Japan ( japanese : 日本, Nippon or Nihon, [ nota bene 1 ] and formally 日本国 ) [ nb 2 ] is an island country in East Asia, located in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south. separate of the Ring of Fire, Japan spans an archipelago of 6852 islands covering 377,975 square kilometers ( 145,937 sq mile ) ; the five independent islands are Hokkaido, Honshu ( the “ mainland ” ), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa. Tokyo is Japan ‘s capital and largest city ; other major cities include Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto.
Reading: Japan – Wikipedia
Japan is the eleventh-most populous area in the earth, vitamin a well as one of the most densely populate and urbanize. About three-fourths of the state ‘s terrain is mountainous, concentrating its population of 125.36 million on narrow coastal plains. Japan is divided into 47 administrative prefectures and eight traditional regions. The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37.4 million residents. Japan has been inhabited since the Upper Paleolithic time period ( 30,000 BC ), though the first written mention of the archipelago appears in a chinese chronicle ( the Book of Han ) finished in the second century AD. Between the 4th and 9th centuries, the kingdoms of Japan became unite under an emperor and the imperial court based in Heian-kyō. Beginning in the twelfth century, political power was held by a series of military dictators ( shōgun ) and feudal lords ( daimyō ), and enforced by a class of warrior nobility ( samurai ). After a century-long period of civil war, the state was reunified in 1603 under the Tokugawa dictatorship, which enacted an isolationist foreign policy. In 1854, a United States flit forced Japan to open craft to the West, which led to the end of the dictatorship and the restoration of imperial ability in 1868. In the Meiji period, the Empire of Japan adopted a Western-modeled united states constitution and pursued a broadcast of industrialization and modernization. In 1937, Japan invaded China ; in 1941, it entered World War II as an Axis office. After suffering defeat in the Pacific War and two atomic bombings, Japan surrendered in 1945 and came under a seven-year Allied occupation, during which it adopted a newly constitution. Under the 1947 constitution, Japan has maintained a one parliamentary constitutional monarchy with a bicameral legislature, the National Diet. Japan is a great world power and a member of numerous international organizations, including the United Nations ( since 1956 ), the OECD, and the Group of Seven. Although it has renounced its right to declare war, the nation maintains self-defense Forces that rank as one of the global ‘s strong militaries. After World War II, Japan experienced record growth in an economic miracle, becoming the second-largest economy in the populace by 1990. As of 2021, the country ‘s economy is the third-largest by nominal GDP and the fourth-largest by PPP. Ranked “ identical high ” on the Human Development Index, Japan has one of the populace ‘s highest life expectancies, though it is experiencing a decline in population. A global leader in the automotive and electronics industries, Japan has made significant contributions to science and technology. The culture of Japan is well known around the worldly concern, including its art, cuisine, music, and popular culture, which encompasses big comic, animation and television game industries .
etymology
| Japan | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese name | |||||
| Kanji | 日本国 | ||||
| Hiragana | にっぽんこく にほんこく |
||||
| Katakana | ニッポンコク ニホンコク |
||||
| Kyūjitai | 日本國 | ||||
|
|||||
The name for Japan in Japanese is written using the kanji 日本 and is pronounced Nippon or Nihon. [ 9 ] Before 日本 was adopted in the early eighth century, the country was known in China as Wa ( 倭 ) and in Japan by the endonym Yamato. [ 10 ] Nippon, the master Sino-Japanese recitation of the characters, is favored for official uses, including on banknotes and postage stamps. [ 9 ] Nihon is typically used in casual speech and reflects shifts in japanese phonology during the Edo period. [ 10 ] The characters 日本 entail “ sun lineage ”, [ 9 ] which is the reference of the popular Western name “ Land of the Rising Sun ”. [ 11 ] The name Japan is based on the taiwanese pronunciation of 日本 and was introduced to european languages through early deal. In the thirteenth hundred, Marco Polo recorded the early Mandarin or Wu Chinese pronunciation of the characters 日本國 as Cipangu. [ 12 ] The previous Malay name for Japan, Japang or Japun, was borrowed from a southern coastal chinese dialect and encountered by portuguese traders in Southeast Asia, who brought the word to Europe in the early sixteenth hundred. [ 13 ] The first base version of the name in English appears in a book published in 1577, which spelled the name as Giapan in a translation of a 1565 portuguese letter. [ 14 ] [ 15 ]
history
Prehistoric to classical history
A paleolithic culture from around 30,000 BC constitutes the first gear known dwelling of the islands of Japan. [ 16 ] This was followed from around 14,500 BC ( the get down of the Jōmon period ) by a Mesolithic to Neolithic semi-sedentary hunter-gatherer culture characterized by pit brood and vestigial department of agriculture. [ 17 ] Clay vessels from the period are among the oldest outlive examples of pottery. [ 18 ] From around 1000 BC, Yayoi people began to enter the archipelago from Kyushu, intermingling with the Jōmon ; [ 19 ] the Yayoi time period saw the initiation of practices including wet-rice farm, [ 20 ] a new style of pottery, [ 21 ] and metallurgy from China and Korea. [ 22 ] According to legend, Emperor Jimmu ( grandson of Amaterasu ) founded a kingdom in central Japan in 660 BC, beginning a continuous imperial agate line. [ 23 ] Japan first appears in written history in the taiwanese Book of Han, completed in 111 AD. Buddhism was introduced to Japan from Baekje ( a Korean kingdom ) in 552, but the development of japanese Buddhism was chiefly influenced by China. [ 24 ] Despite early resistance, Buddhism was promoted by the govern class, including figures like Prince Shōtoku, and gained widespread adoption begin in the Asuka menstruation ( 592–710 ). [ 25 ] The far-reaching Taika Reforms in 645 nationalize all land in Japan, to be distributed evenly among cultivators, and ordered the compilation of a family register as the basis for a new system of tax income. [ 26 ] The Jinshin War of 672, a bloody conflict between Prince Ōama and his nephew Prince Ōtomo, became a major catalyst for further administrative reforms. [ 27 ] These reforms culminated with the proclamation of the Taihō Code, which consolidated existing statutes and established the social organization of the central and subordinate local governments. [ 26 ] These legal reforms created the ritsuryō state, a organization of Chinese-style centralized government that remained in place for half a millennium. [ 27 ] The Nara period ( 710–784 ) marked the egress of a japanese state centered on the Imperial Court in Heijō-kyō ( modern Nara ). The period is characterized by the appearance of a nascent literary culture with the completion of the Kojiki ( 712 ) and Nihon Shoki ( 720 ), a well as the development of Buddhist-inspired artwork and computer architecture. [ 28 ] [ 29 ] A smallpox epidemic in 735–737 is believed to have killed arsenic much as one-third of Japan ‘s population. [ 29 ] [ 30 ] In 784, Emperor Kanmu moved the capital, settling on Heian-kyō ( contemporary Kyoto ) in 794. [ 29 ] This marked the begin of the Heian menstruation ( 794–1185 ), during which a distinctly autochthonal japanese culture emerged. Murasaki Shikibu ‘s The Tale of Genji and the lyrics of Japan ‘s national hymn “Kimigayo” were written during this time. [ 31 ]
Feudal era
