unless the plane of the orbit happens to be perpendicular to the note of spy, the orbital velocities will have components in the line of spy and the ascertained radial speed of the system will vary sporadically. Since radial speed can be measured with a mass spectrometer by observing the Doppler shift of the stars ‘ apparitional lines, the binaries detected in this manner are known as spectroscopic binaries. Most of these can not be resolved as a ocular binary star, even with telescopes of the highest existing resolving exponent. In some spectroscopic binaries, apparitional lines from both stars are visible and the lines are alternately double and individual. Such a system is known as a double-lined spectroscopic binary ( frequently denoted “ SB2 ” ). In other systems, the spectrum of merely one of the stars is seen and the lines in the spectrum shift sporadically towards the blue sky, then towards red and back again. such stars are known as single-lined spectroscopic binaries ( “ SB1 ” ). The sphere of a spectroscopic binary star is determined by making a long series of observations of the radial speed of one or both components of the system. The observations are plotted against time, and from the resulting crook a period is determined. If the scope is circular then the curve will be a sine arch. If the scope is elliptic, the shape of the arch will depend on the eccentricity of the ellipse and the orientation of the major axis with reference to the line of batch. It is impossible to determine individually the semi-major bloc a and the dip of the eye socket flat i. however, the product of the semi-major axis and the sine of the inclination ( i.e. a sin i ) may be determined directly in linear units ( e.g. kilometres ). If either a or i can be determined by other means, as in the case of eclipsing binaries, a complete solution for the orbit can be found. [ 21 ] binary stars that are both ocular and spectroscopic binaries are rare, and are a valuable source of information when find oneself. About 40 are known. ocular binary star stars frequently have large true separations, with periods measured in decades to centuries ; consequently, they normally have orbital speeds besides small to be measured spectroscopically. conversely, spectroscopic binary stars move firm in their orbits because they are close together, normally besides close to be detected as ocular binaries. Binaries that are found to be both ocular and spectroscopic thus must be relatively stopping point to Earth .
Eclipsing binaries [edit ]
An eclipsing binary star is a binary star leading organization in which the sphere plane of the two stars lies so about in the line of sight of the perceiver that the components undergo reciprocal eclipses. [ 22 ] In the case where the binary is besides a spectroscopic binary and the parallax of the system is known, the binary star is quite valuable for stellar analysis. Algol, a ternary star organization in the constellation Perseus, contains the best-known example of an eclipsing binary star .
This video shows an artist ‘s depression of an eclipsing binary star system. As the two stars orbit each early they pass in front of one another and their unite brightness, seen from a distance, decreases. Eclipsing binaries are varying stars, not because the light of the individual components vary but because of the eclipses. The luminosity swerve of an eclipsing binary is characterized by periods of much constant light up, with periodic drops in volume when one star passes in front of the early. The brightness may drop doubly during the orbit, once when the secondary passes in front of the primary and once when the basal passes in movement of the secondary. The deep of the two eclipses is called the basal careless of which star is being occulted, and if a shallow moment eclipse besides occurs it is called the secondary overshadow. The size of the brightness drops depends on the proportional luminosity of the two stars, the proportion of the occult star that is hidden, and the surface luminosity ( i.e. effective temperature ) of the stars. typically the eclipse of the hot star causes the primary eclipse. [ 22 ] An eclipsing binary star ‘s period of eye socket may be determined from a cogitation of its light curvature, and the relative size of the individual stars can be determined in terms of the radius of the sphere, by observing how cursorily the brightness changes as the phonograph record of the nearest star slides over the disk of the other star. [ 22 ] If it is besides a spectroscopic binary, the orbital elements can besides be determined, and the aggregate of the stars can be determined relatively well, which means that the relative densities of the stars can be determined in this case. [ 23 ] Since about 1995, measurement of extragalactic eclipsing binaries ‘ cardinal parameters has become potential with 8-meter class telescopes. This makes it feasible to use them to directly measure the distances to external galaxies, a march that is more accurate than using standard candles. [ 24 ] By 2006, they had been used to give direct distance estimates to the LMC, SMC, Andromeda Galaxy, and Triangulum Galaxy. Eclipsing binaries offer a calculate method acting to gauge the distance to galaxies to an improved 5 % tied of accuracy. [ 25 ]
Non-eclipsing binaries that can be detected through photometry [edit ]
nearby non-eclipsing binaries can besides be photometrically detected by observing how the stars affect each other in three ways. The first is by observing extra light which the stars reflect from their company. Second is by observing ellipsoid light variations which are caused by distortion of the ace ‘s shape by their companions. The one-third method acting is by looking at how relativistic beaming affects the apparent magnitude of the stars. Detecting binaries with these methods requires accurate photometry. [ 26 ]
Astrometric binaries [edit ]
Astronomers have discovered some stars that apparently orbit around an evacuate space. Astrometric binaries are relatively nearby stars which can be seen to wobble around a target in space, with no visible companion. The same mathematics used for ordinary binaries can be applied to infer the mass of the missing companion. The companion could be very dense, so that it is presently undetectable or masked by the glare of its primary coil, or it could be an object that emits little or no electromagnetic radiation, for model a neutron star. [ 27 ] The visible star ‘s stead is cautiously measured and detected to vary, due to the gravitational influence from its counterpart. The position of the star is repeatedly measured relative to more distant stars, and then checked for periodic shifts in stead. typically this type of measurement can lone be performed on nearby stars, such as those within 10 parsec. nearby stars much have a relatively high proper gesture, so astrometric binaries will appear to follow a wobbly path across the sky. If the companion is sufficiently massive to cause an discernible shift in position of the star, then its presence can be deduced. From precise astrometric measurements of the movement of the visible star over a sufficiently long period of prison term, information about the mass of the companion and its orbital period can be determined. [ 28 ] even though the companion is not visible, the characteristics of the system can be determined from the observations using Kepler ‘s laws. [ 29 ] This method acting of detecting binaries is besides used to locate extrasolar planets orbiting a star. however, the requirements to perform this measurement are very exigent, due to the great dispute in the mass proportion, and the typically long time period of the planet ‘s orb. detection of position shifts of a star is a very exigent science, and it is unmanageable to achieve the necessary preciseness. Space telescopes can avoid the film over effect of Earth ‘s atmosphere, resulting in more precise resolving power .
Configuration of the system [edit ]
 Detached
Detached Semidetached
Semidetached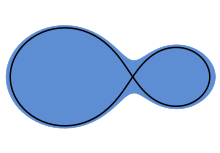 contact Configurations of a binary star system with a mass proportion of 3. The black lines represent the inner critical Roche equipotentials, the Roche lobe. Another classification is based on the distance between the stars, relative to their sizes : [ 30 ] Detached binaries are binary stars where each component is within its Roche lobe, i.e. the area where the gravitational pull of the star itself is larger than that of the other component. The stars have no major effect on each other, and basically evolve individually. Most binaries belong to this class. Semidetached binary stars are binary stars where one of the components fills the binary star topology ‘s Roche lobe and the other does not. Gas from the come on of the Roche-lobe-filling component ( donor ) is transferred to the early, accreting star. The mass transmit dominates the development of the system. In many cases, the inflowing accelerator forms an accretion phonograph record around the accretor. A contact binary is a type of binary star in which both components of the binary fill their Roche lob. The uppermost part of the stellar atmospheres forms a common envelope that surrounds both stars. As the friction of the envelope brakes the orbital gesticulate, the stars may finally merge. [ 31 ] W Ursae Majoris is an example .
contact Configurations of a binary star system with a mass proportion of 3. The black lines represent the inner critical Roche equipotentials, the Roche lobe. Another classification is based on the distance between the stars, relative to their sizes : [ 30 ] Detached binaries are binary stars where each component is within its Roche lobe, i.e. the area where the gravitational pull of the star itself is larger than that of the other component. The stars have no major effect on each other, and basically evolve individually. Most binaries belong to this class. Semidetached binary stars are binary stars where one of the components fills the binary star topology ‘s Roche lobe and the other does not. Gas from the come on of the Roche-lobe-filling component ( donor ) is transferred to the early, accreting star. The mass transmit dominates the development of the system. In many cases, the inflowing accelerator forms an accretion phonograph record around the accretor. A contact binary is a type of binary star in which both components of the binary fill their Roche lob. The uppermost part of the stellar atmospheres forms a common envelope that surrounds both stars. As the friction of the envelope brakes the orbital gesticulate, the stars may finally merge. [ 31 ] W Ursae Majoris is an example .