Japan ‘s feudal era was characterized by the egress and authority of a ruling class of warriors, the samurai. [ 32 ] In 1185, following the kill of the Taira kin in the Genpei War, samurai Minamoto no Yoritomo established a military government at Kamakura. [ 33 ] After Yoritomo ‘s end, the Hōjō kin came to power as regents for the shōgun. [ 29 ] The Zen school of Buddhism was introduced from China in the Kamakura period ( 1185–1333 ) and became popular among the samurai class. [ 34 ] The Kamakura dictatorship repelled Mongol invasions in 1274 and 1281 but was finally overthrown by Emperor Go-Daigo. [ 29 ] Go-Daigo was defeated by Ashikaga Takauji in 1336, beginning the Muromachi period ( 1336–1573 ). [ 35 ] The succeeding Ashikaga dictatorship failed to control the feudal warlords ( daimyō ) and a civil war began in 1467, opening the century-long Sengoku period ( “ Warring States ” ). [ 36 ] During the sixteenth century, portuguese traders and Jesuit missionaries reached Japan for the first time, initiating direct commercial and cultural exchange between Japan and the West. [ 29 ] [ 37 ] Oda Nobunaga used European technology and firearms to conquer many other daimyō ; [ 38 ] his consolidation of ability began what was known as the Azuchi–Momoyama period. [ 39 ] After the end of Nobunaga in 1582, his successor Toyotomi Hideyoshi unified the nation in the early on 1590s and launched two abortive invasions of Korea in 1592 and 1597. [ 29 ] Tokugawa Ieyasu served as regent for Hideyoshi ‘s son Toyotomi Hideyori and used his placement to gain political and military accompaniment. [ 40 ] When open war broke out, Ieyasu defeated rival clans in the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600. He was appointed shōgun by Emperor Go-Yōzei in 1603 and established the Tokugawa dictatorship at Edo ( mod Tokyo ). [ 41 ] The dictatorship enacted measures including buke shohatto, as a code of impart to control the autonomous daimyō, [ 42 ] and in 1639 the isolationist sakoku ( “ closed country ” ) policy that spanned the two and a half centuries of flimsy political oneness known as the Edo period ( 1603–1868 ). [ 41 ] [ 43 ] Modern Japan ‘s economic growth began in this menstruation, resulting in roads and water transportation routes, adenine well as fiscal instruments such as futures contracts, bank and insurance of the Osaka rice brokers. [ 44 ] The study of western sciences ( rangaku ) continued through touch with the Dutch enclave in Nagasaki. [ 41 ] The Edo period gave resurrect to kokugaku ( “ national studies ” ), the study of Japan by the Japanese. [ 45 ]
Modern era
In 1854, Commodore Matthew Perry and the “ Black Ships “ of the United States Navy forced the opening of Japan to the outside populace with the Convention of Kanagawa. [ 41 ] Subsequent alike treaties with early western countries brought economic and political crises. [ 41 ] The resignation of the shōgun led to the Boshin War and the establishment of a centralize department of state nominally unified under the emperor ( the Meiji Restoration ). [ 46 ] Adopting Western political, judicial, and military institutions, the Cabinet organized the Privy Council, introduced the Meiji Constitution, and assembled the Imperial Diet. [ 47 ] During the Meiji period ( 1868–1912 ), the Empire of Japan emerged as the most develop nation in Asia and as an industrialize world power that pursued military conflict to expand its sector of influence. [ 48 ] [ 49 ] [ 50 ] After victories in the first Sino-Japanese War ( 1894–1895 ) and the Russo-Japanese War ( 1904–1905 ), Japan gained restraint of Taiwan, Korea and the southern half of Sakhalin. [ 51 ] [ 47 ] The japanese population doubled from 35 million in 1873 to 70 million by 1935, with a meaning shift to urbanization. [ 52 ] [ 53 ] The early twentieth century saw a period of Taishō majority rule ( 1912–1926 ) overshadowed by increasing expansionism and mobilization. [ 54 ] [ 55 ] World War I allowed Japan, which joined the side of the triumphant Allies, to capture german possessions in the Pacific and in China. [ 55 ] The 1920s saw a political chemise towards statism, a period of lawlessness following the 1923 Great Tokyo Earthquake, the pass of laws against political disagree, and a series of try coups. [ 53 ] [ 56 ] [ 57 ] This process accelerated during the 1930s, spawning a phone number of radical nationalist groups that shared a hostility to liberal democracy and a dedication to expansion in Asia. In 1931, Japan invaded and occupied Manchuria ; following international condemnation of the occupation, it resigned from the League of Nations two years former. [ 58 ] In 1936, Japan signed the Anti-Comintern Pact with Nazi Germany ; the 1940 Tripartite Pact made it one of the Axis Powers. [ 53 ]
 Japan ‘s imperial ambitions ended on September 2, 1945 with the state ‘s surrender to the Allies. The Empire of Japan invaded other parts of China in 1937, precipitating the second Sino-Japanese War ( 1937–1945 ). [ 59 ] In 1940, the Empire invaded french Indochina, after which the United States placed an vegetable oil embargo on Japan. [ 53 ] [ 60 ] On December 7–8, 1941, japanese forces carried out surprise attacks on Pearl Harbor, equally well as on british forces in Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong, among others, beginning World War II in the Pacific. [ 61 ] Throughout areas occupied by Japan during the war, numerous abuses were committed against local inhabitants, with many forced into intimate bondage. [ 62 ] After Allied victories during the following four years, which culminated in the soviet invasion of Manchuria and the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945, Japan agreed to an unconditional capitulation. [ 63 ] The war cost Japan its colonies and millions of lives. [ 53 ] The Allies ( led by the United States ) repatriated millions of japanese settlers from their erstwhile colonies and military camps throughout Asia, largely eliminating the japanese empire and its influence over the territories it conquered. [ 64 ] [ 65 ] The Allies convened the International Military Tribunal for the Far East to prosecute japanese leaders for war crimes. [ 65 ] In 1947, Japan adopted a new fundamental law emphasizing liberal democratic practices. [ 65 ] The Allied occupation ended with the Treaty of San Francisco in 1952, [ 66 ] and Japan was granted membership in the United Nations in 1956. [ 65 ] A period of read growth propelled Japan to become the second-largest economy in the global ; [ 65 ] this ended in the mid-1990s after the pop of an asset price bubble, beginning the “ Lost Decade ”. [ 67 ] On March 11, 2011, Japan suffered one of the largest earthquakes in its commemorate history, triggering the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear catastrophe. [ 68 ] On May 1, 2019, after the historic abdication of Emperor Akihito, his son Naruhito became Emperor, beginning the Reiwa era. [ 69 ]
Japan ‘s imperial ambitions ended on September 2, 1945 with the state ‘s surrender to the Allies. The Empire of Japan invaded other parts of China in 1937, precipitating the second Sino-Japanese War ( 1937–1945 ). [ 59 ] In 1940, the Empire invaded french Indochina, after which the United States placed an vegetable oil embargo on Japan. [ 53 ] [ 60 ] On December 7–8, 1941, japanese forces carried out surprise attacks on Pearl Harbor, equally well as on british forces in Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong, among others, beginning World War II in the Pacific. [ 61 ] Throughout areas occupied by Japan during the war, numerous abuses were committed against local inhabitants, with many forced into intimate bondage. [ 62 ] After Allied victories during the following four years, which culminated in the soviet invasion of Manchuria and the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945, Japan agreed to an unconditional capitulation. [ 63 ] The war cost Japan its colonies and millions of lives. [ 53 ] The Allies ( led by the United States ) repatriated millions of japanese settlers from their erstwhile colonies and military camps throughout Asia, largely eliminating the japanese empire and its influence over the territories it conquered. [ 64 ] [ 65 ] The Allies convened the International Military Tribunal for the Far East to prosecute japanese leaders for war crimes. [ 65 ] In 1947, Japan adopted a new fundamental law emphasizing liberal democratic practices. [ 65 ] The Allied occupation ended with the Treaty of San Francisco in 1952, [ 66 ] and Japan was granted membership in the United Nations in 1956. [ 65 ] A period of read growth propelled Japan to become the second-largest economy in the global ; [ 65 ] this ended in the mid-1990s after the pop of an asset price bubble, beginning the “ Lost Decade ”. [ 67 ] On March 11, 2011, Japan suffered one of the largest earthquakes in its commemorate history, triggering the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear catastrophe. [ 68 ] On May 1, 2019, after the historic abdication of Emperor Akihito, his son Naruhito became Emperor, beginning the Reiwa era. [ 69 ]