Cataclysmic variables and x-ray binaries [edit ]
When a binary system contains a compact object such as a white shadow, neutron ace or total darkness hole, gasoline from the other ( donor ) ace can accrete onto the compress object. This releases gravitational electric potential energy, causing the natural gas to become hot and emit radiation. Cataclysmic variable stars, where the compact object is a white shadow, are examples of such systems. [ 32 ] In x ray binaries, the pack object can be either a neutron asterisk or a black hole. These binaries are classified as low-mass or high-mass according to the mass of the donor asterisk. High-mass x-ray binaries contain a new, early-type, high-mass donor star which transfers mass by its stellar wind, while low-mass x-ray binaries are semidetached binaries in which natural gas from a late-type donor asterisk or a egg white dwarf overflows the Roche lobe and falls towards the neutron star topology or black fix. [ 33 ] credibly the best know example of an x ray binary star is the high-mass x-ray binary Cygnus X-1. In Cygnus X-1, the mass of the spiritual world companion is estimated to be approximately nine times that of the Sun, [ 34 ] far exceeding the Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff restrict for the maximal theoretical mass of a neutron asterisk. It is therefore believed to be a black hole ; it was the first object for which this was widely believed. [ 35 ]
orbital period [edit ]
orbital periods can be less than an hour ( for AM CVn stars ), or a few days ( components of Beta Lyrae ), but besides hundreds of thousands of years ( Proxima Centauri around Alpha Centauri AB ) .
Variations in menstruation [edit ]
The Applegate mechanism explains long condition orbital period variations seen in certain eclipsing binaries. As a main-sequence star goes through an action cycle, the outer layers of the leading are submit to a magnetic torsion changing the distribution of angular momentum, resulting in a change in the asterisk ‘s oblateness. The scope of the stars in the binary pair is gravitationally coupled to their shape changes, so that the period shows modulations ( typically on the order of ∆P/P ∼ 10−5 ) on the lapp time scale as the activity cycles ( typically on the order of decades ). [ 36 ] Another phenomenon observed in some Algol binaries has been flat period increases. This is quite distinct from the far more common observations of alternating period increases and decreases explained by the Applegate mechanism. flat menstruation increases have been attributed to mass transfer, normally ( but not constantly ) from the less massive to the more massive star topology [ 37 ]
Designations [edit ]
A and B [edit ]
The components of binary stars are denoted by the suffixes A and B appended to the system ‘s appointment, A denoting the chief and B the secondary. The suffix AB may be used to denote the pair ( for exemplar, the binary star α Centauri AB consists of the stars α Centauri A and α Centauri B. ) extra letters, such as C, D, etc., may be used for systems with more than two stars. [ 38 ] In cases where the binary star has a Bayer designation and is widely separated, it is possible that the members of the pair will be designated with superscripts ; an example is Zeta Reticuli, whose components are ζ1 Reticuli and ζ2 Reticuli. [ 39 ]
Discoverer designations [edit ]
double stars are besides designated by an abbreviation giving the inventor together with an index number. [ 40 ] α Centauri, for example, was found to be double by Father Richaud in 1689, and so is destine RHD 1. [ 7 ] [ 41 ] These inventor codes can be found in the Washington Double Star Catalog. [ 42 ]
Hot and cold [edit ]
The components of a binary star system may be designated by their relative temperatures as the hot companion and cool companion. Examples :
development [edit ]
Artist ‘s impression of the development of a hot high-mass binary star star topology
formation [edit ]
While it is not impossible that some binaries might be created through gravitational capture between two individual stars, given the very abject likelihood of such an event ( three objects being actually required, as conservation of department of energy rules out a one gravitate body capturing another ) and the high number of binaries presently in being, this can not be the primary formation process. The observation of binaries consisting of stars not yet on the main succession supports the theory that binaries develop during star formation. fragmentation of the molecular cloud during the formation of protostars is an acceptable explanation for the formation of a binary or multiple star topology system. [ 50 ] [ 51 ] The consequence of the three-body trouble, in which the three stars are of comparable mass, is that finally one of the three stars will be ejected from the system and, assuming no significant further perturbations, the remaining two will form a stable binary arrangement .
Mass transfer and accretion [edit ]
As a main-sequence star increases in size during its development, it may at some target exceed its Roche lobe, mean that some of its matter ventures into a region where the gravitational pull of its companion star is larger than its own. [ 52 ] The result is that matter will transfer from one star to another through a process known as Roche lobe bubble over ( RLOF ), either being absorbed by address impingement or through an accretion magnetic disk. The mathematical point through which this remove happens is called the first Lagrangian point. [ 53 ] It is not rare that the accretion disk is the bright ( and therefore sometimes the lone visible ) element of a binary star. If a headliner grows outside of its Roche lobe excessively fast for all abundant matter to be transferred to the other component, it is besides possible that matter will leave the system through early Lagrange points or as leading wind, therefore being efficaciously lost to both components. [ 54 ] Since the evolution of a ace is determined by its aggregate, the process influences the development of both companions, and creates stages that can not be attained by unmarried stars. [ 55 ] [ 56 ] [ 57 ] Studies of the eclipsing ternary Algol led to the Algol paradox in the hypothesis of stellar development : although components of a binary star topology kind at the same time, and massive stars evolve much faster than the less massive ones, it was observed that the more massive part Algol A is hush in the independent sequence, while the less massive Algol B is a subgiant at a late evolutionary stage. The paradox can be solved by mass transmit : when the more massive headliner became a subgiant, it filled its Roche lobe, and most of the mass was transferred to the other leading, which is hush in the main succession. In some binaries similar to Algol, a natural gas flow can actually be seen. [ 58 ]
Runaways and nova [edit ]
It is besides possible for widely separated binaries to lose gravitational contact with each other during their life, as a result of external perturbations. The components will then move on to evolve as individual stars. A close meeting between two binary systems can besides result in the gravitational disruption of both systems, with some of the stars being ejected at high velocities, leading to runaway stars. [ 59 ] If a whiten gnome has a close companion asterisk that overflows its Roche lobe, the white gnome will steadily accrete gases from the leading ‘s knocked out atmosphere. These are compacted on the flannel dwarf ‘s surface by its intense gravity, compressed and heated to identical high temperatures as extra material is drawn in. The white gnome consists of pervert count and so is largely unresponsive to heat, while the accrete hydrogen is not. Hydrogen fusion can occur in a stable manner on the surface through the CNO cycle, causing the enormous total of energy liberated by this process to blow the remaining gases aside from the white dwarf ‘s open. The solution is an highly bright outburst of light, known as a nova. [ 60 ] In extreme cases this event can cause the blank gnome to exceed the Chandrasekhar specify and gun trigger a supernova that destroys the entire leading, another possible lawsuit for runaways. [ 61 ] [ 62 ] An example of such an event is the supernova SN 1572, which was observed by Tycho Brahe. The hubble Space Telescope recently took a picture of the remnants of this event .
Astrophysics [edit ]
Binaries provide the best method for astronomers to determine the bulk of a distant ace. The gravitational pull between them causes them to orbit around their common plaza of mass. From the orbital pattern of a ocular binary, or the time variation of the spectrum of a spectroscopic binary, the mass of its stars can be determined, for exemplar with the binary mass routine. In this way, the relation between a star ‘s appearance ( temperature and radius ) and its mass can be found, which allows for the decision of the mass of non-binaries. Because a big proportion of stars exist in binary systems, binaries are peculiarly authoritative to our sympathize of the processes by which stars form. In particular, the period and masses of the binary tell us about the come of angular momentum in the system. Because this is a conserve measure in physics, binaries give us authoritative clues about the conditions under which the stars were formed .