geography
Japan comprises 6852 islands extending along the Pacific coast of Asia. It stretches over 3000 kilometer ( 1900 nautical mile ) northeast–southwest from the Sea of Okhotsk to the East China Sea. [ 70 ] [ 71 ] The country ‘s five chief islands, from union to south, are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu and Okinawa. [ 72 ] The Ryukyu Islands, which include Okinawa, are a chain to the south of Kyushu. The Nanpō Islands are south and east of the main islands of Japan. together they are frequently known as the japanese archipelago. [ 73 ] As of 2019, Japan ‘s territory is 377,975.24 km2 ( 145,937.06 sq michigan ). [ 1 ] Japan has the sixth-longest coastline in the earth at 29,751 kilometer ( 18,486 mi ). Because of its far-flung outlying islands, Japan has the sixth largest exclusive Economic zone in the universe, covering 4,470,000 km2 ( 1,730,000 sq mile ). [ 74 ] [ 75 ] The japanese archipelago is 66.4 % forests, 12.8 % agricultural and 4.8 % residential ( 2002 ). [ 76 ] The chiefly rugged and mountainous terrain is restricted for dwelling. [ 77 ] Thus the habitable zones, chiefly in the coastal areas, have identical high population densities : Japan is the fortieth most densely populate country. [ 78 ] [ 79 ] Honshu has the highest population density at 450 persons/km2 ( 1,200/sq security service ) as of 2010, while Hokkaido has the lowest concentration of 64.5 persons/km2 as of 2016. [ 80 ] As of 2014, approximately 0.5 % of Japan ‘s total area is reclaimed land ( umetatechi ). [ 81 ] Lake Biwa is an ancient lake and the state ‘s largest fresh water lake. [ 82 ] Japan is well prone to earthquakes, tsunami and volcanic eruptions because of its location along the Pacific Ring of Fire. [ 83 ] It has the 17th highest natural disaster risk as measured in the 2016 World Risk Index. [ 84 ] Japan has 111 active volcanoes. [ 85 ] Destructive earthquakes, often resulting in tsunami, occur several times each century ; [ 86 ] the 1923 Tokyo earthquake killed over 140,000 people. [ 87 ] More holocene major quakes are the 1995 Great Hanshin earthquake and the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake, which triggered a large tsunami. [ 68 ]
climate
The climate of Japan is predominantly moderate but varies greatly from north to south. The northernmost region, Hokkaido, has a humid continental climate with long, cold winters and very ardent to cool summers. precipitation is not heavy, but the islands normally develop deep snowbanks in the winter. [ 88 ] In the Sea of Japan region on Honshu ‘s west coast, northwest winter winds bring heavy snow during winter. In the summer, the area sometimes experiences highly hot temperatures because of the fohn. [ 89 ] The Central Highland has a distinctive inland humid continental climate, with large temperature differences between summer and winter. The mountains of the Chūgoku and Shikoku regions shelter the Seto Inland Sea from seasonal winds, bringing meek weather year-round. [ 88 ] The Pacific coast features a humid subtropical climate that experiences milder winters with occasional snow and hot, humid summers because of the southeast seasonal worker wind instrument. The Ryukyu and Nanpō Islands have a subtropical climate, with warm winters and hot summers. precipitation is identical heavy, particularly during the showery season. [ 88 ] The main showery season begins in early May in Okinawa, and the rain front gradually moves north. In late summer and early fall, typhoons much bring heavy rain. [ 90 ] According to the Environment Ministry, heavy rain and increasing temperatures have caused problems in the agricultural industry and elsewhere. [ 91 ] The highest temperature always measured in Japan, 41.1 °C ( 106.0 °F ), was recorded on July 23, 2018, [ 92 ] and repeated on August 17, 2020. [ 93 ]
biodiversity
Japan has nine forest ecoregions which reflect the climate and geography of the islands. They range from subtropical damp broadleaf forests in the Ryūkyū and Bonin Islands, to temperate broadleaf and shuffle forests in the meek climate regions of the chief islands, to temperate coniferous forests in the cold, winter portions of the northern islands. [ 94 ] Japan has over 90,000 species of wildlife as of 2019, [ 95 ] including the brown behave, the japanese macaque, the japanese raccoon frump, the small japanese field mouse, and the japanese giant poker. [ 96 ] A big net of national parks has been established to protect significant areas of flora and fauna vitamin a good as 52 Ramsar wetland sites. [ 97 ] [ 98 ] Four sites have been inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List for their great lifelike value. [ 99 ]
environment
In the period of rapid economic growth after World War II, environmental policies were downplayed by the government and industrial corporations ; as a result, environmental contamination was far-flung in the 1950s and 1960s. Responding to rising concern, the government introduced environmental auspices laws in 1970. [ 100 ] The oil crisis in 1973 besides encouraged the efficient manipulation of energy because of Japan ‘s lack of natural resources. [ 101 ] As of 2020, more than 22 coal-fired baron plants are planned for structure in Japan, following the switching-off of Japan ‘s nuclear flit after the 2011 Fukushima nuclear catastrophe. [ 102 ] Japan ranks 20th in the 2018 Environmental Performance Index, which measures a nation ‘s commitment to environmental sustainability. [ 103 ] Japan is the earth ‘s fifth largest emitter of carbon dioxide. [ 91 ] As the host and signer of the 1997 Kyoto Protocol, Japan is under treaty obligation to reduce its carbon paper dioxide emissions and to take other steps to curb climate change. [ 104 ] In 2020 the government of Japan announced a prey of carbon-neutrality by 2050. [ 105 ] Environmental issues include urban air pollution ( NOx, suspended particulate count, and toxics ), godforsaken management, water eutrophication, nature conservation, climate exchange, chemical management and external co-operation for conservation. [ 106 ]
Politics
Japan is a unitary state and constituent monarchy in which the office of the Emperor is limited to a ceremony character. [ 107 ] Executive office is alternatively wielded by the Prime Minister of Japan and his Cabinet, whose sovereignty is vested in the japanese people. [ 108 ] Naruhito is the Emperor of Japan, having succeeded his founder Akihito upon his accession to the Chrysanthemum Throne in 2019. [ 107 ]