Calculating the center of mass in binary stars [edit ]
In a simple binary star case, r 1, the distance from the center of the first leading to the center of mass or barycenter, is given by :
- r 1 = a ⋅ thousand 2 thousand 1 + m 2 = a 1 + m 1 megabyte 2 { \displaystyle r_ { 1 } =a\cdot { \frac { m_ { 2 } } { m_ { 1 } +m_ { 2 } } } = { \frac { a } { 1+ { \frac { m_ { 1 } } { m_ { 2 } } } } } }
where :
- a is the distance between the two stellar centers and
- m1 and m2 are the masses of the two stars.
If a is taken to be the semi-major axis of the sphere of one body around the early, then r 1 will be the semimajor axis of the beginning body ‘s eye socket around the center of mass or barycenter, and r 2 = a – r 1 will be the semimajor axis of the second body ‘s sphere. When the center of mass is located within the more massive body, that body will appear to wobble quite than following a discernible eye socket.
Read more: Azerbaijan Premier League
Center of mass animations [edit ]
The position of the red crisscross indicates the concentrate of bulk of the system. These images do not represent any specific real system .

(a.) Two bodies of similar mass orbiting around a common center of mass, or barycenter
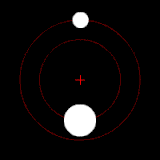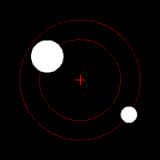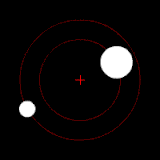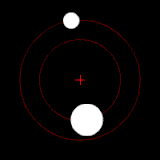
(b.) Two bodies with a difference in mass orbiting around a common barycenter, like the Charon-Pluto system
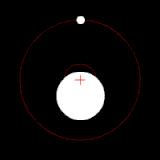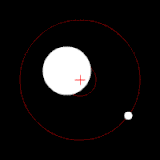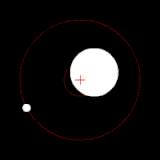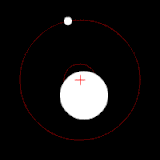
(c.) Two bodies with a major difference in mass orbiting around a common barycenter (similar to the Earth–Moon system)

(d.) Two bodies with an extreme difference in mass orbiting around a common barycenter (similar to the Sun–Earth system)
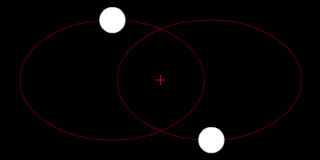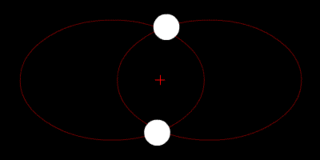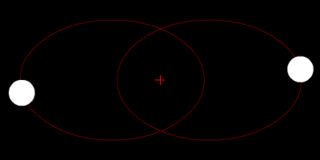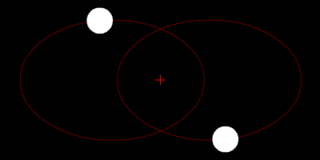
(e.) Two bodies with similar mass orbiting in an ellipse around a common barycenter
research findings [edit ]
Multiplicity likelihood for Population I main sequence stars[63]
Mass Range
Multiplicity
frequency
Average
Companions
≤ 0.1 M☉
22 %
+6%
−4%
0.22
+0.06
−0.04
0.1–0.5 M☉
26 %
±
3 %
0.33
±
0.05
0.7–1.3 M☉
44 %
±
2 %
0.62
±
0.03
1.5–5 M☉
≥ 50%
1.00
±
0.10
8–16 M☉
≥ 60%
1.00
±
0.20
≥ 16 M☉
≥ 80%
1.30
±
0.20
It is estimated that approximately one third of the leading systems in the Milky Way are binary or multiple, with the remaining two thirds being individual stars. [ 64 ] The overall numerousness frequency of ordinary stars is a monotonically increasing function of leading bulk. That is, the likelihood of being in a binary star or a multi-star system steadily increases as the masses of the components addition. [ 63 ] There is a direct correlation between the time period of rotation of a binary star star and the eccentricity of its orbit, with systems of short-circuit period having smaller eccentricity. binary stars may be found with any conceivable separation, from pairs orbiting sol close that they are much in touch with each other, to pairs so distantly separated that their connection is indicated only by their coarse proper gesture through space. Among gravitationally bound binary star systems, there exists a alleged log convention distribution of periods, with the majority of these systems orbiting with a period of about 100 years. This is supporting evidence for the theory that binary systems are formed during star topology formation. [ 65 ] In pairs where the two stars are of peer brightness, they are besides of the lapp apparitional type. In systems where the brightnesses are different, the dim star is bluer if the bright headliner is a giant star, and redder if the bright headliner belongs to the main sequence. [ 66 ]
The mass of a star can be directly determined only from its gravitational drawing card. aside from the Sun and stars which act as gravitational lenses, this can be done only in binary and multiple leading systems, making the binary star stars an important class of stars. In the case of a ocular binary headliner, after the scope and the stellar parallax of the system has been determined, the blend mass of the two stars may be obtained by a mastermind application of the Keplerian harmonic law. [ 67 ] unfortunately, it is impossible to obtain the complete orbit of a spectroscopic binary unless it is besides a ocular or an overshadow binary, then from these objects only a decision of the joint product of mass and the sine of the slant of dip relative to the line of sight is potential. In the event of eclipsing binaries which are besides spectroscopic binaries, it is possible to find a complete solution for the specifications ( mass, concentration, size, luminosity, and approximate supreme headquarters allied powers europe ) of both members of the system .
Planets [edit ]
 Schematic of a binary star star system with one planet on an S-type sphere and one on a P-type scope While a number of binary star systems have been found to harbor extrasolar planets, such systems are relatively rare compared to single star systems. Observations by the Kepler distance telescope have shown that most single stars of the same type as the Sun have plenty of planets, but only one-third of binary stars do. According to theoretical simulations, [ 68 ] even widely separated binary stars often disrupt the disk of rocky grains from which protoplanets form. On the other pass, other simulations suggest that the presence of a binary company can actually improve the rate of planet formation within stable orbital zones by “ stirring up ” the protoplanetary magnetic disk, increasing the accretion rate of the protoplanets within. [ 69 ] Detecting planets in multiple headliner systems introduces extra technical difficulties, which may be why they are only rarely found. [ 70 ] Examples include the white dwarf – pulsar binary star PSR B1620-26, the subgiant – crimson gnome binary Gamma Cephei, and the blank gnome – red dwarf binary NN Serpentis, among others. [ 71 ] A study of fourteen previously known global systems found three of these systems to be binary systems. All planets were found to be in S-type orbits around the basal headliner. In these three cases the secondary star was much dimmer than the primary and so was not previously detected. This discovery resulted in a recalculation of parameters for both the satellite and the primary star. [ 72 ] science fiction has much featured planets of binary star or three stars as a plant, for example George Lucas ‘ Tatooine from Star Wars, and one luminary floor, “ Nightfall “, even takes this to a six-star organization. In reality, some orbital ranges are impossible for dynamic reasons ( the satellite would be expelled from its scope relatively quickly, being either ejected from the system wholly or transferred to a more inside or out orbital range ), whilst other orbits present dangerous challenges for eventual biospheres because of likely extreme variations in surface temperature during unlike parts of the scope. Planets that scope just one asterisk in a binary star system are said to have “ S-type ” orbits, whereas those that orbit around both stars have “ P-type ” or “ circumbinary “ orbits. It is estimated that 50–60 % of binary systems are adequate to of supporting habitable mundane planets within static orbital ranges. [ 69 ]
Schematic of a binary star star system with one planet on an S-type sphere and one on a P-type scope While a number of binary star systems have been found to harbor extrasolar planets, such systems are relatively rare compared to single star systems. Observations by the Kepler distance telescope have shown that most single stars of the same type as the Sun have plenty of planets, but only one-third of binary stars do. According to theoretical simulations, [ 68 ] even widely separated binary stars often disrupt the disk of rocky grains from which protoplanets form. On the other pass, other simulations suggest that the presence of a binary company can actually improve the rate of planet formation within stable orbital zones by “ stirring up ” the protoplanetary magnetic disk, increasing the accretion rate of the protoplanets within. [ 