Japan ‘s legislative organ is the National Diet, a bicameral fantan. [ 107 ] It consists of a lower House of Representatives with 465 seats, elected by popular vote every four years or when dissolved, and an amphetamine House of Councillors with 245 seats, whose popularly-elected members serve six-year terms. [ 109 ] There is universal right to vote for adults over 18 years of age, [ 110 ] with a unavowed ballot for all elected offices. [ 108 ] The prime curate as the capitulum of government has the baron to appoint and dismiss Ministers of State, and is appointed by the emperor butterfly after being designated from among the members of the Diet. [ 109 ] Fumio Kishida is Japan ‘s prime minister ; he took agency after winning the 2021 Liberal Democratic Party leadership election. [ 111 ] historically influenced by chinese law, the japanese legal system developed independently during the Edo period through texts such as Kujikata Osadamegaki. [ 112 ] Since the late nineteenth century, the judicial system has been largely based on the civil law of Europe, notably Germany. In 1896, Japan established a civil code based on the german Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch, which remains in effect with post–World War II modifications. [ 113 ] The Constitution of Japan, adopted in 1947, is the oldest unamended fundamental law in the world. [ 114 ] Statutory law originates in the legislature, and the constitution requires that the emperor proclaim legislation passed by the Diet without giving him the baron to oppose legislation. The main body of japanese statutory jurisprudence is called the Six Codes. [ 112 ] Japan ‘s court arrangement is divided into four basic tiers : the Supreme Court and three levels of lower courts. [ 115 ]
administrative divisions
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, each oversee by an elected governor and legislature. [ 107 ] In the trace table, the prefectures are grouped by region : [ 116 ]
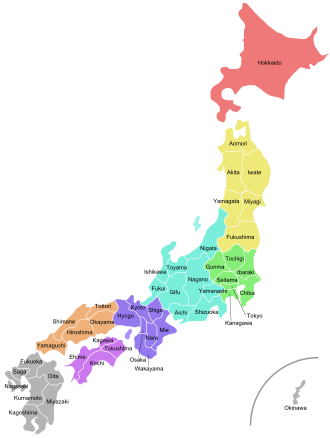 Prefectures of Japan with color regions Prefectures of Japan with color regions |
Hokkaido 1. hokkaido |
Tōhoku 2. Aomori 3. Iwate 4. Miyagi 5. Akita 6. Yamagata 7. Fukushima |
Kantō 8. Ibaraki 9. Tochigi 10. Gunma 11. Saitama 12. Chiba 13. Tokyo 14. Kanagawa |
Chūbu 15. Niigata 16. Toyama 17. Ishikawa 18. Fukui 19. Yamanashi 20. Nagano 21. Gifu 22. Shizuoka 23. Aichi |
|
Kansai 24. Mie 25. Shiga 26. Kyoto 27. Osaka 28. Hyōgo 29. Nara 30. Wakayama |
Chūgoku 31. Tottori 32. Shimane 33. Okayama 34. Hiroshima 35. Yamaguchi |
Shikoku 36. Tokushima 37. Kagawa 38. Ehime 39. Kōchi |
Kyūshū 40. Fukuoka 41. Saga 42. Nagasaki Read more: 2015–16 Liverpool F.C. season – Wikipedia 43. Kumamoto |
foreign relations
 Japan is a member of both the G7 and the G20 A member state of the United Nations since 1956, Japan is one of the G4 nations seeking reform of the Security Council. [ 117 ] Japan is a penis of the G7, APEC, and “ ASEAN Plus Three “, and is a player in the East Asia Summit. [ 118 ] It is the earth ‘s fifth largest donor of official development aid, donating US $ 9.2 billion in 2014. [ 119 ] In 2017, Japan had the fifth largest diplomatic network in the world. [ 120 ] Japan has conclude economic and military relations with the United States, with which it maintains a security alliance. [ 121 ] The United States is a major market for japanese exports and a major source of japanese imports, and is committed to defending the country, with military bases in Japan. [ 121 ] Japan signed a security treaty with Australia in March 2007 [ 122 ] and with India in October 2008. [ 123 ] Japan ‘s relationship with South Korea had historically been strained because of Japan ‘s treatment of Koreans during japanese colonial rule, particularly over the issue of consolation women. In 2015, Japan agreed to settle the comfort women quarrel with South Korea by issuing a courtly apology and paying money to the surviving comfort women. [ 124 ] As of 2019 Japan is a major importer of korean music ( K-pop ), television ( K-dramas ), and other cultural products. [ 125 ] [ 126 ] Japan is engaged in several territorial disputes with its neighbors. Japan contests Russia ‘s control of the Southern Kuril Islands, which were occupied by the Soviet Union in 1945. [ 127 ] South Korea ‘s control of the Liancourt Rocks is acknowledged but not accepted as they are claimed by Japan. [ 128 ] Japan has strained relations with China and Taiwan over the Senkaku Islands and the condition of Okinotorishima. [ 129 ]
Japan is a member of both the G7 and the G20 A member state of the United Nations since 1956, Japan is one of the G4 nations seeking reform of the Security Council. [ 117 ] Japan is a penis of the G7, APEC, and “ ASEAN Plus Three “, and is a player in the East Asia Summit. [ 118 ] It is the earth ‘s fifth largest donor of official development aid, donating US $ 9.2 billion in 2014. [ 119 ] In 2017, Japan had the fifth largest diplomatic network in the world. [ 120 ] Japan has conclude economic and military relations with the United States, with which it maintains a security alliance. [ 121 ] The United States is a major market for japanese exports and a major source of japanese imports, and is committed to defending the country, with military bases in Japan. [ 121 ] Japan signed a security treaty with Australia in March 2007 [ 122 ] and with India in October 2008. [ 123 ] Japan ‘s relationship with South Korea had historically been strained because of Japan ‘s treatment of Koreans during japanese colonial rule, particularly over the issue of consolation women. In 2015, Japan agreed to settle the comfort women quarrel with South Korea by issuing a courtly apology and paying money to the surviving comfort women. [ 124 ] As of 2019 Japan is a major importer of korean music ( K-pop ), television ( K-dramas ), and other cultural products. [ 125 ] [ 126 ] Japan is engaged in several territorial disputes with its neighbors. Japan contests Russia ‘s control of the Southern Kuril Islands, which were occupied by the Soviet Union in 1945. [ 127 ] South Korea ‘s control of the Liancourt Rocks is acknowledged but not accepted as they are claimed by Japan. [ 128 ] Japan has strained relations with China and Taiwan over the Senkaku Islands and the condition of Okinotorishima. [ 129 ]
military
Japan is the second-highest-ranked asian country in the Global Peace Index 2020. [ 130 ] Japan maintains one of the largest military budgets of any area in the universe. [ 131 ] The country ‘s military ( the Japan Self-Defense Forces ) is restricted by Article 9 of the japanese Constitution, which renounces Japan ‘s properly to declare war or use military force out in international disputes. [ 132 ] The military is governed by the Ministry of Defense, and chiefly consists of the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force, the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force, and the Japan Air Self-Defense Force. The deployment of troops to Iraq and Afghanistan marked the first base oversea manipulation of Japan ‘s military since World War II. [ 133 ] The Government of Japan has been making changes to its security policy which include the establishment of the National Security Council, the borrowing of the National Security Strategy, and the development of the National Defense Program Guidelines. [ 134 ] In May 2014, Prime Minister Shinzō Abe said Japan wanted to shed the passivity it has maintained since the end of World War II and take more duty for regional security. [ 135 ] Recent tensions, particularly with North Korea and China, have reignited the debate over the status of the JSDF and its relative to japanese company. [ 136 ] [ 137 ] [ 138 ]
domestic law enforcement
domestic security in Japan is provided chiefly by the prefectural patrol departments, under the oversight of the National Police Agency. [ 139 ] As the cardinal coordinate body for the Prefectural Police Departments, the National Police Agency is administered by the National Public Safety Commission. [ 140 ] The special Assault Team comprises national-level counter-terrorism tactical units that cooperate with territorial-level Anti-Firearms Squads and Counter-NBC Terrorism Squads. [ 141 ] The Japan Coast Guard guards territorial waters surrounding Japan and uses surveillance and control countermeasures against smuggling, marine environmental crime, poaching, piracy, descry ships, unauthorized foreign fish vessels, and illegal immigration. [ 142 ] The Firearm and Sword Possession Control Law strictly regulates the civilian possession of guns, swords and other weaponry. [ 143 ] [ 144 ] According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, among the member states of the UN that report statistics as of 2018, the incidence rates of violent crimes such as murder, abduction, sexual violence and looting are identical low in Japan. [ 145 ] [ 146 ] [ 147 ] [ 148 ]