69 ] Detecting planets in multiple headliner systems introduces extra technical difficulties, which may be why they are only rarely found. [ 70 ] Examples include the white dwarf – pulsar binary star PSR B1620-26, the subgiant – crimson gnome binary Gamma Cephei, and the blank gnome – red dwarf binary NN Serpentis, among others. [ 71 ] A study of fourteen previously known global systems found three of these systems to be binary systems. All planets were found to be in S-type orbits around the basal headliner. In these three cases the secondary star was much dimmer than the primary and so was not previously detected. This discovery resulted in a recalculation of parameters for both the satellite and the primary star. [ 72 ] science fiction has much featured planets of binary star or three stars as a plant, for example George Lucas ‘ Tatooine from Star Wars, and one luminary floor, “ Nightfall “, even takes this to a six-star organization. In reality, some orbital ranges are impossible for dynamic reasons ( the satellite would be expelled from its scope relatively quickly, being either ejected from the system wholly or transferred to a more inside or out orbital range ), whilst other orbits present dangerous challenges for eventual biospheres because of likely extreme variations in surface temperature during unlike parts of the scope. Planets that scope just one asterisk in a binary star system are said to have “ S-type ” orbits, whereas those that orbit around both stars have “ P-type ” or “ circumbinary “ orbits. It is estimated that 50–60 % of binary systems are adequate to of supporting habitable mundane planets within static orbital ranges. [ 69 ]
Examples [edit ]
 The two visibly distinguishable components of Albireo The big outdistance between the components, ampere well as their dispute in color, make Albireo one of the easiest discernible ocular binaries. The brightest penis, which is the third-brightest star in the constellation Cygnus, is actually a near binary itself. besides in the Cygnus configuration is Cygnus X-1, an x ray source considered to be a bootleg hole. It is a high-mass x ray binary, with the optical counterpart being a variable star. [ 73 ] Sirius is another binary and the brightest star in the night time flip, with a ocular apparent magnitude of −1.46. It is located in the constellation Canis Major. In 1844 Friedrich Bessel deduced that Sirius was a binary. In 1862 Alvan Graham Clark discovered the companion ( Sirius B ; the visible headliner is Sirius A ). In 1915 astronomers at the Mount Wilson Observatory determined that Sirius B was a white shadow, the first to be discovered. In 2005, using the hubble Space Telescope, astronomers determined Sirius B to be 12,000 kilometer ( 7,456 secret intelligence service ) in diameter, with a aggregate that is 98 % of the Sun. [ 74 ]
The two visibly distinguishable components of Albireo The big outdistance between the components, ampere well as their dispute in color, make Albireo one of the easiest discernible ocular binaries. The brightest penis, which is the third-brightest star in the constellation Cygnus, is actually a near binary itself. besides in the Cygnus configuration is Cygnus X-1, an x ray source considered to be a bootleg hole. It is a high-mass x ray binary, with the optical counterpart being a variable star. [ 73 ] Sirius is another binary and the brightest star in the night time flip, with a ocular apparent magnitude of −1.46. It is located in the constellation Canis Major. In 1844 Friedrich Bessel deduced that Sirius was a binary. In 1862 Alvan Graham Clark discovered the companion ( Sirius B ; the visible headliner is Sirius A ). In 1915 astronomers at the Mount Wilson Observatory determined that Sirius B was a white shadow, the first to be discovered. In 2005, using the hubble Space Telescope, astronomers determined Sirius B to be 12,000 kilometer ( 7,456 secret intelligence service ) in diameter, with a aggregate that is 98 % of the Sun. [ 74 ]