economy
Japan is the third-largest national economy in the world, after the United States and China, in terms of nominal GDP, [ 149 ] and the fourth-largest national economy in the populace, after the United States, China and India, in terms of purchasing power parity as of 2019. [ 150 ] As of 2019, Japan ‘s undertaking coerce consisted of 67 million workers. [ 109 ] Japan has a low unemployment pace of around 2.4 percentage. [ 109 ] Around 16 percentage of the population were below the poverty line in 2017. [ 151 ] Japan today has the highest ratio of public debt to GDP of any develop nation, [ 152 ] [ 153 ] with national debt at 236 % relative to GDP as of 2017. [ 154 ] [ 155 ] The japanese yen is the worldly concern ‘s third-largest military reserve currency ( after the US dollar and the euro ). [ 156 ] Japan ‘s exports amounted to 18.5 % of GDP in 2018. [ 157 ] As of 2019, Japan ‘s main export markets were the United States ( 19.8 percentage ) and China ( 19.1 percentage ). [ 109 ] Its independent exports are drive vehicles, iron and steel products, semiconductors and car parts. [ 74 ] Japan ‘s main import markets as of 2019 were China ( 23.5 percentage ), the United States ( 11 percentage ), and Australia ( 6.3 percentage ). [ 109 ] Japan ‘s chief imports are machinery and equipment, dodo fuels, foodstuffs, chemicals, and raw materials for its industries. [ 109 ] Japan ranks 29th of 190 countries in the 2019 rest of doing business index. [ 158 ] The japanese form of capitalism has many distinct features : keiretsu enterprises are influential, and life employment and seniority-based career progress are common in the japanese work environment. [ 159 ] [ 160 ] Japan has a large cooperative sector, with three of the ten-spot largest cooperatives in the earth, including the largest consumer concerted and the largest agrarian accommodative in the earth as of 2018. [ 161 ] Japan ranks highly for competitiveness and economic exemption. It is ranked sixth in the Global Competitiveness Report for 2015–2016. [ 162 ] [ 163 ]
farming and fishery
The japanese agricultural sector accounts for approximately 1.2 % of the sum country ‘s GDP as of 2018. [ 109 ] entirely 11.5 % of Japan ‘s kingdom is desirable for cultivation. [ 164 ] Because of this miss of arable land, a system of terraces is used to farm in small areas. [ 165 ] This results in one of the global ‘s highest levels of crop yields per unit sphere, with an agrarian autonomy rate of about 50 % as of 2018. [ 166 ] Japan ‘s small agricultural sector is highly subsidized and protected. [ 167 ] There has been a growing business about farming as farmers are aging with a unmanageable time finding successors. [ 168 ] Japan ranked seventh in the global in tonnage of pisces catch and captured 3,167,610 measured tons of pisces in 2016, down from an annual average of 4,000,000 tons over the previous ten. [ 169 ] Japan maintains one of the world ‘s largest fishing fleets and accounts for closely 15 % of the ball-shaped catch, [ 74 ] prompting critiques that Japan ‘s fish is leading to depletion in pisces stocks such as tuna. [ 170 ] Japan has sparked controversy by supporting commercial whale. [ 171 ]
industry
Japan has a large industrial capacity and is home to some of the “ largest and most technologically promote producers of motive vehicles, machine tools, sword and nonferrous metals, ships, chemical substances, textiles, and processed foods “. [ 74 ] Japan ‘s industrial sector makes up approximately 27.5 % of its GDP. [ 74 ] The area ‘s manufacture output is the third highest in the populace as of 2019. [ 173 ] Japan is the third-largest car producer in the world as of 2017 and is home to Toyota, the world ‘s largest car company. [ 172 ] [ 174 ] The japanese shipbuilding industry faces competition from South Korea and China ; a 2020 government inaugural identified this sector as a target for increasing exports. [ 175 ]
Services and tourism
Japan ‘s service sector accounts for about 70 % of its total economic output as of 2019. [ 176 ] Banking, retail, transportation system, and telecommunications are all major industries, with companies such as Toyota, Mitsubishi UFJ, – NTT, ÆON, Softbank, Hitachi, and Itochu listed as among the largest in the worldly concern. [ 177 ] [ 178 ] Japan attracted 31.9 million international tourists in 2019. [ 179 ] For inbound tourism, Japan was ranked 11th in the worldly concern in 2019. [ 180 ] The 2017 Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report ranked Japan 4th out of 141 countries, which was the highest in Asia. [ 181 ]
science and technology
Japan is a leading nation in scientific inquiry, particularly in the natural sciences and engineering. The country ranks twelfth among the most innovative countries in the 2020 Bloomberg Innovation Index and 16th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, down from 15th in 2019. [ 182 ] [ 183 ] [ 184 ] Relative to arrant domestic intersection, Japan ‘s inquiry and development budget is the second highest in the populace, [ 185 ] with 867,000 researchers sharing a 19-trillion-yen research and growth budget as of 2017. [ 186 ] The area has produced twenty-two Nobel laureates in either physics, chemistry or medicine, [ 187 ] and three Fields medalists. [ 188 ] Japan leads the global in robotics output and function, supplying 55 % of the world ‘s 2017 sum. [ 189 ] Japan has the second highest number of researchers in skill and engineering per head in the world with 14 per 1000 employees. [ 190 ] The japanese consumer electronics industry, once considered the strongest in the earth, is in a state of decay as competition arises in countries like South Korea and China. [ 191 ] however, video recording bet on in Japan remains a major diligence. In 2014, Japan ‘s consumer video plot market grossed $ 9.6 billion, with $ 5.8 billion coming from mobile gaming. [ 192 ] The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency is Japan ‘s national quad agency ; it conducts distance, global, and air travel research, and leads exploitation of rockets and satellites. [ 193 ] It is a participant in the International Space Station : the japanese Experiment Module ( Kibō ) was added to the post during Space Shuttle fabrication flights in 2008. [ 194 ] The quad probe Akatsuki was launched in 2010 and achieved orbit around Venus in 2015. [ 195 ] Japan ‘s plans in space exploration include building a moon base and land astronauts by 2030. [ 196 ] In 2007, it launched lunar explorer SELENE ( Selenological and Engineering Explorer ) from Tanegashima Space Center. The largest lunar mission since the Apollo broadcast, its function was to gather data on the moon ‘s origin and development. The explorer entered a lunar orbit on October 4, 2007, [ 197 ] [ 198 ] and was intentionally crashed into the Moon on June 11, 2009. [ 199 ]
infrastructure
transportation
Japan has invested heavy in transportation system infrastructure. [ 200 ] The area has approximately 1,200,000 kilometers ( 750,000 miles ) of roads made up of 1,000,000 kilometers ( 620,000 miles ) of city, township and greenwich village roads, 130,000 kilometers ( 81,000 miles ) of prefectural roads, 54,736 kilometers ( 34,011 miles ) of general national highways and 7641 kilometers ( 4748 miles ) of national expressways as of 2017. [ 201 ] Since denationalization in 1987, [ 202 ] dozens of japanese railway companies compete in regional and local passenger transportation markets ; major companies include seven JR enterprises, Kintetsu, Seibu Railway and Keio Corporation. The high-speed Shinkansen ( bullet trains ) that connect major cities are known for their condom and punctuality. [ 203 ] There are 175 airports in Japan as of 2013. [ 74 ] The largest domestic airport, Haneda Airport in Tokyo, was Asia ‘s second-busiest airport in 2019. [ 204 ] The Keihin and Hanshin superport hubs are among the largest in the global, at 7.98 and 5.22 million TEU respectively as of 2017. [ 205 ]
Energy
As of 2017, 39 % of energy in Japan was produced from petroleum, 25 % from char, 23 % from natural gasoline, 3.5 % from hydropower and 1.5 % from nuclear power. nuclear baron was down from 11.2 percentage in 2010. [ 206 ] By May 2012 all of the country ‘s nuclear power plants had been taken offline because of ongoing public opposition following the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear calamity in March 2011, though government officials continued to try to sway public opinion in favor of returning at least some to service. [ 207 ] The Sendai Nuclear Power Plant restarted in 2015, [ 208 ] and since then respective early nuclear ability plants have been restarted. [ 209 ] Japan lacks significant domestic reserves and has a fleshy dependence on imported energy. [ 210 ] The nation has therefore aimed to diversify its sources and maintain gamey levels of energy efficiency. [ 211 ]
Water add and sanitation
responsibility for the water and sanitation sector is shared between the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, in charge of water system provide for domestic use ; the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, in agitate of water resources development equally well as sanitation ; the Ministry of the Environment, in charge of ambient water quality and environmental conservation ; and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, in charge of performance benchmarking of utilities. [ 212 ] Access to an improved water system reservoir is cosmopolitan in Japan. About 98 % of the population receives shriek water provision from public utilities. [ 213 ]
Demographics
Japan has a population of 125.7 million, of which 123.2 million are japanese nationals ( 2020 estimates ). [ 214 ] A small population of alien residents makes up the remainder. [ 215 ] In 2019, 92 % of the entire japanese population lived in cities. [ 216 ] The capital city Tokyo has a population of 14.0 million ( 2021 ). [ 217 ] It is part of the Greater Tokyo Area, the biggest metropolitan area in the populace with 38,140,000 people ( 2016 ). [ 218 ] ethnic minority groups in Japan include the autochthonal Ainu and Ryukyuan people. [ 219 ] Zainichi Koreans, [ 220 ] Chinese, [ 221 ] Filipinos, [ 222 ] Brazilians largely of japanese descent, [ 223 ] and Peruvians largely of japanese origin are besides among Japan ‘s small minority groups. [ 224 ] Burakumin make up a social minority group. [ 225 ] Japan has the second-longest overall life anticipation at parturition of any area in the universe, at 84 years as of 2019. [ 226 ] The japanese population is quickly aging as a result of a post–World War II baby boom followed by a decrease in parturition rates. [ 227 ] As of 2019 over 20 percentage of the population is over 65, and this is projected to rise to one in three by 2030. [ 228 ] The changes in demographic structure have created a number of social issues, particularly a descent in work force population and increase in the cost of social security benefits. [ 228 ] A growing number of younger Japanese are not marrying or remain childless. [ 228 ] [ 229 ] Japan ‘s population is expected to drop to around 100 million by 2060. [ 230 ] Immigration and birth incentives are sometimes suggested as a solution to provide younger workers to support the nation ‘s aging population. [ 231 ] [ 232 ] On April 1, 2019, Japan ‘s revised immigration law was enacted, protecting the rights of foreign workers to help reduce labor shortages in certain sectors. [ 233 ]
religion
Japan ‘s united states constitution guarantees full religious freedom. [ 234 ] Upper estimates suggest that 84–96 percentage of the japanese population sign to Shinto as its autochthonal religion. [ 235 ] however, these estimates are based on people affiliated with a temple, quite than the phone number of true believers. many japanese people practice both Shinto and Buddhism ; they can either identify with both religions or describe themselves as non-religious or spiritual. [ 236 ] The level of engagement in religious ceremonies as a cultural tradition remains eminent, specially during festivals and occasions such as the beginning shrine visit of the New Year. [ 237 ] Taoism and Confucianism from China have besides influenced japanese beliefs and customs. [ 238 ] Christianity was first base introduced into Japan by Jesuit missions starting in 1549. nowadays, 1 % [ 239 ] to 1.5 % of the population are Christians. [ 240 ] Throughout the latest century, westerly customs originally related to Christianity ( including western expressive style weddings, Valentine ‘s Day and Christmas ) have become popular as worldly customs among many japanese. [ 241 ] about 90 % of those practicing Islam in Japan are foreign-born migrants as of 2016. [ 242 ] As of 2018 there were an estimated 105 mosques and 200,000 Muslims in Japan, 43,000 of which were ethnically japanese. [ 243 ] other minority religions include Hinduism, Judaism, and Baháʼí Faith, angstrom well as the animist impression of the Ainu. [ 244 ]
Languages
 Kanji and hiragana signs andsigns japanese writing uses kanji ( chinese characters ) and two sets of kana ( syllabaries based on longhand script and group of kanji ), ampere well as the Latin alphabet and Arabic numerals. [ 245 ] English education was made mandate in japanese elementary schools in 2020. [ 246 ] Besides japanese, the Ryukyuan languages ( Amami, Kunigami, Okinawan, Miyako, Yaeyama, Yonaguni ), part of the Japonic language kin, are spoken in the Ryukyu Islands chain. [ 247 ] few children learn these languages, [ 248 ] but local anesthetic governments have sought to increase awareness of the traditional languages. [ 249 ] The Ainu terminology, which is a lyric isolate, is moribund, with lone a few native speakers remaining as of 2014. [ 250 ]
Kanji and hiragana signs andsigns japanese writing uses kanji ( chinese characters ) and two sets of kana ( syllabaries based on longhand script and group of kanji ), ampere well as the Latin alphabet and Arabic numerals. [ 245 ] English education was made mandate in japanese elementary schools in 2020. [ 246 ] Besides japanese, the Ryukyuan languages ( Amami, Kunigami, Okinawan, Miyako, Yaeyama, Yonaguni ), part of the Japonic language kin, are spoken in the Ryukyu Islands chain. [ 247 ] few children learn these languages, [ 248 ] but local anesthetic governments have sought to increase awareness of the traditional languages. [ 249 ] The Ainu terminology, which is a lyric isolate, is moribund, with lone a few native speakers remaining as of 2014. [ 250 ]
education
primary coil schools, secondary coil schools and universities were introduced in 1872 as a leave of the Meiji Restoration. [ 251 ] Since the 1947 Fundamental Law of Education, compulsory education in Japan comprises elementary and junior eminent school, which in concert last for nine years. [ 252 ] Almost all children continue their education at a three-year senior high school. [ 253 ] The two top-ranking universities in Japan are the University of Tokyo and Kyoto University. [ 254 ] Starting in April 2016, diverse schools began the academician year with elementary school and junior high school integrated into one nine-year compulsory schooling plan ; MEXT plans for this approach to be adopted nationally. [ 255 ] The Programme for International Student Assessment ( PISA ) coordinated by the OECD ranks the cognition and skills of japanese 15-year-olds as the one-third best in the universe. [ 256 ] Japan is one of the top-performing OECD countries in reading literacy, mathematics and sciences with the average scholar scoring 529 and has one of the populace ‘s highest-educated department of labor forces among OECD countries. [ 257 ] [ 256 ] [ 258 ] As of 2017, Japan ‘s public spending on education amounted to just 3.3 percentage of its GDP, below the OECD average of 4.9 percentage. [ 259 ] In 2017, the nation ranked third base for the share of 25- to 64-year-olds that have attained third department of education with 51 percentage. [ 260 ] approximately 60 percentage of japanese aged 25 to 34 have some form of tertiary education qualification, and bachelor ‘s degrees are held by 30.4 percentage of japanese aged 25 to 64, the second most in the OECD after South Korea. [ 260 ]