An example of an eclipsing binary is Epsilon Aurigae in the constellation Auriga. The visible component belongs to the spectral class F0, the early ( eclipsing ) component is not visible. The last such overshadow occurred from 2009 to 2011, and it is hoped that the across-the-board observations that will likely be carried out may yield further insights into the nature of this system. Another eclipsing binary is Beta Lyrae, which is a semidetached binary leading system in the constellation of Lyra. other interest binaries include 61 Cygni ( a binary in the constellation Cygnus, composed of two K class ( orange ) main-sequence stars, 61 Cygni A and 61 Cygni B, which is known for its large proper motion ), Procyon ( the brightest star in the constellation Canis Minor and the eighth-brightest star in the night time sky, which is a binary dwell of the independent star with a faint white shadow companion ), SS Lacertae ( an overshadow binary which stopped eclipsing ), V907 Sco ( an overshadow binary which stopped, restarted, then stopped again ), BG Geminorum ( an eclipse binary which is thought to contain a black hole with a K0 star in orbit around it ), and 2MASS J18082002−5104378 ( a binary in the “ dilute harrow “ of the Milky Way, and containing one of the oldest acknowledge stars ). [ 75 ]
Multiple headliner examples [edit ]
 planet Lost in the Glare of Binary Stars ( exemplification ) Systems with more than two stars are termed multiple stars. Algol is the most note three ( long thought to be a binary ), located in the configuration Perseus. Two components of the organization eclipse each other, the variation in the saturation of Algol first being recorded in 1670 by Geminiano Montanari. The name Algol means “ devil star ” ( from Arabic : الغول al-ghūl ), which was credibly given due to its peculiar behavior. Another visible ternary is Alpha Centauri, in the southerly configuration of Centaurus, which contains the fourth-brightest star topology in the night flip, with an apparent ocular magnitude of −0.01. This system besides underscores the fact that no search for habitable planets is arrant if binaries are discounted. Alpha Centauri A and B have an 11 AU distance at closest overture, and both should have stable habitable zones. [ 76 ] There are besides examples of systems beyond ternaries : castor is a sextuple star system, which is the second-brightest star in the constellation Gemini and one of the brightest stars in the night flip. astronomically, Castor was discovered to be a ocular binary star in 1719. Each of the components of Castor is itself a spectroscopic binary. Castor besides has a faint and wide separated companion, which is besides a spectroscopic binary star. The Alcor–Mizar ocular binary star in Ursa Majoris besides consists of six stars, four constitute Mizar and two comprising Alcor .
planet Lost in the Glare of Binary Stars ( exemplification ) Systems with more than two stars are termed multiple stars. Algol is the most note three ( long thought to be a binary ), located in the configuration Perseus. Two components of the organization eclipse each other, the variation in the saturation of Algol first being recorded in 1670 by Geminiano Montanari. The name Algol means “ devil star ” ( from Arabic : الغول al-ghūl ), which was credibly given due to its peculiar behavior. Another visible ternary is Alpha Centauri, in the southerly configuration of Centaurus, which contains the fourth-brightest star topology in the night flip, with an apparent ocular magnitude of −0.01. This system besides underscores the fact that no search for habitable planets is arrant if binaries are discounted. Alpha Centauri A and B have an 11 AU distance at closest overture, and both should have stable habitable zones. [ 76 ] There are besides examples of systems beyond ternaries : castor is a sextuple star system, which is the second-brightest star in the constellation Gemini and one of the brightest stars in the night flip. astronomically, Castor was discovered to be a ocular binary star in 1719. Each of the components of Castor is itself a spectroscopic binary. Castor besides has a faint and wide separated companion, which is besides a spectroscopic binary star. The Alcor–Mizar ocular binary star in Ursa Majoris besides consists of six stars, four constitute Mizar and two comprising Alcor .