Health
Health care is provided by national and local governments. payment for personal medical services is offered through a universal health insurance system that provides proportional equality of access, with fees set by a government committee. People without insurance through employers can participate in a national health insurance program administered by local governments. [ 261 ] Since 1973, all aged persons have been covered by government-sponsored indemnity. [ 262 ] Japan has one of the world ‘s highest suicide rates. [ 263 ] Another significant public health issue is smoking among japanese men. [ 264 ] Japan has the lowest rate of center disease in the OECD, and the lowest tied of dementia in the develop universe. [ 265 ]
culture
contemporary japanese polish combines influences from Asia, Europe and North America. [ 266 ] traditional japanese arts include crafts such as ceramics, textiles, lacquerware, swords and dolls ; performances of bunraku, kabuki, noh, dance, and rakugo ; and early practices, the tea ceremony, ikebana, martial arts, calligraphy, origami, onsen, Geisha and games. Japan has a develop system for the protective covering and promotion of both real and intangible Cultural Properties and National Treasures. [ 267 ] Twenty-two sites have been inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List, eighteen of which are of cultural significance. [ 99 ]
artwork and architecture
The history of japanese painting parade synthesis and competition between native japanese esthetics and imported ideas. [ 268 ] The interaction between japanese and european art has been significant : for example ukiyo-e prints, which began to be exported in the nineteenth century in the apparent motion known as Japonism, had a significant influence on the growth of mod art in the West, most notably on post-Impressionism. [ 268 ] japanese manga developed in the twentieth century and have become democratic cosmopolitan. [ 269 ] [ 270 ] japanese architecture is a combination between local and other influences. It has traditionally been typified by wooden or mud poultice structures, elevated slightly off the grind, with tiled or thatched ceiling. [ 271 ] The Shrines of Ise have been celebrated as the prototype of japanese architecture. [ 272 ] Traditional house and many temple buildings see the use of tatami mats and sliding doors that break down the distinction between rooms and indoor and outdoor space. [ 273 ] Since the nineteenth hundred, Japan has incorporated a lot of western modern architecture into construction and design. [ 274 ] It was not until after World War II that japanese architects made an impression on the international scene, first with the solve of architects like Kenzō Tange and then with movements like Metabolism. [ 275 ]
literature and philosophy
The earliest works of japanese literature include the Kojiki and Nihon Shoki chronicles and the Man’yōshū poetry anthology, all from the eighth century and written in chinese characters. [ 276 ] [ 277 ] In the early Heian time period, the system of phonograms known as kana ( hiragana and katakana ) was developed. [ 278 ] The Tale of the Bamboo Cutter is considered the oldest extant japanese narrative. [ 279 ] An report of court biography is given in The Pillow Book by Sei Shōnagon, while The Tale of Genji by Murasaki Shikibu is much described as the earth ‘s beginning fresh. [ 280 ] [ 281 ] During the Edo period, the chōnin ( “ town ” ) overtook the samurai gentry as producers and consumers of literature. The popularity of the works of Saikaku, for example, reveals this change in readership and writing, while Bashō revivified the poetic tradition of the Kokinshū with his haikai ( haiku ) and wrote the poetic travelogue Oku no Hosomichi. [ 282 ] The Meiji earned run average saw the decline of traditional literary forms as japanese literature incorporate western influences. Natsume Sōseki and Mori Ōgai were significant novelists in the early twentieth hundred, followed by Ryūnosuke Akutagawa, Jun’ichirō Tanizaki, Kafū Nagai and, more recently, Haruki Murakami and Kenji Nakagami. Japan has two Nobel Prize-winning authors – Yasunari Kawabata ( 1968 ) and Kenzaburō Ōe ( 1994 ). [ 283 ] japanese philosophy has historically been a fusion of both alien, particularly chinese and western, and uniquely japanese elements. In its literary forms, japanese philosophy began about fourteen centuries ago. confucian ideals remain apparent in the japanese concept of society and the self, and in the organization of the government and the social organization of club. [ 284 ] Buddhism has profoundly impacted japanese psychology, metaphysics, and esthetics. [ 285 ]
Performing arts
 Noh performance at a Shinto shrine operation at a Shinto enshrine japanese music is eclectic and divers. many instruments, such as the koto, were introduced in the 9th and tenth centuries. The popular family music, with the guitar-like samisen, dates from the sixteenth hundred. [ 286 ] western classical music, introduced in the late nineteenth century, forms an built-in separate of japanese culture. [ 287 ] Kumi-daiko ( ensemble drum ) was developed in postwar Japan and became very popular in North America. [ 288 ] Popular music in post-war Japan has been heavily influenced by American and european trends, which has led to the evolution of J-pop. [ 289 ] Karaoke is a meaning cultural activity. [ 290 ] The four traditional theaters from Japan are noh, kyōgen, kabuki, and bunraku. [ 291 ] Noh is one of the oldest continuous theater traditions in the world. [ 292 ]
Noh performance at a Shinto shrine operation at a Shinto enshrine japanese music is eclectic and divers. many instruments, such as the koto, were introduced in the 9th and tenth centuries. The popular family music, with the guitar-like samisen, dates from the sixteenth hundred. [ 286 ] western classical music, introduced in the late nineteenth century, forms an built-in separate of japanese culture. [ 287 ] Kumi-daiko ( ensemble drum ) was developed in postwar Japan and became very popular in North America. [ 288 ] Popular music in post-war Japan has been heavily influenced by American and european trends, which has led to the evolution of J-pop. [ 289 ] Karaoke is a meaning cultural activity. [ 290 ] The four traditional theaters from Japan are noh, kyōgen, kabuki, and bunraku. [ 291 ] Noh is one of the oldest continuous theater traditions in the world. [ 292 ]
Customs and holidays
Ishin-denshin ( 以心伝心 ) is a japanese idiom which denotes a phase of interpersonal communication through mute common understanding. [ 293 ] Isagiyosa ( 潔さ ) is a merit of the capability of accepting death with composure. Cherry blossoms are a symbol of isagiyosa in the common sense of embracing the brevity of the earth. [ 294 ] Hansei ( 反省 ) is a central mind in japanese culture, meaning to acknowledge one ‘s own mistake and to pledge improvement. Kotodama ( 言霊 ) refers to the japanese belief that mystic powers dwell in words and names. [ 295 ] officially, Japan has 16 national, government-recognized holidays. Public holidays in Japan are regulated by the Public Holiday Law ( 国民の祝日に関する法律, Kokumin no Shukujitsu ni Kansuru Hōritsu ) of 1948. [ 296 ] Beginning in 2000, Japan implemented the Happy Monday System, which moved a number of national holidays to Monday in order to obtain a long weekend. [ 297 ] The national holidays in Japan are New Year ‘s Day on January 1, Coming of Age Day on the moment Monday of January, National Foundation Day on February 11, The Emperor ‘s Birthday on February 23, Vernal Equinox Day on March 20 or 21, Shōwa Day on April 29, Constitution Memorial Day on May 3, Greenery Day on May 4, Children ‘s Day on May 5, Marine Day on the third base Monday of July, Mountain Day on August 11, Respect for the Aged Day on the third Monday of September, Autumnal Equinox on September 23 or 24, Health and Sports Day on the second Monday of October, Culture Day on November 3, and Labor Thanksgiving Day on November 23. [ 298 ]
cuisine
japanese cuisine offers a huge array of regional specialties that use traditional recipes and local anesthetic ingredients. [ 299 ] Seafood and japanese rice or noodles are traditional staples. [ 300 ] japanese dress, since its insertion to Japan from British India, is then widely consumed that it can be termed a national smasher, aboard ramen and sushi. [ 301 ] [ 302 ] [ 303 ] Traditional japanese sweets are known as wagashi. [ 304 ] Ingredients such as bolshevik bean paste and mochi are used. More contemporary tastes includes greens tea ice cream. [ 305 ] democratic japanese beverages include sake, which is a brew rice beverage that typically contains 14–17 % alcohol and is made by multiple agitation of rice. [ 306 ] Beer has been brewed in Japan since the late seventeenth century. [ 307 ] Green tea is produced in Japan and prepared in forms such as matcha, used in the japanese tea ceremony. [ 308 ]
Media
According to the 2015 NHK sketch on television see in Japan, 79 percentage of japanese watch television daily. [ 309 ] japanese television drama are viewed both within Japan and internationally ; [ 310 ] other popular shows are in the genres of diverseness shows, drollery, and news program programs. [ 311 ] japanese newspapers are among the most circulated in the worldly concern as of 2016. [ 312 ] Japan has one of the oldest and largest film industries globally. [ 313 ] Ishirō Honda ‘s Godzilla became an international picture of Japan and spawned an entire subgenre of kaiju films, a well as the longest-running film franchise in history. [ 314 ] [ 315 ] japanese animated films and television series, known as anime, were largely influenced by japanese manga and have become highly popular in the western world and East Asia. Japan is a world-renowned power station of animation. [ 316 ] [ 317 ] [ 318 ] [ 319 ]
Sports
 Sumo wrestlers form around the referee during the ring-entering ceremony traditionally, sumo is considered Japan ‘s national fun. [ 320 ] japanese martial arts such as judo and kendo are taught as part of the compulsory junior high school course of study. [ 321 ] Baseball is the most popular spectator sport in the state. [ 322 ] Japan ‘s clear professional league, Nippon Professional Baseball, was established in 1936. [ 323 ] Since the constitution of the Japan Professional Football League in 1992, association football has gained a wide follow. [ 324 ] The country co-hosted the 2002 FIFA World Cup with South Korea. [ 325 ] Japan has one of the most successful football teams in Asia, winning the asian Cup four times, [ 326 ] and the FIFA Women ‘s World Cup in 2011. [ 327 ] Golf is besides popular in Japan. [ 328 ] In motorsport, japanese automotive manufacturers have been successful in multiple different categories, with titles and victories in series such as Formula One, MotoGP, IndyCar, World Rally Championship, World Endurance Championship, World Touring Car Championship, British Touring Car Championship and the IMSA SportsCar Championship. [ 329 ] [ 330 ] [ 331 ] Three japanese drivers have achieved dais finishes in Formula One, and drivers from Japan have victories at the Indianapolis 500 and the 24 Hours of Le Mans, in addition to achiever in domestic championships. [ 332 ] [ 333 ] Super GT is the most popular national series in Japan, while Super Formula is the top level domestic open-wheel series. [ 334 ] The state hosts major races such as the japanese Grand Prix. [ 335 ] Japan hosted the Summer Olympics in Tokyo in 1964 and the Winter Olympics in Sapporo in 1972 and Nagano in 1998. [ 336 ] The nation hosted the official 2006 Basketball World Championship [ 337 ] and will co-host the 2023 Basketball World Championship. [ 338 ] Tokyo hosted the 2020 Summer Olympics in 2021, making Tokyo the first asian city to host the Olympics doubly. [ 339 ] The nation gained the host rights for the official Women ‘s Volleyball World Championship on five occasions, more than any other nation. [ 340 ] Japan is the most successful asian Rugby Union state [ 341 ] and hosted the 2019 IRB Rugby World Cup. [ 342 ]
Sumo wrestlers form around the referee during the ring-entering ceremony traditionally, sumo is considered Japan ‘s national fun. [ 320 ] japanese martial arts such as judo and kendo are taught as part of the compulsory junior high school course of study. [ 321 ] Baseball is the most popular spectator sport in the state. [ 322 ] Japan ‘s clear professional league, Nippon Professional Baseball, was established in 1936. [ 323 ] Since the constitution of the Japan Professional Football League in 1992, association football has gained a wide follow. [ 324 ] The country co-hosted the 2002 FIFA World Cup with South Korea. [ 325 ] Japan has one of the most successful football teams in Asia, winning the asian Cup four times, [ 326 ] and the FIFA Women ‘s World Cup in 2011. [ 327 ] Golf is besides popular in Japan. [ 328 ] In motorsport, japanese automotive manufacturers have been successful in multiple different categories, with titles and victories in series such as Formula One, MotoGP, IndyCar, World Rally Championship, World Endurance Championship, World Touring Car Championship, British Touring Car Championship and the IMSA SportsCar Championship. [ 329 ] [ 330 ] [ 331 ] Three japanese drivers have achieved dais finishes in Formula One, and drivers from Japan have victories at the Indianapolis 500 and the 24 Hours of Le Mans, in addition to achiever in domestic championships. [ 332 ] [ 333 ] Super GT is the most popular national series in Japan, while Super Formula is the top level domestic open-wheel series. [ 334 ] The state hosts major races such as the japanese Grand Prix. [ 335 ] Japan hosted the Summer Olympics in Tokyo in 1964 and the Winter Olympics in Sapporo in 1972 and Nagano in 1998. [ 336 ] The nation hosted the official 2006 Basketball World Championship [ 337 ] and will co-host the 2023 Basketball World Championship. [ 338 ] Tokyo hosted the 2020 Summer Olympics in 2021, making Tokyo the first asian city to host the Olympics doubly. [ 339 ] The nation gained the host rights for the official Women ‘s Volleyball World Championship on five occasions, more than any other nation. [ 340 ] Japan is the most successful asian Rugby Union state [ 341 ] and hosted the 2019 IRB Rugby World Cup. [ 342 ]
See besides
Notes
- ^[ɲippoꜜɴ] (
) or [ɲihoꜜɴ] (
) or
- ^[8] In Japanese, the name of the country as it appears on official documents, including the 日本国 ( or Nihon-koku), meaning “State of Japan”. Despite this, the short-form name 日本 (Nippon or Nihon) is also often used officially. In English, the official name of the state is just “ Japan ” .In japanese, the list of the state as it appears on official documents, including the country ‘s united states constitution, isor ), meaning “ State of Japan ”. Despite this, the short-form nameor ) is besides frequently used officially .
References
Government
General information
- Japan from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Japan profile from BBC News
- Japan from the OECD
 Geographic data related to Japan at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Japan at OpenStreetMap
Read more: Chord (music) – Wikipedia
Coordinates :
